Korean J Radiol.
2004 Mar;5(1):31-38. 10.3348/kjr.2004.5.1.31.
Combined Radiofrequency Ablation and Acetic Acid Hypertonic Saline Solution Instillation: An In Vivo Study of Rabbit Liver
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leejm@radcom.snu.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Chonju, Korea.
- KMID: 1066243
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2004.5.1.31
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
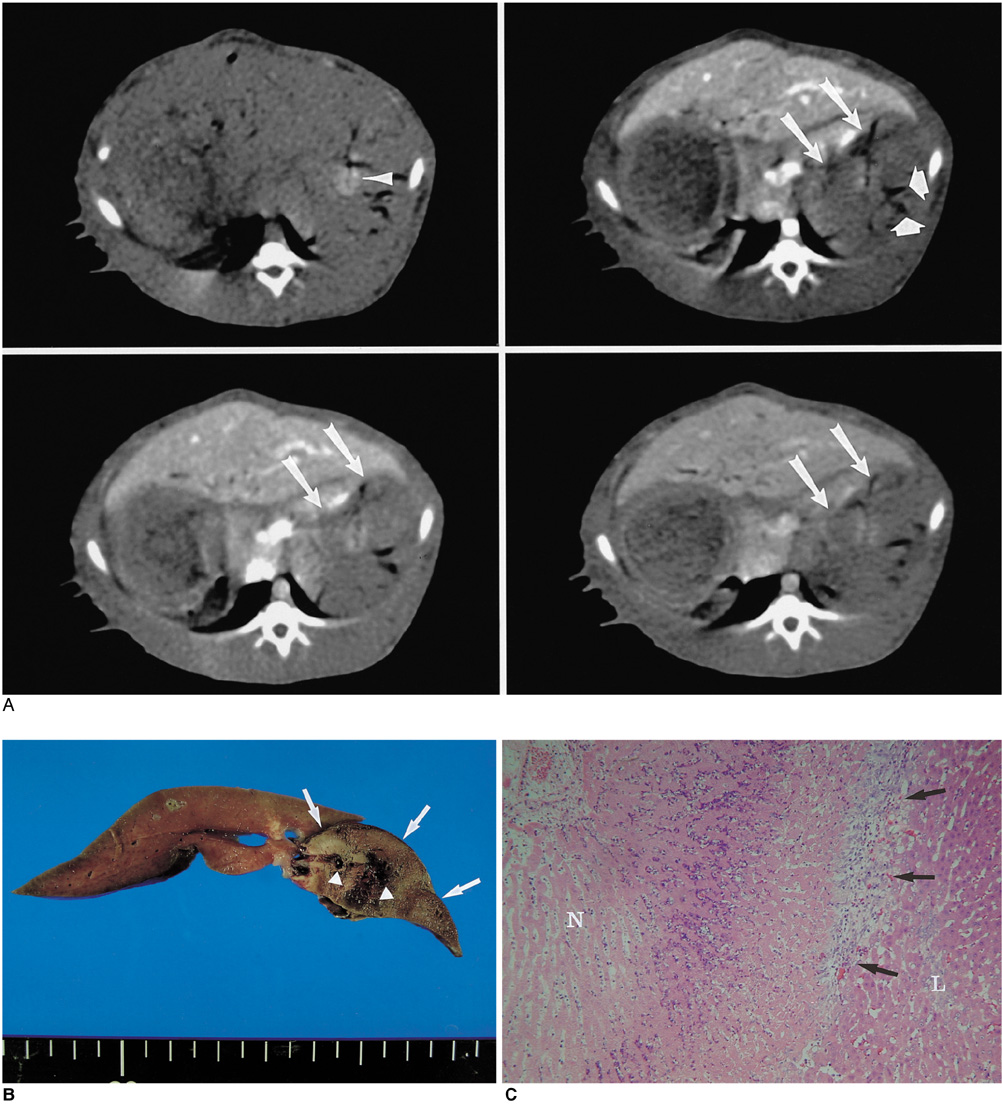
We wanted to determine whether combined radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and acetic acid-hypertonic saline solution (AHS) instillation can increase the extent of thermally mediated coagulation in in vivo rabbit liver tissue. We also wished to determine the optimal concentration of the solution in order to maximize its effect on extent of the RFA-induced coagulation. MAERIALS AND METHODS: Forty thermal ablation zones were produced in 40 rabbits by using a 17-gauge internally cooled electrode with a 1-cm active tip under ultrasound guidance. The rabbits were assigned to one of four groups: group A: RFA alone (n=10) ; group B: RFA with 50% AHS instillation (n=10) ; group C: RFA with 25% AHS instillation (n=10) ; group D: RFA with 15% AHS instillation (n=10). A range of acetic acid concentrations diluted in 36% NaCl to a total volume of 1 mL were instilled into the liver before RFA. The RF energy (30 W) was applied for three minutes. After RFA, in each group, the maximum diameters of the thermal ablation zones in the gross specimens were compared. Technical success and the complications that arose were evaluated by CT and on the basis of autopsy findings. RESULTS: All procedures are technically successful. There were six procedure-related complications (6/40; 15%) : two localized perihepatic hematomas and four chemical peritonitis. The incidence of chemical peritonitis was highest for group B with the 50% AHS solution instillation (30%). With instillation of 15% AHS solution, a marked decrease of tissue impedance (24.5+/-15.6 omega) and an increase of current (250 mA) occurred as compared to RFA alone. With instillation of the solutions before RFA (group B, C and D), this produced a greater mean diameter of coagulation necrosis than the diameters for rabbits not instilled with the solution (group A) (p < 0.05). However, there was no significant difference between group B, C, and D. CONCLUSION: Combined AHS instillation and RFA can increase the dimension of coagulation necrosis in the liver with a single application. A low concentration of AHS (15%) showed similar effects in increasing the extent of RF-induced coagulation, but there were less side effects as compared to the high concentration of AHS.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gazelle GS, Goldberg SN, Solbiati L, Livraghi T. Tumor ablation with radio-frequency energy. Radiology. 2000. 217:633–646.2. Curley SA, Izzo F, Ellis LM, Vauthey JN, Vallone P. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular cancer in 110 patients with cirrhosis. Ann Surg. 2000. 232:381–391.3. Curley SA, Izzo F, Delrio P, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of unresectable primary and metastatic hepatic malignancies: results in 123 patients. Ann Surg. 1999. 230:1–8.4. Dupuy DE, Goldberg SN. Image-guided radiofrequency tumor ablation: challenges and opportunities-part II. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001. 12:1135–1148.5. Lim HK. Radiofrequency thermal ablation of hepatocellular carcinomas. Korean J Radiol. 2000. 1:175–184.6. Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: radiofrequency ablation of medium and large lesions. Radiology. 2000. 214:761–768.7. de Baere T, Elias D, Dromain C, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of 100 hepatic metastases with a mean follow-up of more than 1 year. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. 175:1619–1625.8. Lim H, Goldberg SN, Dodd GD, et al. Essential techniques for successful radiofrequency thermal ablation of malignant hepatic tumors. RadioGraphics. 2001. 21:S17–S39.9. Dodd GD, Frank MS, Aribandi M, Chopra S, Chintapalli KN. Radiofrequency thermal ablation: computer analysis created by overlapping ablations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002. 177:777–782.10. Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Monti F, et al. Saline-enhanced radiofrequency tissue ablation in the treatment of liver metastases. Radiology. 1997. 202:205–210.11. Goldberg SN, Ahmed M, Gazelle GS, et al. Radio-frequency thermal ablation with NaCl solution injection: effect of electrical conductivity on tissue heating and coagulation-phantom and porcine liver study. Radiology. 2001. 219:157–165.12. Ahmed M, Lobo SM, Weinstein J, et al. Improved coagulation with saline solution pretreatment during radiofrequency tumor ablation in a canine model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002. 13:717–724.13. Lee JM, Kim YK, Lee YH, Kim SW, Li CA, Kim CS. Percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation with hypertonic saline injection: in vivo study in a rabbit liver model. Korean J Radiol. 2003. 4:27–34.14. Kainumao O, Asano T, Aoyama H, et al. Combined therapy with radiofrequency thermal ablation and intra-arterial infusion chemotherapy for hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999. 46:1071–1077.15. Goldberg SN, Kruskal JB, Oliver BS, Clouse ME, Gazelle GS. Percutaneous tumor ablation: increased coagulation by combining radio-frequency ablation and ethanol instillation in a rat breast tumor modal. Radiology. 2000. 217:827–831.16. Lee JM, Lee YH, Kim YK, et al. Combined treatment of radiofrequency ablation and acetic acid injection: an in vivo feasibility study in rabbit liver. Eur Radiol. 2004. (in press).17. Rossi S, Garbagnati F, Lencioni R, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation of nonresectable hepatocellular carcinoma after occlusion of tumor blood supply. Radiology. 2000. 217:119–126.18. Ohnishi K, Ohyama N, Ito S, Fujiwara K. Small hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment with US-guided transtumoral injection of acetic acid. Radiology. 1994. 190:53–57.19. Liang HL, Yang CF, Pan HB, et al. Small hepatocellular carcinoma: safety and efficacy of single high-dose percutaneous acetic acid injection for treatment. Radiology. 2000. 214:769–774.20. Arrive L, Rosmorduc O, Dahan H, et al. Percutaneous acetic acid injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma: using CT fluoroscopy to evaluate distribution of acetic acid mixed with an iodinated contrast agent. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. 180:159–162.21. Haaga JR. Haaga JR, Lanzieri CF, editors. Interventional CT-guided procedures. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the whole body. 1994. 3rd ed. St.Louis: Mosby Yearbook;1572–1693.22. Lee JD, Lee JM, Kim SW, Kim CS, Mun WS. MR imaging-histopathologic correlation of radiofrequency thermal ablation lesion in a rabbit liver model: observation during acute and chronic stages. Korean J Radiol. 2001. 2:151–158.23. Lang TA, Secic M. Lang TA, Secic M, editors. Analyzing multiple variables. How to report statistics in medicine. 1997. 1st ed. Philadelphia: American College of Physicians;127–135.24. Koda M, Tanaka H, Murawaki Y, et al. Liver perforation: a serious complication of percutaneous acetic acid injection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 2000. 47:1110–1112.25. Ahmed M, Weinstein J, Liu Z, et al. Image-guided percutaneous chemical and radiofrequency tumor ablation in an animal model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003. 14:1045–1052.26. Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Mueller PR. Thermal ablation therapy for focal malignancy: a unified approach to underlying principles, techniques, and diagnostic imaging guidance. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. 174:323–331.27. Patterson EJ, Scudamore CH, Owen DA, Nagy AG, Buczkowski AK. Radiofrequency ablation of porcine liver in vivo: effects of blood flow and treatment time on lesion size. Ann Surg. 1998. 227:559–566.28. Goldberg SN, Hahn PF, Halpern E, Fogle R, Gazelle GS. Radiofrequency thermal ablation: effect of pharmacologic modulation of blood flow on coagulation diameter. Radiology. 1998. 209:761–769.29. McGahan JP, Dodd GD. Radiofrequency ablation of the liver: current status. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001. 176:3–16.30. Shiina S, Tagawa K, Niwa Y, et al. Percutaneous ethanol injection therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: results in 146 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993. 160:1023–1028.31. Livraghi T, Vettori C, Lazzaroni S. Liver metastases: results of percutaneous ethanol injection in 14 patients. Radiology. 1991. 179:709–712.32. Nath S, Haines DE. Biophysics and pathology of catheter energy delivery systems. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1995. 37:185–204.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Percutaneous Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation with Hypertonic Saline Injection: In Vivo Study in a Rabbit Liver Model
- The Effect of Subconjunctival Injection of Hypertonic Saline Solution
- Hepatic Radiofrequency Ablation Using Multiple Probes: Ex Vivo and In Vivo Comparative Studies of Monopolar versus Multipolar Modes
- A Comparison of the Cerebral and Hemodynamic Effects of Mannitol and Hypertonic Saline in a Rabbit Model of Brain Injury
- Comparison of Wet Radiofrequency Ablation with Dry Radiofrequency Ablation and Radiofrequency Ablation Using Hypertonic Saline Preinjection: Ex Vivo Bovine Liver