Korean J Ophthalmol.
2011 Aug;25(4):289-293. 10.3341/kjo.2011.25.4.289.
A Case of Pediatric Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Presenting with Divergence Insufficiency
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Yonsei University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. khyeye@paran.com
- KMID: 1018421
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2011.25.4.289
Abstract
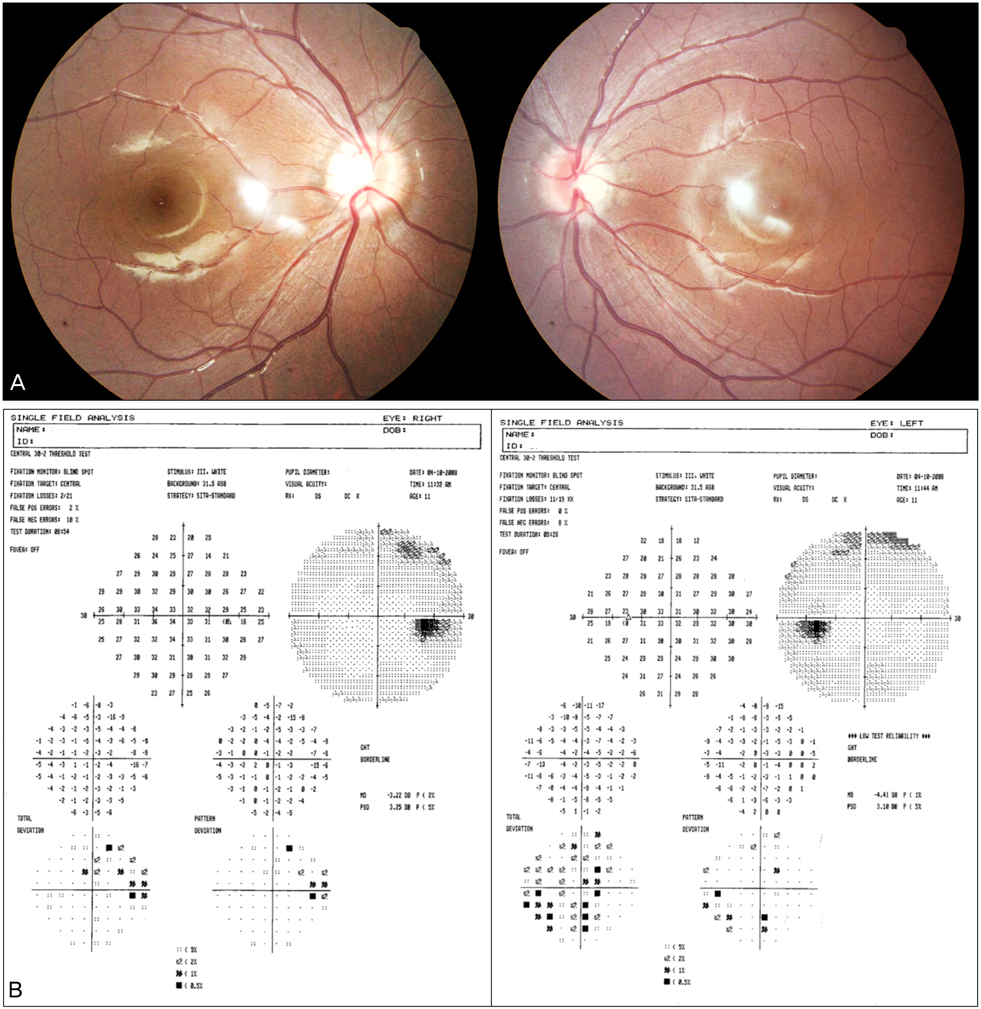
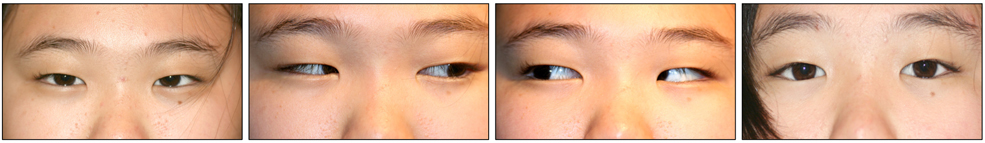
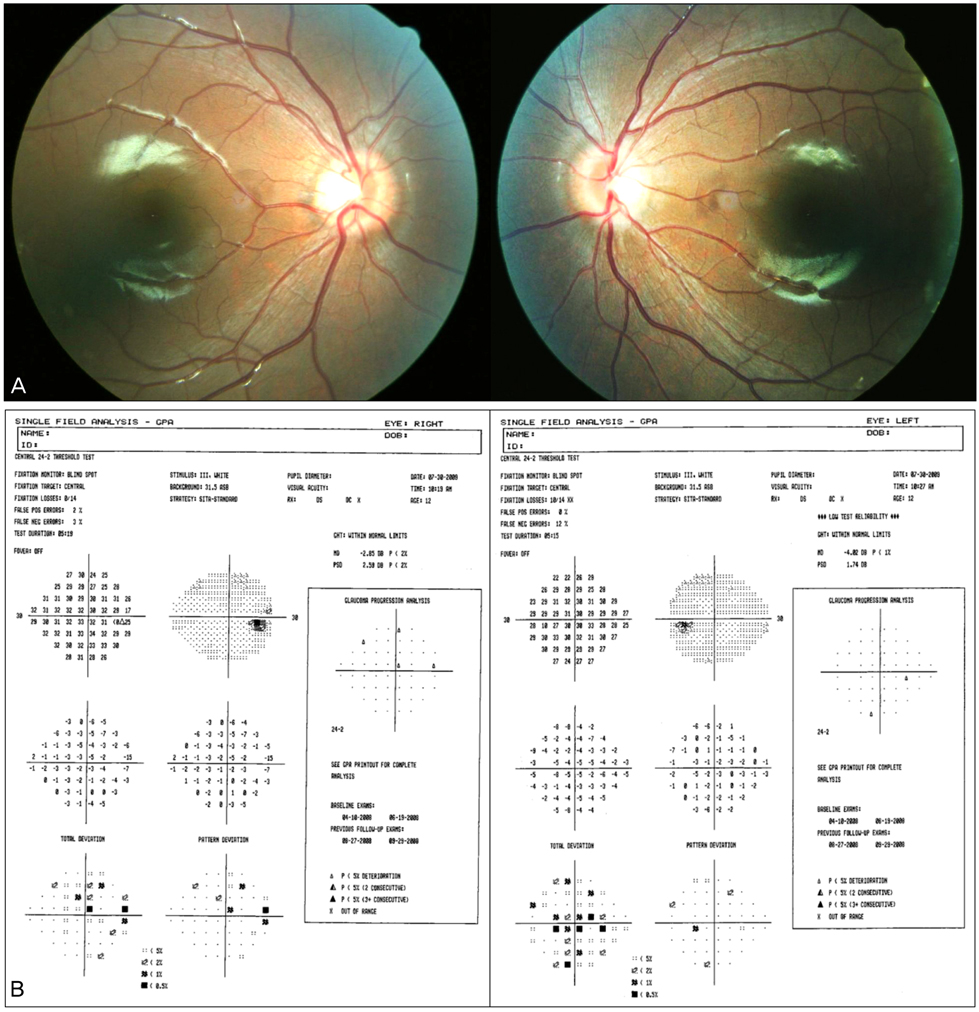
- An 11-year-old female presenting diplopia only at distance was found to have comitant esotropia of 20 prism diopters (PD) at distance and normal alignment at nearer proximity. Other ocular movement, including abduction, was normal and a thorough neurologic examination was also normal. The deviation angle of esotropia was increased to 35 PD in 6 months, and a brain magnetic resonance imaging with venogram at that time demonstrated no intracranial lesion. A lumbar puncture showed increased opening pressure but the cerebrospinal fluid composition was normal. The patient was diagnosed as having idiopathic intracranial hypertension and treated with oral acetazolamide. Three months after treatment, the deviation angle decreased to 10 PD. This is a case report of divergence insufficiency in pediatric idiopathic intracranial hypertension, with an increasing deviation angle of esotropia. Although sixth cranial nerve palsy is a common neurologic manifestation in intracranial hypertension, clinicians should be aware of the possibility of divergence insufficiency. Also, ophthalmoparesis may not be apparent and typical at first presentation, as seen in this case, and therefore ophthalmologists should be aware of this fact, while conducting careful and proper evaluation, follow-up, and intervention.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acetazolamide/administration & dosage
Administration, Oral
Child
Diagnosis, Differential
Diuretics/administration & dosage
Esotropia/diagnosis/*etiology/physiopathology
Exotropia/diagnosis/*etiology/physiopathology
Eye Movements
Female
Follow-Up Studies
Humans
Intracranial Pressure
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Pseudotumor Cerebri/*complications/diagnosis/drug therapy
Spinal Puncture/methods
Vision, Binocular
Visual Acuity
Figure
Reference
-
1. Prangen Ade H, Koch FL. Divergence insufficiency: a clinical study. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1937. 35:136–148.2. Simpson GV. Primary divergence insufficiency. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1973. 71:152–161.3. Dunnington JH. Paralysis of divergence with report of three cases due to epidemic encephalitis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1923. 52:39–49.4. Tekeli O, Tomaç S, Gursel E, Hasiripi H. Divergence paralysis & intracranial hypertension due to neurobrucellosis. A case report. Binocul Vis Strabismus Q. 1999. 14:117–118.5. Pinchoff BS, Slavin ML, Rosenstein D, Hyman R. Divergence paralysis as the initial sign in the Miller Fisher syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1986. 101:741–742.6. Chamlin M, Davidoff LM. Divergence paralysis with increased intracranial pressure. J Neurosurg. 1950. 7:539–543.7. Friedman DI, Jacobson DM. Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Neurology. 2002. 59:1492–1495.8. Dandy WE. Intracranial pressure without brain tumor: diagnosis and treatment. Ann Surg. 1937. 106:492–513.9. Smith JL. Whence pseudotumor cerebri? J Clin Neuroophthalmol. 1985. 5:55–56.10. Gordon K. Pediatric pseudotumor cerebri: descriptive epidemiology. Can J Neurol Sci. 1997. 24:219–221.11. Wall M, George D. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension. A prospective study of 50 patients. Brain. 1991. 114(Pt 1A):155–180.12. Babikian P, Corbett J, Bell W. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension in children: the Iowa experience. J Child Neurol. 1994. 9:144–149.13. Kesler A, Fattal-Valevski A. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension in the pediatric population. J Child Neurol. 2002. 17:745–748.14. Phillips PH, Repka MX, Lambert SR. Pseudotumor cerebri in children. J AAPOS. 1998. 2:33–38.15. Wolf A, Hutcheson KA. Advances in evaluation and management of pediatric idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2008. 19:391–397.16. Rangwala LM, Liu GT. Pediatric idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Surv Ophthalmol. 2007. 52:597–617.17. Genizi J, Lahat E, Zelnik N, et al. Childhood-onset idiopathic intracranial hypertension: relation of sex and obesity. Pediatr Neurol. 2007. 36:247–249.18. Parinuad H. Clinique nerveunse: paralysis des mouvements associesdes yeux. Neurology. 1883. 5:145–172.19. Duane A. A new classification of the motor anomalies of the eyes based upon physiological principles. Ann Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1886. 247–260. 969–1008.20. Duane A. A case of divergence paralysis and its bearing upon the theory of squint and heterophoria. Arch Ophthalmol. 1899. 28:2671–2681.21. Duane A. Paralysis of divergence. Ophthalmology. 1905. 2:1–19.22. Bruce BB, Newman NJ, Biousse V. Ophthalmoparesis in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006. 142:878–880.23. Kirkham TH, Bird AC, Sanders MD. Divergence paralysis with raised intracranial pressure. An electro-oculographic study. Br J Ophthalmol. 1972. 56:776–782.24. Jampolsky A. Ocular divergence mechanisms. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1970. 68:730–822.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endovascular Treatment of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Report
- Effect of Transverse Sinus Stenting on Diffuse Leukoencephalopathy with Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
- Spontaneous Lateral Sphenoid Cephalocele in Association with Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Case Report
- A Case of Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Associated with Obesity
- Intracranial Hypotension Leading to Intracranial Hypertension with Ocular Manifestations