J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2016 Sep;57(9):1480-1483. 10.3341/jkos.2016.57.9.1480.
A Case of Phacoanaphylactic Uveitis Presenting as Endophthalmitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. maya12kim@naver.com
- 2Gyeongsang Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2351882
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2016.57.9.1480
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report a case of phacoanaphylactic uveitis presenting as endophthalmitis.
CASE SUMMARY
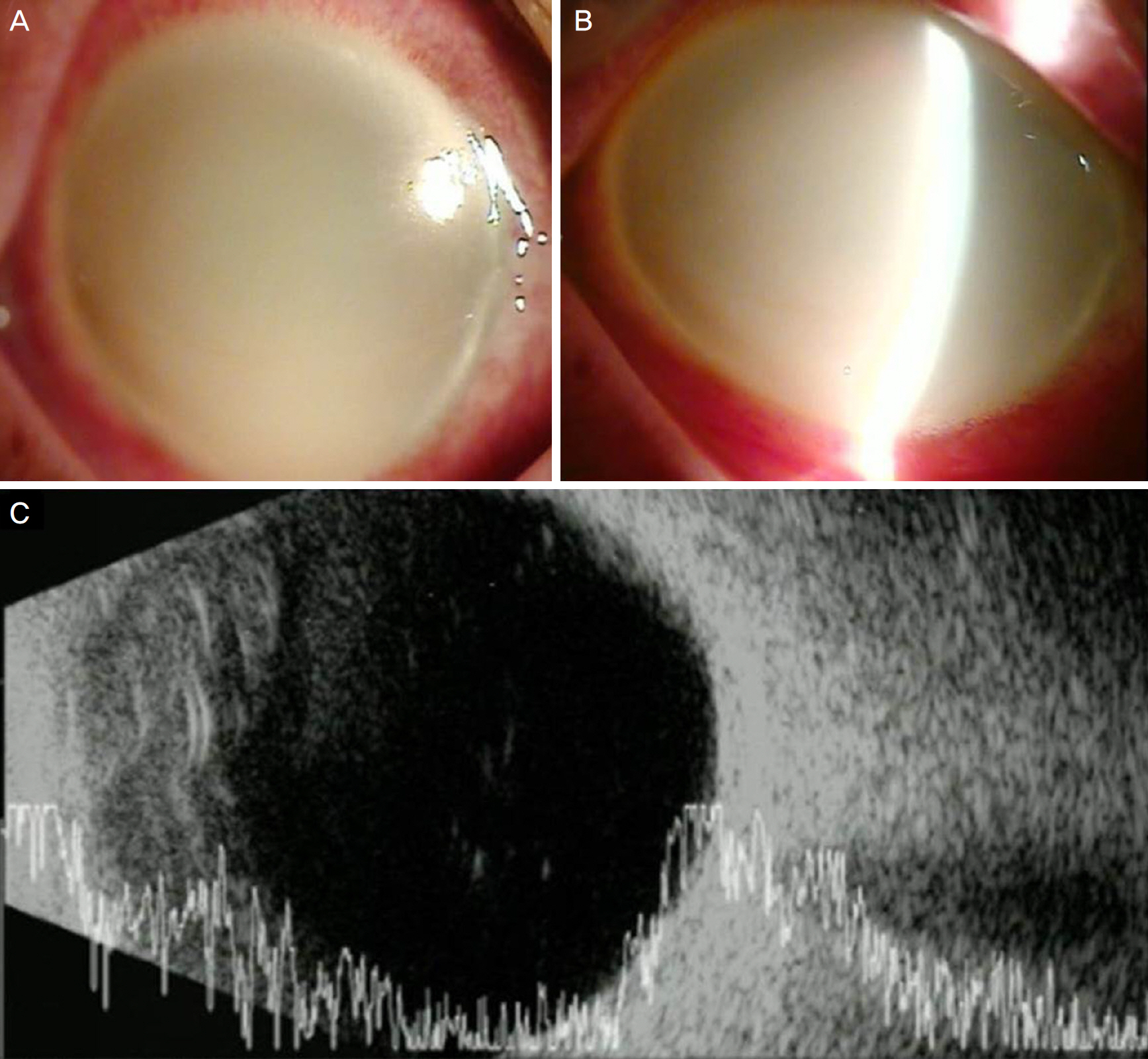
A 77-year-old woman presented with sudden visual disturbance and painful red right eye. She did not have a history of trauma or surgery in her right eye. Her best corrected visual acuity was hand movement in the right eye and log MAR 0.22 in the left eye; intraocular pressure was 27 mm Hg in the right eye and 15 mm Hg in the left eye. Slit-lamp examination revealed corneal edema and prominent inflammation with hypopyon in the anterior chamber. B-scan showed vitreous opacity behind the lens. Based on the diagnosis of endophthalmitis, anterior chamber paracentesis and irrigation were performed. After irrigation, a hypermature cataract with intact anterior capsule was observed. Therefore, we performed extracapsular cataract extraction and intravitreal antibiotics injection. Gram staining of the aqueous humor revealed numerous macrophages filled with lens protein but no organisms. She was treated with hourly topical corticosteroid and an antibiotic agent. One month later, the anterior chamber is clear, and the cultures remained negative.
CONCLUSIONS
We report a case of spontaneous phacoanaphylactic uveitis presenting as endophthalmitis in a patient with no history of eye trauma or surgery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Margo CE, Lessner A, Goldey SH, Sherwood M. Lens-induced abdominal after Nd:YAG laser iridotomy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1992; 113:97–8.2. Hochman M, Sugino IK, Lesko C, et al. Diagnosis of phacoanaphylactic endophthalmitis by fine needle aspiration biopsy. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers. 1999; 30:152–4.
Article3. Van Der Woerdt A. Lens-induced uveitis. Vet Ophthalmol. 2000; 3:227–34.
Article4. Thach AB, Marak GE Jr, McLean IW, Green WR. Phacoanaphylactic endophthalmitis: a clinicopathologic review. Int Ophthalmol. 1991; 15:271–9.
Article5. Jang HD, Kim DY. A case of anterior lens capsule rupture from blunt ocular trauma. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:103–6.
Article6. Murase KH, Goto H, Kezuka T, et al. A case of lens induced uveitis following metastatic endophthalmitis. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2007; 51:304–6.7. Yoo WS, Kim BJ, Chung IY, et al. A case of phacolytic glaucoma with anterior lens capsule disruption identified by scanning electron microscopy. BMC Ophthalmol. 2014; 14:133.
Article8. Kang HM, Park JW, Chung EJ. A retained lens fragment induced anterior uveitis and corneal edema 15 years after cataract surgery. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2011; 25:60–2.
Article9. Kalogeropoulos CD, Malamou-Mitsi VD, Asproudis I, Psilas K. The contribution of aqueous humor cytology in the differential abdominal of anterior uvea inflammations. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2004; 12:215–25.10. Tanito M, Kaidzu S, Katsube T, et al. Diagnostic western blot for lens-specific proteins in aqueous fluid after traumatic lens-induced uveitis. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2009; 53:436–9.
Article11. Rathinam SR, Cunningham ET Jr. Spontaneous hyphaema and acute ocular hypertension associated with severe lens-induced uveitis. Eye (Lond). 2010; 24:1822–4.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Propionibacterium acnes Endophthalmitis after Extracapsular Cataract Extraction and Posterior Chamber Lens Implantation
- A Case of Aspergillus Endocarditis Presenting as Endophthalmitis
- Exogenous Fungal Endophthalmitis by Exophiala xenobiotica Infection after Cataract Surgery
- Clinical Results of 500 Cases of Intraocular Lens Implantation(I)
- A Case of Acute Anterior Uveitis Associated with HLA-B27 Positivity after Intravitreal Injection of Bevacizumab