Clin Orthop Surg.
2011 Mar;3(1):69-76. 10.4055/cios.2011.3.1.69.
Staged Protocol in Treatment of Open Distal Tibia Fracture: Using Lateral MIPO
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yeungnam University Hospital, Daegu, Korea. ossoj@med.yu.ac.kr
- KMID: 999463
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2011.3.1.69
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
To evaluate the radiological, clinical results in patients with open distal tibia factures, who were treated with a staged treatment protocol using the lateral minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) technique.
METHODS
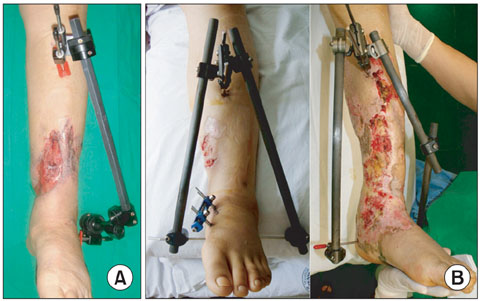
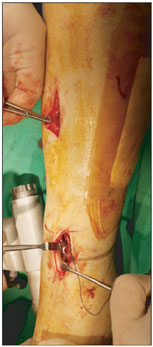
From January 2007 to June 2009, 10 patients with open distal tibia fractures (Gustilo-Anderson classification II, 3; IIIA, 1; IIIB, 6) were treated using a staged treatment protocol. The initial debridement and application of an external fixator were performed within 24 hours and the mean interval from injury to definitive surgical treatment was 15 days (range, 6 to 52 days). Eight weeks later, an additional bone graft was performed in 3 patients. The follow-up duration was more than 1 year.
RESULTS
The mean fracture healing time was 21 weeks (range, 17 to 28 weeks), and the average Iowa ankle rating score was 84.5 points. At the last follow-up, there was no non-union, angular deformity > 5degrees, shortening > 10 mm or infection. In 10 patients, 2 patients had a superficial wound infection, and another 2 patients showed limitation of ankle joint motion.
CONCLUSIONS
This staged treatment protocol using a lateral MIPO technique is a useful alternative method for achieving high functional recovery with good healing and low complication rates in patients with an open distal tibia fracture.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Selection and Recommended Usage Guide of Temporary External Fixator
Seung-Jae Lim, Ki-Sun Sung, Chang-Wug Oh
J Korean Fract Soc. 2013;26(2):164-169. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.2.164.Treatment of Type IIIb Open Tibial Fractures
Seong Yeon Lim, Il Jae Lee, Jae Ho Joe, Hyung Keun Song
J Korean Fract Soc. 2014;27(4):267-273. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.4.267.
Reference
-
1. Anglen JO. Early outcome of hybrid external fixation for fracture of the distal tibia. J Orthop Trauma. 1999. 13(2):92–97.
Article2. Borg T, Larsson S, Lindsjo U. Percutaneous plating of distal tibial fractures. Preliminary results in 21 patients. Injury. 2004. 35(6):608–614.3. Collinge C, Kuper M, Larson K, Protzman R. Minimally invasive plating of high-energy metaphyseal distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2007. 21(6):355–361.
Article4. Sirkin M, Sanders R, DiPasquale T, Herscovici D Jr. A staged protocol for soft tissue management in the treatment of complex pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:8 Suppl. S32–S38.
Article5. Yang JH, Kweon SH, Kim JW, Park JY, Kim HJ, Lim CM. Two-staged delayed minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis for distal tibial open fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2008. 21(1):24–30.
Article6. Chang SA, Ahn HS, Byun YS, Kim JH, Bang HH, Kyun DY. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in unstable fractures of the distal tibia. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005. 18(2):155–159.
Article7. Borens O, Kloen P, Richmond J, Roederer G, Levine DS, Helfet DL. Minimally invasive treatment of pilon fractures with a low profile plate: preliminary results in 17 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009. 129(5):649–659.
Article8. Helfet DL, Suk M. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis of fractures of the distal tibia. Instr Course Lect. 2004. 53:471–475.9. Lee YS, Chen SH, Lin JC, Chen YO, Huang CR, Cheng CY. Surgical treatment of distal tibia fractures: a comparison of medial and lateral plating. Orthopedics. 2009. 32(3):163.10. Maffulli N, Toms AD, McMurtie A, Oliva F. Percutaneous plating of distal tibial fractures. Int Orthop. 2004. 28(3):159–162.
Article11. Hong KD, Ha SS, Chung NS, Sim JC, Ahn SC. Lateral plate fixation of distal tibial metaphyseal fracture using minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis technique. J Korean Fract Soc. 2006. 19(1):24–28.
Article12. Milner SA. A more accurate method of measurement of angulation after fractures of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997. 79(6):972–974.
Article13. Merchant TC, Dietz FR. Long-term follow-up after fractures of the tibial and fibular shafts. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989. 71(4):599–606.
Article14. Gardner MJ, Mehta S, Barei DP, Nork SE. Treatment protocol for open AO/OTA type C3 pilon fractures with segmental bone loss. J Orthop Trauma. 2008. 22(7):451–457.
Article15. Hasenboehler E, Rikli D, Babst R. Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture: a retrospective study of 32 patients. Injury. 2007. 38(3):365–370.
Article16. Teeny SM, Wiss DA. Open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plafond fractures. Variables contributing to poor results and complications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993. (292):108–117.17. Holbrook JL, Swiontkowski MF, Sanders R. Treatment of open fractures of the tibial shaft: Ender nailing versus external fixation. A randomized, prospective comparison. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989. 71(8):1231–1238.18. Manninen MJ, Lindahl J, Kankare J, Hirvensalo E. Lateral approach for fixation of the fractures of the distal tibia: outcome of 20 patients. Technical note. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007. 127(5):349–353.
Article19. Shepherd LE, Costigan WM, Gardocki RJ, Ghiassi AD, Patzakis MJ, Stevanovic MV. Local or free muscle flaps and unreamed interlocked nails for open tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998. (350):90–96.
Article20. Wolinsky P, Lee M. The distal approach for anterolateral plate fixation of the tibia: an anatomic study. J Orthop Trauma. 2008. 22(6):404–407.
Article21. Borrelli J Jr, Prickett W, Song E, Becker D, Ricci W. Extraosseous blood supply of the tibia and the effects of different plating techniques: a human cadaveric study. J Orthop Trauma. 2002. 16(10):691–695.
Article22. Oh CW, Kyung HS, Park IH, Kim PT, Ihn JC. Distal tibia metaphyseal fractures treated by percutaneous plate osteosynthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003. (408):286–291.
Article23. Pai V, Coulter G. Minimally invasive plate fixation of the tibia. Int Orthop. 2007. 31(4):491–496.
Article24. Redfern DJ, Syed SU, Davies SJ. Fractures of the distal tibia: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Injury. 2004. 35(6):615–620.
Article25. Salton HL, Rush S, Schuberth J. Tibial plafond fractures: limited incision reduction with percutaneous fixation. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2007. 46(4):261–269.
Article26. Krackhardt T, Dilger J, Flesch I, Hontzsch D, Eingartner C, Weise K. Fractures of the distal tibia treated with closed reduction and minimally invasive plating. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005. 125(2):87–94.
Article27. Saleh M, Shanahan MD, Fern ED. Intra-articular fractures of the distal tibia: surgical management by limited internal fixation and articulated distraction. Injury. 1993. 24(1):37–40.
Article28. Marsh JL, Bonar S, Nepola JV, Decoster TA, Hurwitz SR. Use of an articulated external fixator for fractures of the tibial plafond. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995. 77(10):1498–1509.
Article29. Pugh KJ, Wolinsky PR, McAndrew MP, Johnson KD. Tibial pilon fractures: a comparison of treatment methods. J Trauma. 1999. 47(5):937–941.
Article30. Parrett BM, Matros E, Pribaz JJ, Orgill DP. Lower extremity trauma: trends in the management of soft-tissue reconstruction of open tibia-fibula fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006. 117(4):1315–1322.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of The Pilon Fracture involving Tibial Shaft using Two Staged MIPO Technique
- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis in Unstable Fractures of the Distal Tibia
- Surgical Treatment of Distal Tibia Fractures
- Lateral Plate Fixation of Distal Tibial Metaphyseal Fracture Using Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Technique
- A Comparison between Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis & Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing in Distal Tibia Fractures