Clin Orthop Surg.
2009 Dec;1(4):214-221. 10.4055/cios.2009.1.4.214.
Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using a Unilateral Single Cage and a Local Morselized Bone Graft in the Degenerative Lumbar Spine
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. ssurgeon@gsnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 999404
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2009.1.4.214
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
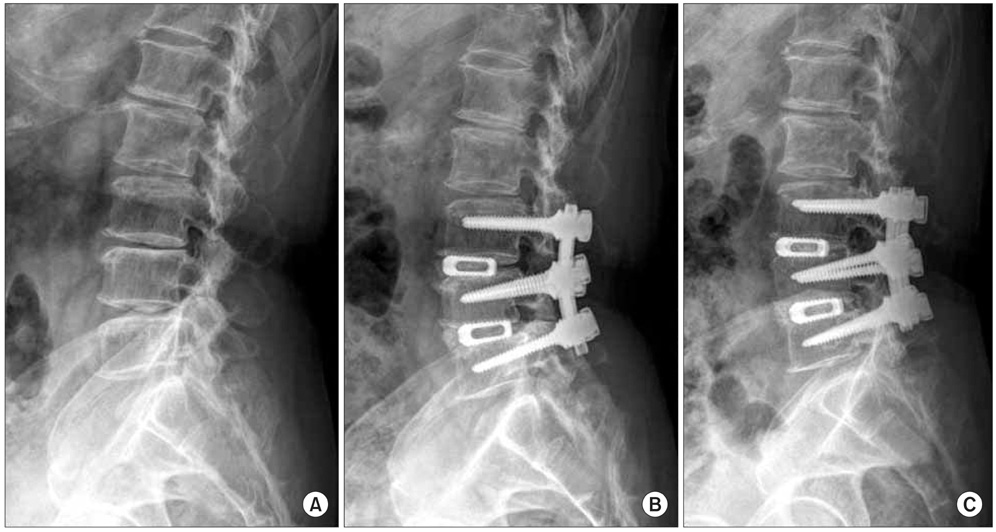
We retrospectively evaluated the clinical and radiological outcomes of posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) with using a unilateral single cage and a local morselized bone graft.
METHODS
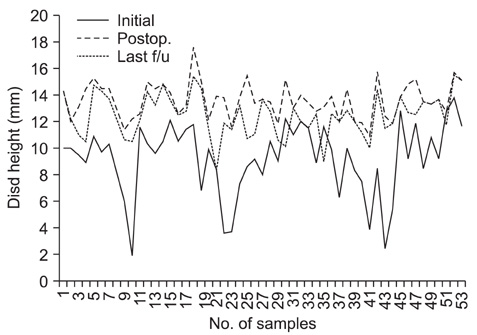
Fifty three patients who underwent PLIF with a unilateral single cage filled with local morselized bone graft were enrolled in this study. The average follow-up duration was 31.1 months. The clinical outcomes were evaluated with using the visual analogue scale (VAS) at the pre-operative period, at 1 year post-operation and at the last follow-up, the Oswestry Disability Index, the Prolo scale and the Kim & Kim criteria at the last follow-up; the radiological outcomes were evaluated according to the change of bone bridging, the radiolucency, the instablity and the disc height.
RESULTS
For the clinical evaluation, the VAS pain index, the Oswestry Disability Index, the Prolo scale and the Kim & Kim criteria showed excellent outcomes. For the the radiological evaluation, 52 cases showed complete bone union at the last follow-up. Regarding the complications, only 1 patient had cage breakage during follow-up.
CONCLUSIONS
PLIF using a unilateral single cage filled with a local morselized bone graft has the advantages of a shorter operation time, less blood loss and a shorter hospital stay, as compared with the PLIF using bilateral cages, for treating degenerative lumbar spine disease. This technique also provides excellent outcomes according to the clinical and radiological evaluation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Blood Loss, Surgical
Bone Transplantation/*methods
Female
Follow-Up Studies
Humans
Intervertebral Disk Degeneration/*radiography/*surgery
Lumbar Vertebrae/pathology/*radiography/*surgery
Male
Middle Aged
Prosthesis Implantation/methods
Retrospective Studies
Spinal Fusion/*methods
Spinal Stenosis/surgery
Spondylolisthesis/surgery
Time and Motion Studies
Treatment Outcome
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chiang MF, Zhong ZC, Chen CS, Cheng CK, Shih SL. Biomechanical comparison of instrumented posterior lumbar interbody fusion with one or two cages by finite element analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006. 31(19):E682–E689.
Article2. Huang KF, Chen TY. Clinical results of a single central interbody fusion cage and transpedicle screws fixation for recurrent herniated lumbar disc and low-grade spondylolisthesis. Chang Gung Med J. 2003. 26(3):170–177.3. Bagby GW. Arthrodesis by the distraction-compression method using a stainless steel implant. Orthopedics. 1988. 11(6):931–934.
Article4. Axelsson P, Johnsson R, Stromqvist B, Arvidsson M, Herrlin K. Posterolateral lumbar fusion: outcome of 71 consecutive operations after 4 (2-7) years. Acta Orthop Scand. 1994. 65(3):309–314.
Article5. Diedrich O, Luring C, Pennekamp PH, Perlick L, Wallny T, Kraft CN. Effect of posterior lumbar interbody fusion on the lumbar sagittal spinal profile. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 2003. 141(4):425–432.6. Cloward RB. The treatment of ruptured lumbar intervertebral discs by vertebral body fusion: I. Indications, operative technique, after care. J Neurosurg. 1953. 10(2):154–168.
Article7. Butts MK, Kuslich SD, Bechorold JE. Biomechanical analysis of a new method for spinal interbody fusion. Mechanical Eng. 1987. 12. 13–18.8. Carmouche JJ, Molinari RW. Epidural abscess and discitis complicating instrumented posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a case report. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2004. 29(23):E542–E546.
Article9. Shin HC, Yi S, Kim KN, Kim SH, Yoon DH. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion via a unilateral approach. Yonsei Med J. 2006. 47(3):319–325.
Article10. Briggs H, Miligan PR. Chip fusion of the low back following exploration of the spinal canal. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1944. 26(1):125–130.11. Chen L, Tang T, Yang H. Complications associated with posterior lumbar interbody fusion using Bagby and Kuslich method for treatment of spondylolisthesis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2003. 116(1):99–103.12. Fogel GR, Toohey JS, Neidre A, Brantigan JW. Outcomes of L1-L2 posterior lumbar interbody fusion with the Lumbar I/F cage and the variable screw placement system: reporting unexpected poor fusion results at L1-L2. Spine J. 2006. 6(4):421–427.
Article13. Kim KT, Suk KS, Kim JM. Future development of interbody fusion cages. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2001. 8(3):386–491.
Article14. Hashimoto T, Shigenobu K, Kanayama M, et al. Clinical results of single-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion using the Brantigan I/F carbon cage filled with a mixture of local morselized bone and bioactive ceramic granules. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002. 27(3):258–262.
Article15. Miura Y, Imagama S, Yoda M, Mitsuguchi H, Kachi H. Is local bone viable as a source of bone graft in posterior lumbar interbody fusion? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003. 28(20):2386–2389.
Article16. Kim NH, Kim DJ. Anterior interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis. Orthopedics. 1991. 14(10):1069–1076.
Article17. Choy WS, Kim WJ, Kim KH, et al. The results of the posterior lumbar interbody fusion using titanium mesh cage for spondylolisthesis. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1999. 6(1):129–134.18. Weiner BK, Fraser RD. Spine update lumbar interbody cages. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998. 23(5):634–640.19. Brantigan JW, Neidre A. Achievement of normal sagittal plane alignment using a wedged carbon fiber reinforced polymer fusion cage in treatment of spondylolisthesis. Spine J. 2003. 3(3):186–196.
Article20. Zhao J, Hai Y, Ordway NR, Park CK, Yuan HA. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using posterolateral placement of a single cylindrical threaded cage. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000. 25(4):425–430.
Article21. Diedrich O, Perlick L, Schmitt O, Kraft CN. Radiographic spinal profile changes induced by cage design after posterior lumbar interbody fusion preliminary report of a study with wedged implants. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. 26(12):E274–E280.22. Lin PM. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion technique: complications and pitfalls. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985. (193):90–102.23. Chen L, Yang H, Tang T. Cage migration in spondylolisthesis treated with posterior lumbar interbody fusion using BAK cages. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005. 30(19):2171–2175.
Article24. Hitchon PW, Goel V, Rogge T, Dooris A, Drake J, Torner J. Spinal stability with anterior or posterior ray threaded fusion cages. J Neurosurg. 2000. 93:1 Suppl. 102–108.
Article25. Tencer AF, Hampton D, Eddy S. Biomechanical properties of threaded inserts for lumbar interbody spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1995. 20(22):2408–2414.
Article26. Wang ST, Goel VK, Kubo S, et al. Comparison of stabilities between obliquely and conventionally inserted Bagby and Kuslich cages as posterior lumbar interbody fusion in a cadaver model. J Chin Med Assoc. 2003. 66(11):676–681.27. Fogel GR, Toohey JS, Neidre A, Brantigan JW. Is one cage enough in posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a comparison of unilateral single cage interbody fusion to bilateral cages. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2007. 20(1):60–65.
Article28. Molinari RW, Sloboda J, Johnstone FL. Are 2 cages needed with instrumented PLIF? A comparison of 1 versus 2 interbody cages in a military population. Am J Orthop. 2003. 32(7):337–343.29. Oxland TR, Lund T. Biomechanics of stand-alone cages and cages in combination with posterior fixation: a literature review. Eur Spine J. 2000. 9:Suppl 1. S95–S101.
Article30. Zhao J, Hou T, Wang X, Ma S. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using one diagonal fusion cage with transpedicular screw/rod fixation. Eur Spine J. 2003. 12(2):173–177.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Unilateral Posterolateral Fusion with Local Bone and Single Cage: Comparison with Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion and Autologous Iliac Bone
- Does the Cage Position in Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Determine Unilateral versus Bilateral Screw Placement?: A Review of the Literature
- Anterior Interbody Fusion using a Horizontal Cylinder Cage in a Degenerative Lumbar Spine
- Evaluation of Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- Minimally Invasive Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Indications, Outcomes and Complications