J Korean Acad Nurs.
2009 Jun;39(3):376-385. 10.4040/jkan.2009.39.3.376.
Smoking Behavior and Predictors of Smoking Initiation in Childhood and Early Adolescence
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing Science, East-West Nursing Research Institute, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. spark@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 999307
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.3.376
Abstract
-
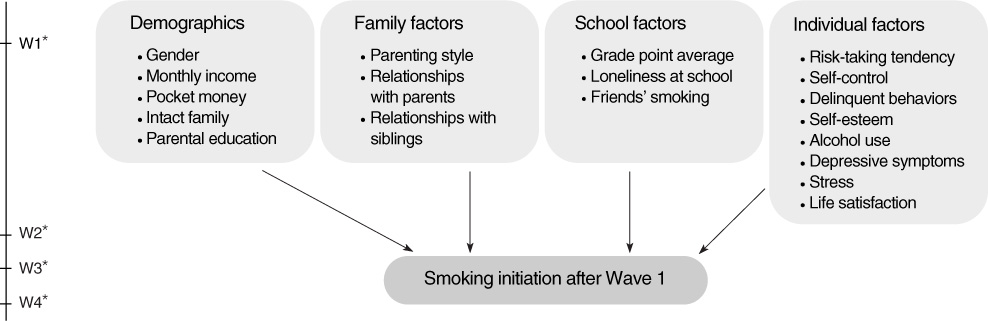
PURPOSE: The purposes of this study were (a) to identify smoking behavior by following a cohort representative of the population of 4th grade elementary schoolers in South Korea over a four-year period (2004-2007), and (b) to explore predictors of smoking initiation among non-smokers in Wave 1.
METHODS
Secondary data, the Korea Youth Panel Study, was analyzed in this study. First, frequencies or percentages were calculated to identify smoking behavior (i.e., smoking initiation, smoking intensity, and smoking duration). Second, binary logistic regression analysis was performed to examine significant factors related to smoking initiation.
RESULTS
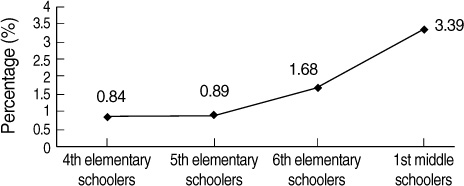
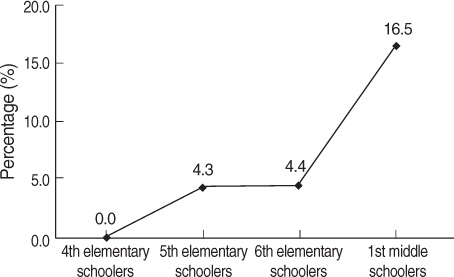
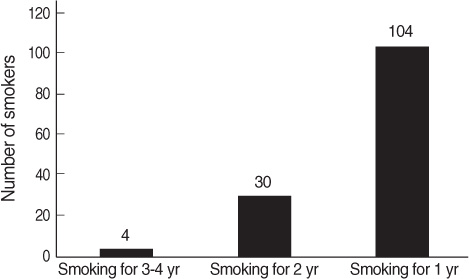
Smoking initiation and daily smoking were more pronounced when the participants entered middle school. In bivariate analysis, statistically significant predictors of smoking initiation were loneliness at school, self-control, delinquent behavior, depressive symptoms, and stress. However, after controlling for other factors, only a high level of risk-taking tendency and a greater number of delinquent behaviors remained statistically significant.
CONCLUSION
Based on greater involvement in smoking among first-year middle schoolers, smoking prevention strategies should be provided to elementary schoolers rather than middle schoolers. A risk-taking tendency and delinquent behaviors should be considered as proxy measures to detect the high-risk group for smoking initiation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Influence of Experiences of Witnessing Tobacco Advertising and Preferences of Tobacco Companies' Social Responsibility on Current and Future Smoking Intentions in Adolescents
Sung Rae Shin, Sun Hwa Shin, Bok Keun Lee, Jin Hee Yang
J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2014;25(1):33-43. doi: 10.12799/jkachn.2014.25.1.33.
Reference
-
1. Allison PD. Logistic regression using the SAS system: Theory and application. 1999a. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing.2. Alison PD. Multiple regression: A primer. 1999b. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing.3. Audrain-McGovern J, Rodriguez D, Tercyak KP, Neuner G, Moss HB. The impact of self-control indices on peer smoking and adolescent smoking progression. Journal of Pediatric Psychology. 2006. 31:139–151.4. Byeon YS, Shoon LH. Relation of the blood pressure, lipids and body mass index by smoking status among adolescents. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2007. 37:1020–1026.5. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Annual smoking-attributable mortality, years of potential life lost, and economic costs-United States, 1995-1999. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 2002. 51:300–303.6. Chen J, Millar W. Age of smoking initiation: Implications for quitting. Health Reports. 1998. 9(4):39–46.7. Doherty EE, Green KM, Ensminger ME. Investigating the long-term influence of adolescent delinquency on drug use initiation. Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 2008. 93:72–84.8. Donohew L, Palmgreen P, Zimmerman R, Harrington N, Lane D. Romer D, editor. Health risk takers and prevention. Reducing adolescent risk: Toward an integrated approach. 2003. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing;171–182.9. Donovan KA. Smoking cessation programs for adolescents. Journal of School Nursing. 2000. 16(4):36–43.10. Evans DL. Evans DL, Foa EB, Gur RE, Hendin H, O'Brien CP, Seligman MEP, Walsh BT, editors. Depression and bipolar disorder. Treating and preventing adolescent mental health disorder: What we know and what we don't know. 2005. New York, NY: Oxford University Press;3–69.11. Fletcher A, Bonell C, Hargreaves J. School effects on young people's drug use: A systematic review of intervention and observational studies. Journal of Adolescent Health. 2008. 42:209–220.12. Fryer CS. Smoking cessation was difficult for adolescents because of daily life stressors and the need for major lifestyle changes. Evidence-Based Nursing. 2008. 11:27.13. Hatcher L. A step-by-step approach to using the SAS system for factor analysis and structural equation modeling. 1994. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing.14. Horvath P, Zuckerman M. Sensation seeking, risk appraisal, and risky behavior. Personality and Individual Difference. 1993. 14:41–52.15. Jessor R, Donovan , Costa FM. Beyond adolescence: Problem behavior and young adult development. 1991. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.16. Kim HS. The influence of a family dynamic environment, personality, smoking on delinquent behavior among Korean adolescents. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2001. 31:641–655.17. Leatherdale ST, Manske S. The relationship between student smoking in the school environment and smoking onset in elementary school students. Cancer, Epidemiology, Biomakeres & Prevention. 2005. 14:1762–1765.18. Ministry for Health Welfare and Family Affairs. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Statistics on adolescent risk behaviors. 2007. Seoul: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.19. The reality of smoking. Ministry for Health Welfare and Family Affairs, & Korean Association of Smoking and Health. 2008. Retrieved November 3, 2008. from http://www.kash.or.kr/user_new/pds_view.asp.20. National Youth Policy Institute. Korea Youth Panel Survey: User's guide of the cohort of elementary schoolers. 2008. Seoul: Author.21. Health at a glance 2007: OECD Indicators. Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development. 2007. Retrieved November 9, 2008. from 781-6 http://lysander.sourceoecd.org/vl=1456912/cl=11/nw=1/rpsv/health2007/3-1.htmhttp://lysander.sourceoecd.org/vl=1456912/cl=11/nw=1/rpsv/health2007/3-1.htm.22. Pandeya N, Williams GM, Sadhegi S, Green1 AC, Webb PM, Whiteman DC. Associations of duration, intensity, and quantity of smoking with adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2008. 168:105–114.23. Park S. Predictors of the transition from experimental to regular smoking in adolescence and young adulthood. 2006. Philadelphia, PA, USA: University of Pennsylvania;Unpublished doctoral dissertation.24. Park S, Weaver T, Romer D. Predictors of the transition from experimental to daily smoking among adolescents in the United States. Journal for Specialists in Pediatric Nursing. (in press).25. Shin SR. Analysis of smoking and smoking cessation related nursing research in Korea and its future direction. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2006. 36:415–425.26. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Results from the 2007 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: National Findings (NSDUH Series H-34, DHHS Publication No. SMA 08-4343). Rockville, MD: Author.27. Tyas SL, Pederson L. Psychosocial factors related to adolescent smoking: A critical review of the literature. Tobacco Control. 1998. 7:409–420.28. Wiencke JK, Thurston SW, Kelsey KT, Varkonyi A, Wain JC, Mark EJ, et al. Early age at smoking initiation and tobacco carcinogen DNA damage in the lung. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 1999. 91:614–619.29. Wilson N, Battistich V, Syme L, Boyce T. Does elementary school alcohol, tobacco, and marijuana use increase middle school risk? Journal of Adolescent Health. 2002. 30:442–447.30. Survey of smoking behaviors among Korean middle and high schoolers in 2007. Yonsei University, & Korean Association of Smoking and Health. 2007. Retrieved November 4, 2008. from http://www.kash.or.kr/user_new/pds_view.asp.31. Survey of smoking behaviors among Korean middle and high schoolers in 2008. Yonsei University, & Korean Association of Smoking and Health. 2008. Retrieved November 4, 2008. from http://www.kash.or.kr/user_new/pds_view.asp.32. Zhu BP, Liu M, Shelton D, Liu S, Giovino GA. Cigarette smoking and its risk factors among elementary school students in Beijing. American Journal of Public Health. 1996. 86:368–375.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Importance of Parental Attitudes and Behavior upon Adolescent Smoking Behavior
- Analysis for Influences of Individual Characteristics, Experience, Cognition, and Affect Relating to Smoking Quitting Behavior on Commitment to a Plan of and Practice for Smoking Quitting Behavior
- The Importance of Smoking Definitions for the Study of Adolescent Smoking Behavior
- A Survey on Smoking of Adolescence
- Influence of Parents' Parenting Efficacy on Health Promotion Behavior in Early Childhood