Korean J Gastroenterol.
2011 Jan;57(1):42-46. 10.4166/kjg.2011.57.1.42.
A Case of Liver Abscess Caused by Fusobacterium nucleatum in a Patient with Recurrent Periodontal Diseases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji University College of Medicine, Eulji University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. yhj822@medimail.co.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Eulji University College of Medicine, Eulji University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 991468
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2011.57.1.42
Abstract
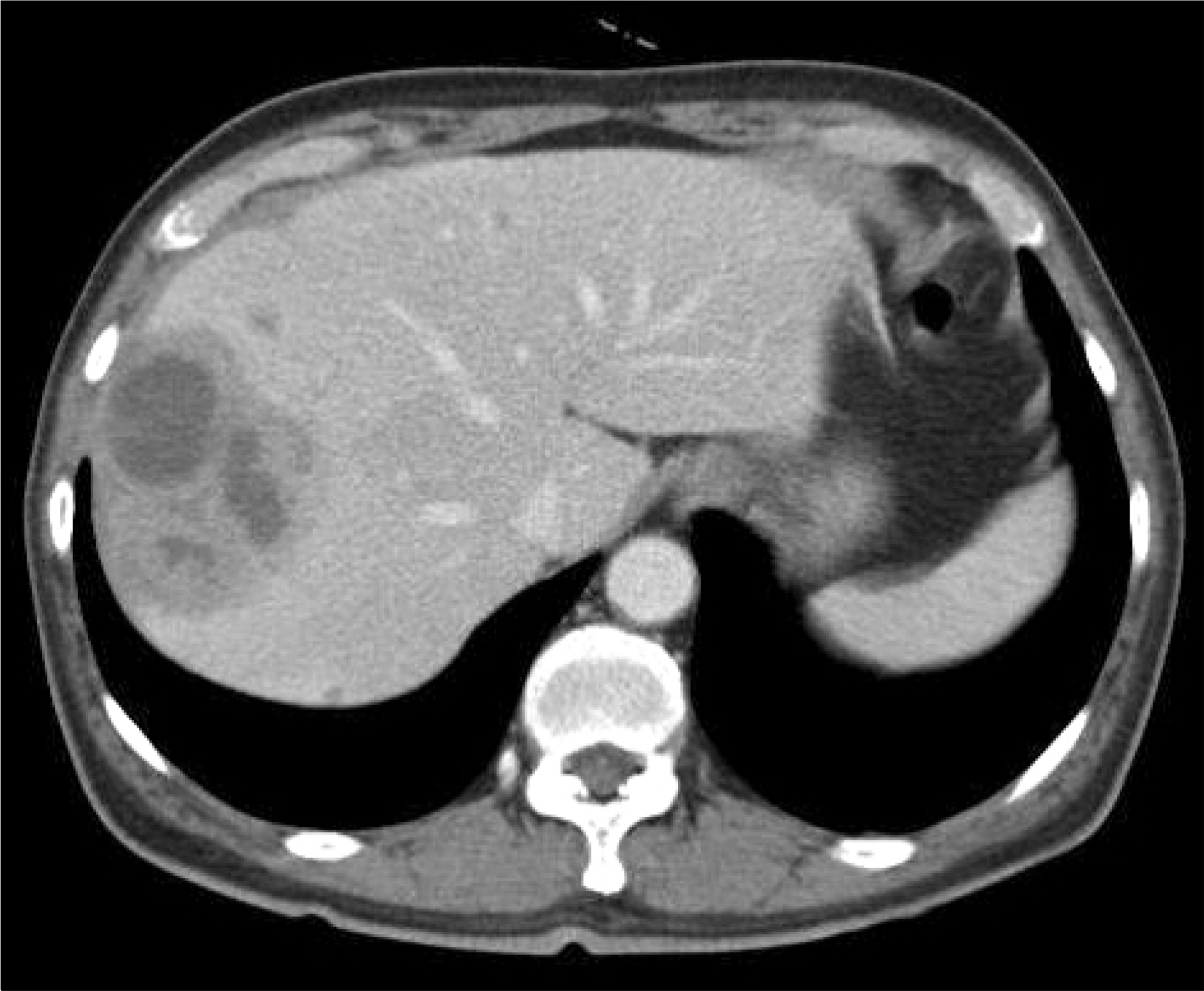
- Fusobacteria are anaerobic gram-negative, non-spore forming bacilli found in normal flora of the oral cavity, urogenital tract, and gastrointestinal tract. Fusobacterium nucleatum has been seldom reported as a cause of liver abscess, particularly in immunocompetent hosts. A 55-year-old man with frequent periodontal disease visited our hospital with intermittent fever and headache for 2 months. Abdominal CT scan revealed an 8.2x6 cm mass in the right hepatic lobe with central low density. Abscess culture revealed F. nucleatum as the causative organism. Percutaneous abscess drainage and intravenous administration of antibiotics for 4 weeks improved symptoms and decreased the abscess size. We report a rare case of liver abscess due to F. nucleatum in an immunocompetent man with periodontal disease.
MeSH Terms
-
Ampicillin/therapeutic use
Anti-Bacterial Agents/therapeutic use
Fusobacterium Infections/complications/*diagnosis/drug therapy
Fusobacterium nucleatum/*isolation & purification
Humans
Injections, Intravenous
Liver Abscess/*diagnosis/etiology/microbiology
Male
Middle Aged
Periodontal Diseases/*diagnosis
Sulbactam/therapeutic use
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Chen W, Chen CH, Chiu KL, et al. Clinical outcome and prognostic factors of patients with pyogenic liver abscess requiring intensive care. Crit Care Med. 2008; 36:1184–1188.
Article2. Chu KM, Fan ST, Lai EC, Lo CM, Wong J. Pyogenic liver abscess. An audit of experience over the past decade. Arch Surg. 1996; 131:148–152.3. Rubin RH, Swartz MN, Malt R. Hepatic abscess: changes in clinical, bacteriologic and therapeutic aspects. Am J Med. 1974; 57:601–610.
Article4. Pitt HA, Zuidema GD. Factors influencing mortality in the treatment of pyogenic hepatic abscess. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1975; 140:228–234.5. Greenstein AJ, Lowenthal D, Hammer GS, Schaffner F, Aufses AH Jr. Continuing changing patterns of disease in pyogenic liver abscess: a study of 38 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 1984; 79:217–226.6. Bourgault AM, Lamothe F, Dolcé P, Saint-Jean L, Saint-Antoine P. Fusobacterium bacteremia: clinical experience with 40 cases. Clin Infect Dis. 1997; 25(Suppl 2):S181–183.
Article7. Etienne M, Gueit I, Abboud P, Pons JL, Jacquot S, Caron F. Fusobacterium nucleatum hepatic abscess with pylephlebitis associated with idiopathic CD4(+) T lympho-cytopenia. Clin Infect Dis. 2001; 32:326–328.
Article8. Wie SH, Chang UI, Kim JD, et al. Clinical features of 141 cases of pyogenic liver abscess over a 10-year period and antibiotic sensitivity to the causative organisms. Infect Chemother. 2008; 40:199–206.
Article9. Nah BK, Kim YS, Moon HS, et al. Recent changes of organism and treatment in pyogenic liver abscess. Korean J Hepatol. 2003; 9:275–283.10. Wang JH, Liu YC, Lee SS, et al. Primary liver abscess due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in Taiwan. Clin Infect Dis. 1998; 26:1434–1438.11. Kurland JE, Brann OS. Pyogenic and amebic liver abscesses. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2004; 6:273–279.
Article12. Infectious Diseases Society of Taiwan; Taiwan Surgical Society of Gastroenterology. Medical Foundation in Memory of Dr. Deh-Lin Cheng. Foundation of Professor Wei-Chuan Hsieh for Infectious Diseases Research and Education. CY Lee's Research Foundation for Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Vaccines. Guidelines for anti-microbial therapy of intraabdominal infections in adults. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2008; 41:279–281.13. Sabbaj J, Sutter VL, Finegold SM. Anaerobic pyogenic liver abscess. Ann Intern Med. 1972; 77:627–638.
Article14. Yoo HM, Kim WH, Yim DS, Kang JK, Park IS, Choi HJ. A clinical study on pyogenic liver abscesses. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1992; 24:1347–1361.15. Lee OJ, Kim YC. A clinical study on liver abscess. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1994; 26:506–520.16. Kajiya T, Uemura T, Kajiya M, et al. Pyogenic liver abscess related to dental disease in an immunocompetent host. Intern Med. 2008; 47:675–678.
Article17. Bennett KW, Eley A. Fusobacteria: new taxonomy and related diseases. J Med Microbiol. 1993; 39:246–254.
Article18. Appelbaum PC, Spangler SK, Jacobs MR. Beta-lactamase production and susceptibilities to amoxicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, ticarcillin, ticarcillin-clavulanate, ce-foxitin, imipenem, and metronidazole of 320 non-Bacter-oides fragilis Bacteroides isolates and 129 fusobacteria from 28 U.S. centers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990; 34:1546–1550.
Article19. Hecht DW. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in anaerobic bacteria: worrisome developments. Clin Infect Dis. 2004; 39:92–97.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Liver Abscess Due to Fusobacterium nucleatum
- Fusobacterium nucleatum modulates serum binding to Porphyromonas gingivalis biofilm
- Effect of Weissella cibaria on Fusobacterium nucleatum-induced Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-8 Production in KB Cells
- Prior Exposure of Mice to Fusobacterium Nucleatum Modulates Host Response to Porphyromonas Gingivalis
- Concomitant Liver and Brain Abscesses Caused by Parvimonas Micra