Korean J Radiol.
2000 Jun;1(2):73-78. 10.3348/kjr.2000.1.2.73.
Cytomegalovirus Pneumonia: High - Resolution CT Findings in Ten Non-AIDS Immunocompromised Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kslee@smc.samsung.co.kr
- KMID: 966476
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2000.1.2.73
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
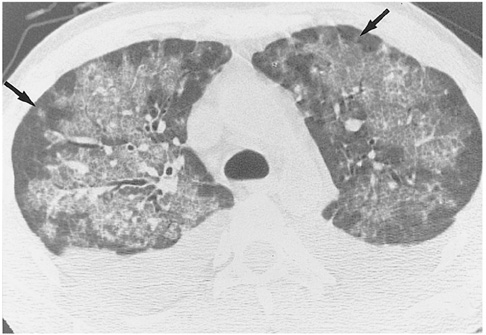
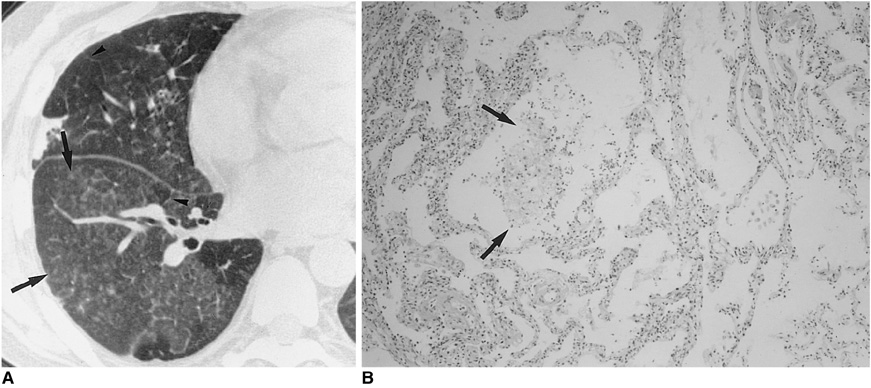
To describe the HRCT findings of cytomegalovirus (CMV) pneumonia in non-AIDS immunocompromised patients. MATERIALS AND METHODS: This retrospective study involved the ten all non-AIDS immunocompromised patients with biopsy-proven CMV pneumonia and without other pulmonary infection encountered at our Medical Center between January 1997 and May 1999. HRCT scans were retrospectively analysed by two chest radiologists and decisions regarding the findings were reached by consensus. RESULTS: The most frequent CT pattern was ground-glass opacity, seen in all patients, with bilateral patchy (n = 8) and diffuse (n = 2) distribution. Other findings included poorly-defined small nodules (n = 9) and consolidation (n = 7). There was no zonal predominance. The small nodules, bilateral in eight cases and unilateral in one, were all located in the centrilobular region. Consolidation (n = 7), with patchy distribution, was bilateral in five of seven patients (71%). Pleural effusion and bilateral areas of thickened interlobular septa were seen in six patients (60%). CONCLUSION: CMV pneumonia in non-AIDS immunocompromised patients appears on HRCT scans as bilateral mixed areas of ground-glass opacity, poorly-defined centrilobular small nodules, and consolidation. Interlobular septal thickening and pleural effusion are frequently associated.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Characteristics of Cytomegalovirus Diseases among Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients : A 10-year Experience at an University Hospital in Korea
Su-Mi Choi, Dong-Gun Lee, Sun Hee Park, Si-Hyun Kim, Yoo-Jin Kim, Chang-Ki Min, Hee-Je Kim, Seok Lee, Jung-Hyun Choi, Jin-Hong Yoo, Dong-Wook Kim, Jong-Wook Lee, Woo-Sung Min, Wan-Shik Shin, Chun-Choo Kim
Infect Chemother. 2009;41(1):9-19. doi: 10.3947/ic.2009.41.1.9.
Reference
-
1. Rubin RH, Cosimi AB, Tolkoff-Rubin NE, Russel PS, Hirsch MS. Infectious disease syndromes attributable to cytomegalovirus and their significance among renal transplantation recipients. Transplantation. 1977. 24:458–464.2. Abdallah PS, Mark JBD, Merigan TC. Diagnosis of cytomegalovirus pneumonia in compromised hosts. Am J Med. 1976. 61:326–332.3. Ravin CE, Smith GW, Ahern MJ, et al. Cytomegaloviral infection presenting as a solitary pulmonary nodule. Chest. 1977. 71:220–222.4. Krowka MJ, Rosenow EC, Hoagland HC. Pulmonary complications of bone marrow transplantation. Chest. 1985. 87:237–246.5. Schulman LL. Cytomegalovirus pneumonitis and lobar consolidation. Chest. 1987. 91:558–561.6. Klotman ME, Hamilton JD. Cytomegalovirus pneumonia. Semin Respir Infect. 1987. 2:95–103.7. Wallace JM, Hannah J. Cytomegalovirus pneumonitis in patients with AIDS. Findings in an autopsy series. Chest. 1987. 92:198–203.8. Johnson PC, Hogg KM, Sarosi GA. The rapid diagnosis of pulmonary infections in solid organ transplant recipients. Semin Respir Infect. 1990. 5:2–9.9. McGuinness G, Scholes JV, Garay SM, Leitman BS, McCauley DI, Naidich DP. Cytomegalovirus pneumonitis: spectrum of parenchymal CT findings with pathologic correlation in 21 AIDS patients. Radiology. 1994. 192:451–459.10. Aafedt BC, Halvorsen RA, Tylen U, Hertz M. Cytomegalovirus pneumonia: computed tomography findings. J Can Assoc Radiol. 1990. 41:276–280.11. Northfelt DW, Sollitto RA, Miller TR, Hollander H. Cytomegalovirus pneumonitis. An unusual cause of pulmonary nodule in a patient with AIDS. Chest. 1993. 103:1918–1920.12. Berger LA. Imaging in the diagnosis of infections in immunocompromised patients. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 1998. 11:431–436.13. Austin JH, Schulman LL, Mastrobattista JD. Pulmonary infection after cardiac transplantation: clinical and radiologic correlations. Radiology. 1998. 72:259–265.14. Shreeniwas R, Schulman LL, Berkmen YM, McGregor CC, Austin JHM. Opportunistic bronchopulmonary infections after lung transplantation: clinical and radiographic findings. Radiology. 1996. 200:349–356.15. Afessa B, Gay PC, Plevak DJ, et al. Pulmonary complications of orthotopic liver transplantation. Mayo Clin Proc. 1993. 68:427–434.16. Kang EY, Patz EF, Müller NL. Cytomegalovirus pneumonia in transplant patients: CT findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1996. 20:295–299.17. Zantel J, Leij L, Prop J, Harmsen MC. The Human cytomegalovirus: a viral complication in transplantation. Clin Transplant. 1998. 12:145–158.18. Moore EH, Webb WR, Amend WJC. Pulmonary infections in renal transplantation patients treated with cyclosporine. Radiology. 1988. 167:97–103.19. Leung AN, Grosselin MV, Napper CH, et al. Pulmonary infections after bone marrow transplantation: clinical and radiographic findings. Radiology. 1999. 210:699–710.20. Husni RN, Gordon SM, Longworth DL, et al. Cytomegalovirus infection is a risk factor for invasive aspergillosis in lung transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis. 1998. 26:753–755.21. Chien J, Chan CK, Chamberlain D, et al. Cytomegalovirus pneumonia in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. An immunopathologic process? Chest. 1990. 98:1034–1307.22. Worthy SA, Flint JD, Müller NL. Pulmonary complications after bone marrow transplantation: high-resolution CT and pathologic findings. RadioGraphics. 1997. 17:1359–1371.23. Aukrust P, Farstad IN, Froland SS, Holter E. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) pneumonitis in AIDS patients: the result of intensive CMV replication? Eur Respir J. 1992. 5:362–364.24. KIM HS, LEE JS. Cytomegalovirus pneumonia in immunocompromised patients: HRCT findings. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1999. 41:1133–1138.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage Associated with Cytomegalovirus Pneumonia
- Radiographic Findings of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Non-AIDS Immunocompromised adult Patients: Comparison with Immunocompetent Adult Patients
- 4 Cases of Reactivated Cytomegalovirus Retinitis in Immunocompromised Patients
- A Case of Cytomegalovirus Induced Perineal Ulcer in An AIDS Patient
- Two Cases of Cutaneous Cytomegalovirus Infection in Immunocompromised Patients