Korean J Radiol.
2010 Jun;11(3):320-326. 10.3348/kjr.2010.11.3.320.
Dual-Energy Subtraction Imaging for Diagnosing Vocal Cord Paralysis with Flat Panel Detector Radiography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Tokyo Women's Medical University Medical Center East, Tokyo 116-8567, Japan. machira@dnh.twmu.ac.jp
- 2Department of Otolarygology, Tokyo Women's Medical University Medical Center East, Tokyo 116-8567, Japan.
- 3GE Healthcare, WI 53188, USA.
- KMID: 946272
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2010.11.3.320
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
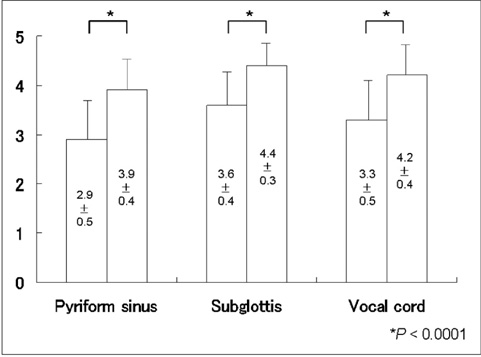
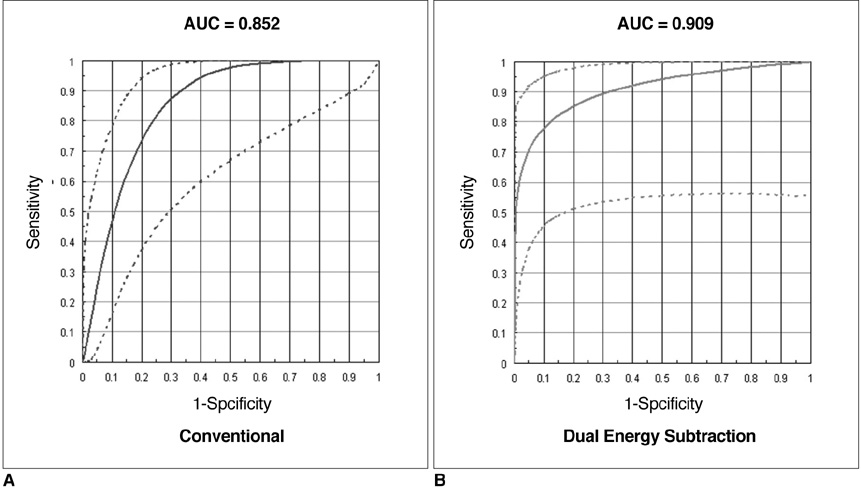
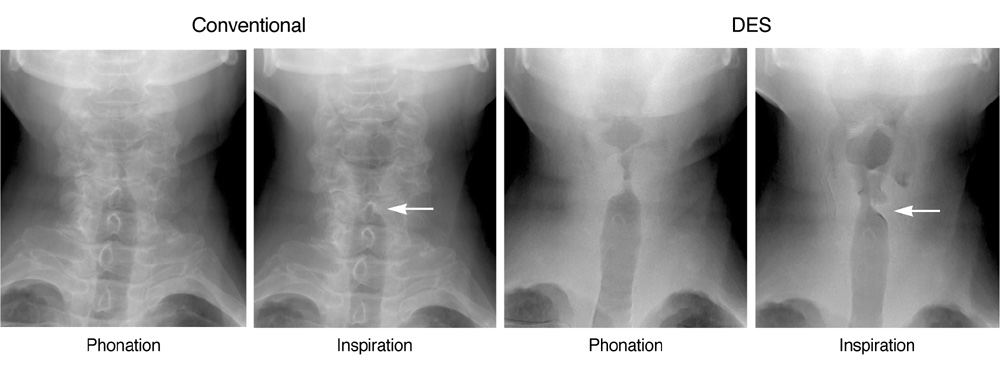
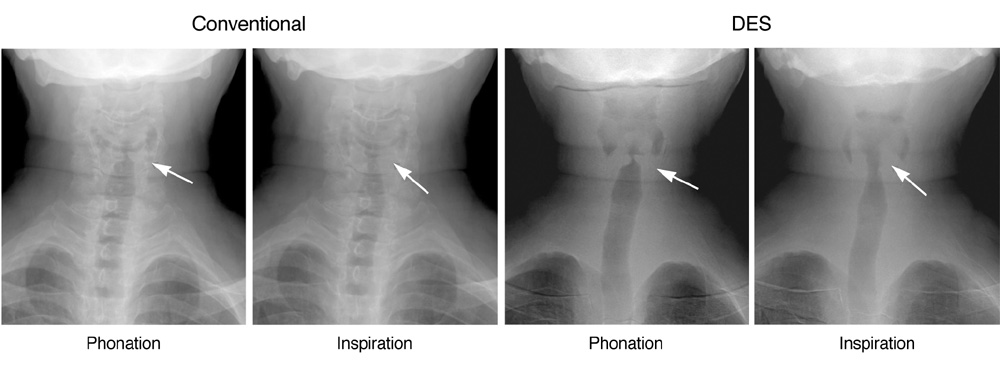
To investigate the clinical feasibility of dual energy subtraction (DES) imaging to improve the delineation of the vocal cord and diagnostic accuracy of vocal cord paralysis as compared with the anterior-posterior view of flat panel detector (FPD) neck radiography. MATERIALS AND METHODS: For 122 consecutive patients who underwent both a flexible laryngoscopy and conventional/DES FPD radiography, three blinded readers retrospectively graded the radiographs during phonation and inspiration on a scale of 1 (poor) to 5 (excellent) for the delineation of the vocal cord, and in consensus, reviewed the diagnostic accuracy of vocal cord paralysis employing the laryngoscopy as the reference. We compared vocal cord delineation scores and accuracy of vocal cord paralysis diagnosis by both conventional and DES techniques using kappa statistics and assessing the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). RESULTS: Vocal cord delineation scores by DES (mean, 4.2 +/- 0.4) were significantly higher than those by conventional imaging (mean, 3.3 +/- 0.5) (p < 0.0001). Sensitivity for diagnosing vocal cord paralysis by the conventional technique was 25%, whereas the specificity was 94%. Sensitivity by DES was 75%, whereas the specificity was 96%. The diagnostic accuracy by DES was significantly superior (kappa = 0.60, AUC = 0.909) to that by conventional technique (kappa = 0.18, AUC = 0.852) (p = 0.038). CONCLUSION: Dual energy subtraction is a superior method compared to the conventional FPD radiography for delineating the vocal cord and accurately diagnosing vocal cord paralysis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Absorptiometry, Photon/*instrumentation/*methods
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Child
Child, Preschool
Feasibility Studies
Female
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Observer Variation
Reproducibility of Results
Sensitivity and Specificity
Subtraction Technique
Vocal Cord Paralysis/*radiography
Vocal Cords/radiography
*X-Ray Intensifying Screens
Young Adult
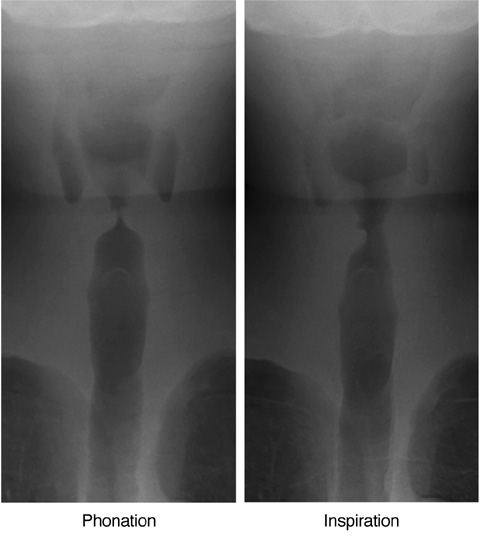
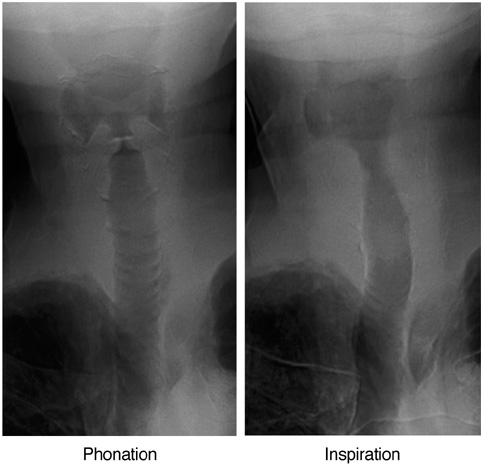
Figure
Reference
-
1. Carderon R, Ceballos J, McGraw JP. Tomographic aspect of paralysis of the vocal cords. Radiology. 1954. 63:407–410.2. Isshiki N, Ishikawa T. Diagnostic value of tomography in unilateral vocal cord paralysis. Laryngoscope. 1976. 86:1573–1578.3. Agha FP. Recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis: a laryngographic and computed tomographic study. Radiology. 1983. 148:149–155.4. Yumoto E, Sanuki T, Hyodo M. Three dimensional endoscopic images of vocal fold paralysis by computed tomography. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999. 125:883–890.5. Yumoto E, Oyamada Y, Nakano K, Nakayama Y, Yamashita Y. Three-dimensional characteristics of the larynx with immobile vocal fold. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004. 130:967–974.6. Ricke J, Fishbach F, Freund T, Teichgräber U, Hänninen EL, Röttgen R, et al. Clinical results of CsI-detector-based dual-exposure dual energy in chest radiography. Eur Radiol. 2003. 13:2577–2582.7. McAdams HP, Samei E, Dobbins J 3rd, Tourassi GD, Ravin CE. Recent advances in chest radiography. Radiology. 2006. 241:663–683.8. Fink C, Hallscheidt PJ, Noeldge G, Kampschulte A, Radeleff B, Hosch WP, et al. Clinical comparative study with a large-area amorphous silicon flat-panel detector: image quality and visibility of anatomic structures on chest radiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002. 178:481–486.9. Strotzer M, Gmeinwieser JK, Völk M, Fründ R, Seitz J, Feuerbach S. Detection of simulated chest lesions with normal and reduced radiation dose: comparison of conventional screen-film radiography and a flat-panel X-ray detector based on amorphous silicon. Invest Radiol. 1998. 33:98–103.10. Bacher K, Smeets P, Bonnarens K, De Hauwere A, Verstraete K, Thierens H. Dose reduction in patients undergoing chest imaging: digital amorphous silicon flat-panel detector radiography versus conventional film-screen radiography and phosphor-based computed radiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003. 181:923–929.11. Tagashira H, Arakawa K, Yoshimoto M, Mochizuki T, Murase K. Detectability of lung nodules using flat panel detector with dual energy subtraction by two shot method: evaluation by ROC method. Eur J Radiol. 2007. 64:279–284.12. Sabol JM, Avinash GB, Nicolas F, Claus B, Zhao J, Dobbins JT III. Antonuk LE, Yaffe MJ, editors. Development and characterization of a dual-energy subtraction imaging system for chest radiography based on CsI: T1 amorphous silicon flat-panel technology. Medical Imaging 2002: physics of medical imaging -- proceedings. 2001. vol. 4320. Bellingham, WA: Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers;399–408.13. Metz CE, Herman BA, Shen JH. Maximum-likelihood estimation of receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves from continuously-distributed data. Stat Med. 1998. 17:1033–1053.14. Merati AL, Shemirani N, Smith TL, Toohill RJ. Changing trends in the nature of vocal fold motion impairment. Am J Otolaryngol. 2006. 27:106–108.15. Hagan PJ. Vocal cord paralysis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1963. 72:206–222.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Guillain-Barre Syndrome Presenting as Bilateral Vocal Cord Paralysis
- Unilateral Vocal Cord Paralysis Following Endotracheal Intubation - A case report
- Two Cases of Vocal Cord Paralysis Complicated by Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
- Digital Chest Radiography with an Amorphous Silicon Flat-Panel-Detector Versus a Storage-Phosphor System: Comparison of Soft-Copy Images
- A Case of Bilateral Vocal Cord Paralysis from Progressive Supranuclear Palsy