Korean J Ophthalmol.
2010 Jun;24(3):186-188. 10.3341/kjo.2010.24.3.186.
Presumed Metastasis of Breast Cancer to the Abducens Nucleus Presenting as Gaze Palsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. hjm@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 945993
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2010.24.3.186
Abstract
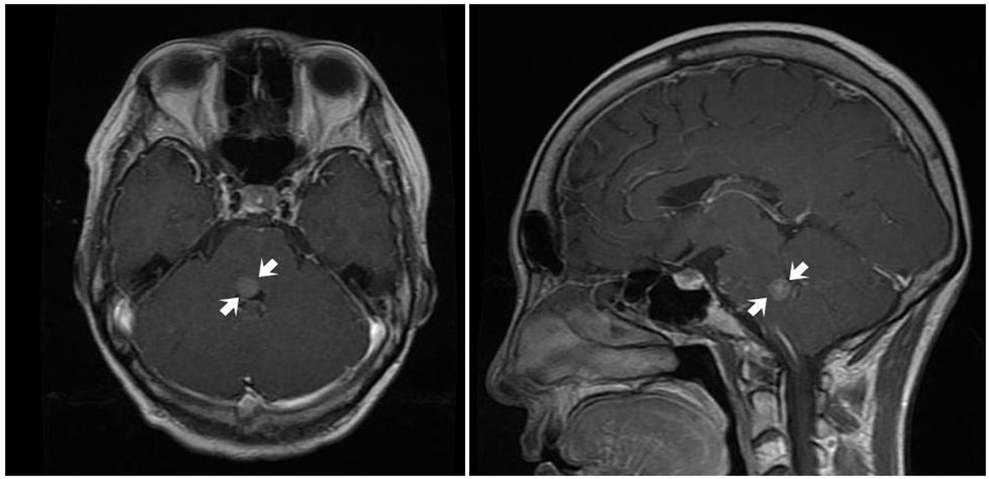
- A 51-year-old woman with breast cancer presented with progressive diplopia. Neuro-ophthalmologic examination revealed right gaze palsy and peripheral facial nerve palsy. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was normal. However, two months later a repeat brain MRI revealed an enhancing round nodular mass at the right facial colliculus of the lower pons, at the location of the abducens nucleus. Localized metastasis to the abducens nucleus can cause gaze palsy in a patient with breast cancer.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pierrot-Deseilligny C, Chain F, Serdaru M, et al. The 'one-and-a-half' syndrome. Electro-oculographic analyses of five cases with deductions about the physiological mechanisms of lateral gaze. Brain. 1981. 104:665–699.2. Crisostomo EA. One-and-a-half syndrome in a patient with metastatic breast disease. J Clin Neuroophthalmol. 1985. 5:270–272.3. Pierrot-Deseilligny C, Goasguen J, Chain F, Lapresle J. Pontine metastasis with dissociated bilateral horizontal gaze paralysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984. 47:159–164.4. Martin JH. Neuroanatomy: text and atlas. 2003. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;259–300.5. Tsukada Y, Fouad A, Pickren JW, Lane WW. Central nervous system metastasis from breast carcinoma: autopsy study. Cancer. 1983. 52:2349–2354.6. Kaal EC, Vecht CJ. CNS complications of breast cancer: current and emerging treatment options. CNS Drugs. 2007. 21:559–579.7. Zimm S, Wampler GL, Stablein D, et al. Intracerebral metastases in solid-tumor patients: natural history and results of treatment. Cancer. 1981. 48:384–394.8. Yen CP, Sheehan J, Patterson G, Steiner L. Gamma knife surgery for metastatic brainstem tumors. J Neurosurg. 2006. 105:213–219.9. Lee SS, Ahn JH, Kim MK, et al. Brain metastases in breast cancer: prognostic factors and management. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008. 111:523–530.10. Victor M, Ropper AH, Adams RD. Adams and Victor's principles of neurology. 2001. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;718.11. Shin MK, Choi CP, Lee MH. A case of herpes zoster with abducens palsy. J Korean Med Sci. 2007. 22:905–907.12. Oh JH, Kim SH, Chi MJ, Cho YA. A case of horizontal gaze palsy with ipsilateral esotropia due to pontine hemorrhage. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007. 48:873–877.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Isolated Unilateral Abducens Nerve Palsy Caused by Clival Metastasis from Rectal Cancer
- The Unilateral Abducens Nerve Palsy with Small Esotropia Caused by Clival Chordoma
- A Case of Abducens Nerve Palsy after Percutaneous Nerve Block for Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Neuroophthalmologic Findings of Intracranial Aneurysm
- Vertical One-and-a-Half Syndrome Accompanying Contralateral Abduction and Incomplete Depression Palsy Due to Thalamo-Mesencephalic Infarction