Korean J Radiol.
2000 Sep;1(3):169-171. 10.3348/kjr.2000.1.3.169.
Delayed Colon Perforation after Palliative Treatment for Rectal Carcinoma with Bare Rectal Stent: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chonbuk National University, Medical School, Chonju, Chonbuk, South Korea. ymhan@moak.chonbuk.ac.kr
- KMID: 877079
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2000.1.3.169
Abstract
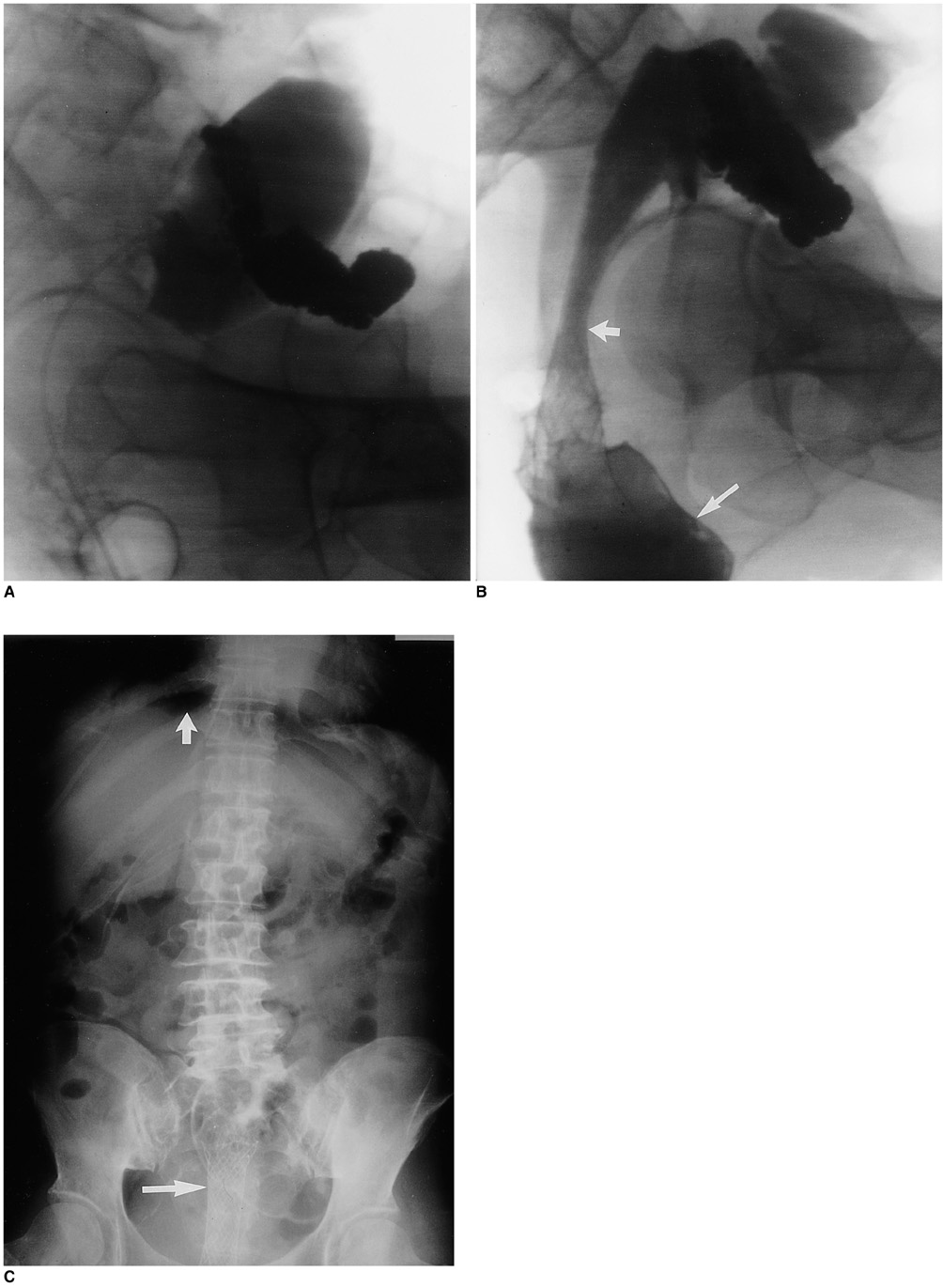
- In order to relieve mechanical obstruction caused by rectal carcinoma, a bare rectal stent was inserted in the sigmoid colon of a 70-year-old female. The proce-dure was successful, and for one month the patient made good progress. She then complained of abdominal pain, however, and plain radiographs of the chest and abdomen revealed the presence of free gas in the ubdiaphragmatic area. Surgical findings showed that a spur at the proximal end of the bare rectal stent had penetrated the rectal mucosal wall. After placing a bare rectal stent for the palliative treatment of colorectal carcinoma, close follow-up to detect possible perforation of the bowel wall is necessary.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Choo IW, Do YS, Suh SW, et al. Malignant colorectal obstruction: treatment with a flexible covered stent. Radiology. 1998. 206:415–421.2. Mainar A, Tejero E, Maynar M, Ferral H, Castaneda-Zuniga W. Colorectal obstruction: treatment with metallic stents. Radiology. 1996. 198:761–764.3. De Gregorio MA, Mainar A, Tejero E, et al. Acute colorectal obstruction: stent placement for palliative treatment - result of a multicenter study. Radiology. 1998. 209:117–120.4. Canon CL, Baron TH, Morgan DE, Dean PA, Koehler RE. Treatment of colonic obstruction with expandable metal stents: radiologic features. AJR. 1997. 168:199–205.5. Mainar A, De Gregorio MA, Tejero E, et al. Acute colorectal obstruction: treatment with self-expandable metallic stents before scheduled surgery - results of a multicenter study. Radiology. 1999. 210:65–69.6. Wallis F, Campbell KL, Eremin O, Hussey JK. Self-expanding metal stents in the management of colorectal carcinoma - a preliminary report. Clin Radiol. 1998. 53:251–254.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Conservative Treatment of Rectal Perforation after Insertion of A Stent and Chemo-Radiotherephy in the Patient with Obstructive Rectal Cancer
- Endoscopic Prosthesis in Malignant Stricture
- Colonic Stent-Related Complications and Their Management
- Spontaneous Rectal Perforation with Transanal Evisceration of the Small Bowel: A Rare Case Report
- Colorectal Perforation After Anorectal Manometry for Low Anterior Resection Syndrome