Korean J Radiol.
2000 Sep;1(3):159-161. 10.3348/kjr.2000.1.3.159.
Bronchus-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (BALT) Lymphoma of the Lung Showing Mosaic Pattern of Inhomogeneous Attenuation on Thin-section CT: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Anyang City, Kyungki-do, Korea. ijlee@www.hallym.or.kr
- KMID: 877076
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2000.1.3.159
Abstract
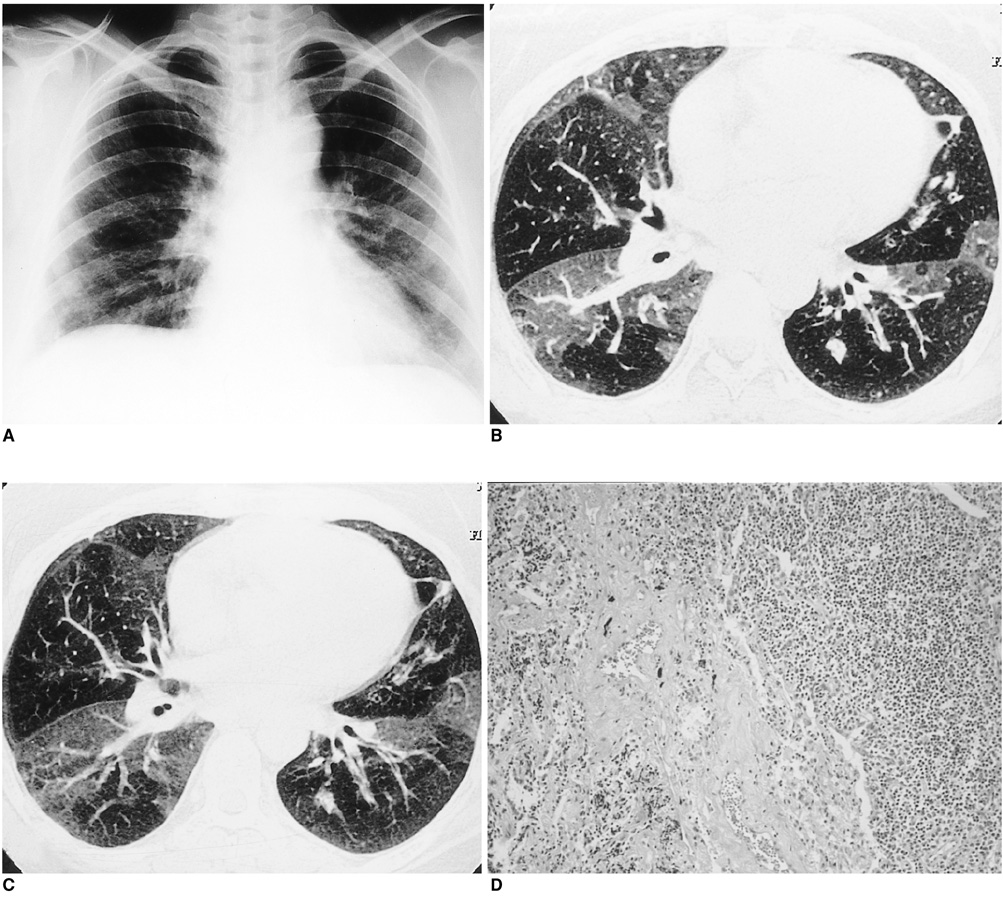
- The authors present a case of histologically proven bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue (BALT) lymphoma of the lung in a patient with primary Sjogren's syn-drome that manifested on thin-section CT scan as a mosaic pattern of inhomoge-neous attenuation due to mixed small airway and infiltrative abnormalities
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma of the Esophagus Coexistent with Bronchus-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma of the Lung
Jae-Joon Chung, Myeong-Jin Kim, Jeong-Hae Kie, Ki Whang Kim
Yonsei Med J. 2005;46(4):562-566. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2005.46.4.562.
Reference
-
1. Lee DK, Im J-G, Lee KS, et al. B-cell lymphoma of bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue (BALT): CT features in 10 patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2000. 24:30–34.2. O'Donnell PG, Jackson SA, Tung KT, Hassan B, Wilkins B, Mead GM. Radiological appearance of lymphomas arising from mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) in the lung. Clin Radiol. 1998. 53:258–263.3. Knisely BL, Mastey LA, Mergo PJ, et al. Pulmonary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma: CT and pathologic findings. AJR. 1999. 172:1321–1326.4. Wislez M, Cadranel J, Antoine M, et al. Lymphoma of pulmonary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue: CT scan findings and pathological correlations. Eur Respir J. 1999. 14:423–429.5. McCulloch GL, Sinnatamby R, Stewart S, Goddard M, Flower CDR. High-resolution computed tomographic appearance of MALToma of the lung. Eur Radiol. 1998. 8:1669–1673.6. Chow WH, Ducheine Y, Hilfer J, Brandstetter RD. Chronic pneumonia. Primary malignant non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the lung arising in mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Chest. 1996. 110:838–840.7. Franquet T, Gimenez A, Monill JM, Diaz C, Geli C. Primary Sjögren's syndrome and associated lung disease: CT findings in 50 patients. AJR. 1997. 169:655–658.8. Hansen LA, Parkash UBS, Colby TV. Pulmonary lymphoma in Sjögren's syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc. 1989. 64:920–931.9. Worthy SA, Müller NL, Hartman TE, Swensen SJ, Padley SPG, Hansell DM. Mosaic attenuation pattern on thin-section CT scans of the lung: differentiation among infiltrative lung, airway, and vascular disease as a cause. Radiology. 1997. 205:465–470.10. Shah RM, Sexauer W, Ostrum BJ, et al. High-resolution CT in the acute exacerbation of cystic fibrosis: evaluation of acute findings, reversibility of those findings, and clinical correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997. 169:375–380.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Bronchus-Associated Lymphoid Tissue(BALT) Lymphoma in the Lung of the Patient with Primary Sjogren's Syndrome
- Cases of the Pulmonary Malignant Lymphoma of the Bronchus-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (BALT)
- Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma of the Esophagus Coexistent with Bronchus-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma of the Lung
- A case of bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue (BALT) lymphoma in the patient with rheumatoid arthritis
- Radiation Therapy for Bronchial Associated Lymphoid Tissue (BALT) Lymphoma : A case report