J Korean Acad Nurs.
2009 Aug;39(4):508-517. 10.4040/jkan.2009.39.4.508.
Development and Application of a Feeding Program for Infants Postoperatively following Cardiac Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Cardiac & Vascular Center, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, School of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, School of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. yoenyi.jung@samsung.com
- KMID: 820228
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.4.508
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: Despite recent advances in the surgical and postoperative management of infants with congenital heart disease, nutritional support for this population is often suboptimal. The purpose of this study was to develop a nutritional program for the postoperative period for infants who have had cardiac surgery and to evaluate effects of the program.
METHODS
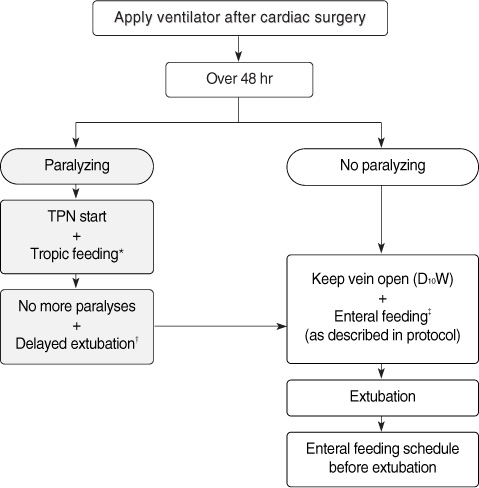
A quasi-experimental design with pretest and posttest measures was used. A newly developed nutritional program including a feeding protocol and feeding flow was provided to the study group (n=19) and usual feeding care to the control group (n=19). The effects of the feeding program were analyzed in terms of total feed intake, total calorie intake, gastric residual volume, and frequency of diarrhea.
RESULTS
Calorie intake and feeding amount in the study group were significantly increased compared to the control group. However, the two groups showed no significant differences in gastric residual volume and frequency of diarrhea.
CONCLUSION
The results indicate that the nutritional program used in the study is an effective nursing intervention program in increasing feeding amount and calorie intake in infants postoperative to cardiac surgery and does not cause feeding-related complications.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition. Pediatric Nutrition Handbook. 1998. 4th ed. Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics.2. Beke DM, Braudis NJ, Lincolin P. Management of the pediatric postoperative cardiac surgery patient. Critical Care Nursing Clinics of North America. 2005. 17:405–416.3. Chan R, Jacobs S, Lee B. Gastrointestinal dysfunctionamong intensive care patients. Critical Care Medicine. 1987. 10:909–914.4. Ciotti G, Holzer R, Pozzi M, Dalzell M. Nutritional support via percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in children with cardiac disease experiencing difficulties with feeding. Cardiology in the Young. 2002. 12:537–541.5. Davey AM, Wagner CL, Cox C, Kendig JW. Feeding premature infants while low umbilical artery catheters are in place: A prospective, randomized trial. Journal of Pediatrics. 1994. 124:795–799.6. De Jonghe B, Appere-De-Vechi C, Fournier M, Tran B, Merrer J, Melchior JP, et al. A Prospective survey of nutritional support practices in intensive care unit patient: What is prescribed? What is delivered? Critical Care Medicine. 2001. 29:8–12.7. Frankenfield DC, Smith JS, Cooley RN. Accelerated nitrogen loss after traumatic injury is not attenuated by achievement of energy balance. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. 1997. 21:324–329.8. Hanekamp MN, Spoel M, Sharman-Koendjbiharie I, Jeroen WB, Albers MJ, Tibboel D. Routine enteral nutrition in neonates on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Pediatric Critical Care Medicine. 2005. 6:275–279.9. Kim JE, Choi BH, Kim KM, Ko JK, Seo DM. Analysis of malnutrition in children with congenital heart disease. Korean Journal of Pediatrics. 2001. 44:161–165.10. Kinney JM. Metabolic responses of the critically ill patient. Critical Care Clinics. 1995. 11:569–585.11. Lee SI, Choi HR. Nutrition for infants and children. 2003. Seoul: Kyomunsa.12. McCulley ME, Jeffries HE, Wells WJ, Starnes VA, Castillo SL, Moromisato DY, et al. Effect of a standardized feeding protocol in infants with hypoplastic left ventricle following first stage palliation. Critical Care Medicine. 2005. 33:A62.13. Moon JR, Huh J, Lee HJ, Kang IS, Kim SH, Jun TG. Diagnosis of feeding difficulty and development of feeding protocol after cardiac surgery in infant. 2006. 04. In : Paper presented at the annual meeting of the Korean Society of Quality Assurance in the Health Care; Jeju:14. Ngdegger A, Eines E. Energy metabolism in infants with congenital heart disease. Nutrition. 2006. 22:697–704.15. Petrillo-Albarano T, Pettignano R, Asfaw M, Easley K. Use of a feeding protocol to improve nutritional support through early, aggressive, enteral nutrition in the pediatric intensive care unit. Pediatric Critical Care Medicine. 2006. 7:340–344.16. Pillo-Blocka F, Aditia I, Sharieff W. Rapid advancement to more concentrated formula in infants after surgery for congenital heart disease reduces duration of hospital stay: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Pediatrics. 2004. 145:761–766.17. Rogers B, Arvedson J. Assessment of infant oral sensorimotor and swallowing function. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities. 2005. 35:74–82.18. Samour PQ, Helm KK, Lang CE. Handbook of pediatric nutrition. 1999. 2nd ed. Baltimore, MD: Aspen Publication.19. Sanchez C, Lopez-Herce J, Carrillo A, Bustinza A, Sancho L, Vigil D. Transpyloric enteral feeding in the postoperativeof cardiac surgery in children. Pediatric Surgery. 2006. 41:1096–1102.20. Sinden AA, Sutphen JL. Pine JW, editor. Growth and nutrition. Moss and Adams' heart disease in infants, children, and adolescent: Including the fetus and young adult. 1995. Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins;366–374.21. Steltzer M, Rudd N, Pick B. Nutrition care for newborns with congenital heart disease. Clinics in Perinatology. 2005. 32:1017–1030.22. Verhoeven JJ, Hazelzet JA, van der Voort E, Joosten KF. Comparison of measured and predicted energy expenditure in mechanically ventilated children. Intensive Care Medicine. 1998. 24:464–468.23. Wall RJ, Dittus RS, Ely EW. Protocol-driven carein the intensive care unit: A tool for quality. Critical Care. 2001. 5:283–285.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Review on Revised Nutrition Guidelines of the Korea National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children
- Development and Implementation of a Feeding Protocol for Infants in a Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit
- Effects of an Oral Stimulation Program on the Transition from Tube to Bottle Feeding in Premature Infants
- The Characteristics of Infants' Temperament, Maternal Feeding Behavior and Feeding Practices in Picky Eaters
- Developing the Mansoura Early Feeding Skills Assessment Scale for Preterm Infants