Korean J Ophthalmol.
2005 Sep;19(3):239-242. 10.3341/kjo.2005.19.3.239.
Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome Associated with Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. cataract@empal.co.kr
- KMID: 754432
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2005.19.3.239
Abstract
- PURPOSE
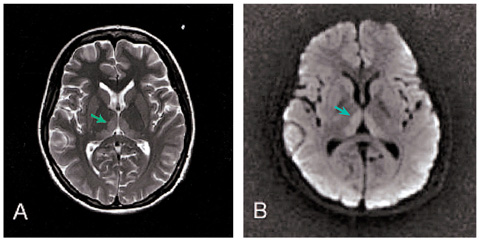
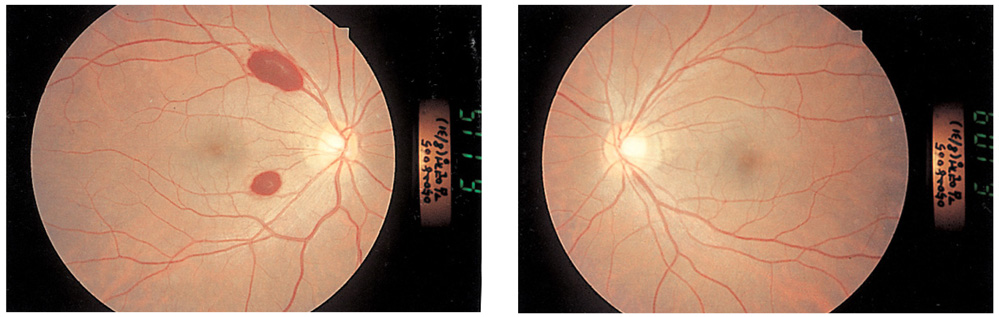
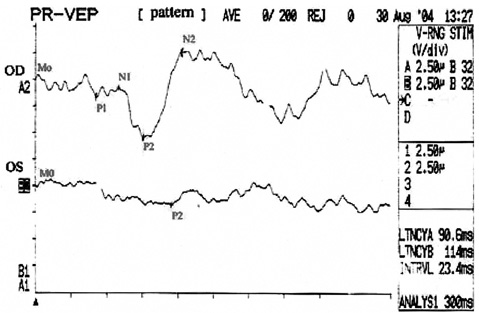
The authors hereby describe a case of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome with accompanying ocular findings that is caused by hyperernesis gravidarum. METHODS: We experienced a 27-year-old female at 12 weeks of pregnancy, who visited our clinic because of weight loss, gait disturbance, decreased mentality and dizziness after prolonged vomiting for 2 months. Neurological examination demonstrated ataxia of gait and loss of orientation. Ophthalmologic examination showed decreased visual acuity, upbeat nystagmus, diplopia and retinal hemorrhage. RESULTS: We report a relatively rare case of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome with ophthalmic symptoms induced by hyperemesis gravidarum. CONCLUSIONS: If a pregnant women has symptoms of severe vomiting along with other ocular findings such as retinal hemorrhage or restricted extraocular movement, one must suspect the diagnosis of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, and should start appropriate treatment immediately.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
A Case of Thiamine (Vitamin B1)-Deficient Optic Neuropathy Associated with Wernicke's Encephalopathy
Jung Yeul Kim, Dong Won Heo, Haeng Jin Lee, Yeon Hee Lee
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013;54(12):1954-1959. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2013.54.12.1954.A Critical Case of Wernicke's Encephalopathy Induced by Hyperemesis Gravidarum
Byung Ju Kang, Min Gu Kim, Jwa Hoon Kim, Mingee Lee, Sang-Beom Jeon, Ha Il Kim, Jin Won Huh
Korean J Crit Care Med. 2015;30(2):128-131. doi: 10.4266/kjccm.2015.30.2.128.
Reference
-
1. Wilson JD. Isselbacher KJ, Braunwald E, Wilson JD, editors. Vitamin deficiency and excess. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 1994. v. 1.:13th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;chap. 77.2. Levine MG, Esser D. Total parenteral nutrition for the treatment of severe hyperemesis gravidarum: maternal nutritional effect and fetal outcome. Obstet Gynecol. 1988. 72:102–107.3. Lee JC, Jeong EH, Roh JS, et al. A case of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome associated with hyperemesis gravidarum. J Korean Obstet Gynecol. 1997. 40:429–433.4. Kim YH, Lee SJ, Yoon JK, et al. Wernicke's syndrome induced by hyperemesis gravidarum. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2001. 42:538–541.5. The National Research Council Committee on Dietary Allowance. Food and Nutrition Board. Recommended Dietary Allowances. 1980. 9th ed. Washington, DC: National Academy of Science;178–185.6. Davis R, Icke GC. Clinical chemistry of thiamin. Adv Clin Chem. 1983. 2:93–140.7. Adams RD, Victor M, Ropper AH. Principles of Neurology. 2001. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;1205–1212.8. Mumford CJ. Papilloedema delaying the diagnosis of Wernicke's encephalopathy in a comatous patient. Postgrad med J. 1989. 65:371–373.9. Bergin PS, Harvey P. Wernicke's encephalopathy and central pontine myelolysis associated with hyperemesis gravidarum. BMJ. 1992. 305:517–518.10. Peter JG. Wernicke's encephalopathy and hyperemesis gravidarum. BMJ. 1992. 305:1096.11. Hammes HP, Du X, Edelstein D, et al. Benfotiamine blocks three major pathways of hyperglycemic damage and prevents experimental diabetic retinopathy. Nat Med. 2003. 9:294–299.12. Maurice V, Martin JB. Isselbacher KF, editor. Nutritional and metabolic diseases of the nervous system. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 1994. v. 2:13th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;chap. 377.13. Ohkoshi N, Ishii A, Shoji S. Wernicke's encephalopathy induced by hyperemesis gravidarum, associated with bilateral caudate lesions on computed tomography and magnetic resonance image. Eur neurology. 1994. 34:177–180.14. Poloni M, Mazarello P, Laforenza U, et al. Thiamin contents of cerebrospinal fluid, plasma and erythrocytes in cerebellar ataxias. Eur Neurol. 1992. 32:154–158.15. Victor M. MR in the diagnosis of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Am J Roentgenol. 1990. 155:1315–1316.16. Burst JCM. Rowland LP, editor. Environmental neurology: Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Merritt's textbook of Neurology. 2000. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Williams & Wilkins;chap. 157.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome Associated with Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- A case of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome associated with severe hyperemesis gravidarum
- A Case of Wernicke - Korsakoff Syndrome Associated with Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- Two Cases of Wernicke's Encephalopathy with Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- A Case of Wernicke's Encephalopathy Associated with Hyperemesis Gravidarum