Korean J Radiol.
2001 Jun;2(2):63-67. 10.3348/kjr.2001.2.2.63.
Hippocampal Sclerosis: Correlation of MR Imaging Findings
- KMID: 754106
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2001.2.2.63
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
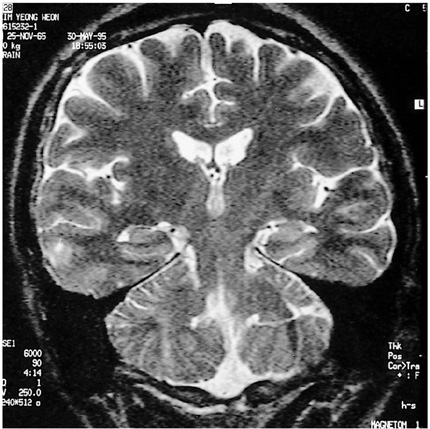
Atrophy and a high T2 signal of the hippocampus are known to be the principal MR imaging findings of hippocampal sclerosis. The purpose of this study was to determine whether or not individual MRI findings correlate with surgical outcome in patients with this condition. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Preoperative MR imaging findings in 57 consecutive patients with pathologically-proven hippocampal sclerosis who underwent anterior temporal lobectomy and were followed-up for 24 months or more were retrospectively reviewed, and the results were compared with the postsurgical out-come (Engel classification). The MR images included routine sagittal T1-weighted and axial T2-weighted spin-echo images, and oblique coronal T1-weighted 3D gradient-echo and T2-weighted 2D fast spin-echo images obtained on either a 1.5 T or 1.0 T unit. The images were visually evaluated by two neuroradiologists blinded to the outcome; their focus was the presence or absence of atrophy and a high T2 hippocampal signal. RESULTS: Hippocampal atrophy was seen in 96% of cases (55/57) [100% (53/53) of the good outcome group (Engel class I and II), and 50% (2/4) of the poor outcome group (class III and IV)]. A high T2 hippocampal signal was seen in 61% of cases (35/57) [62% (33/53) of the good outcome group and 50% (2/4) of the poor outcome group]. All 35 patients with a high T2 signal had hippocampal atrophy. `Normal' hippocampus, as revealed by MR imaging, occurred in 4% of patients (2/57), both of whom showed a poor outcome (Engel class III). The presence or absence of hippocampal atrophy correlated well with surgical outcome (p<0.01). High T2 signal intensity did not, however, significantly correlate with surgical outcome (p>0.05). CONCLUSION: Compared with a high T2 hippocampal signal, hippocampal atrophy is more common and correlates better with surgical outcome. For the prediction of this, it thus appears to be the more useful indicator.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Babb TL, Brown WJ. Engel J, editor. Pathological findings in epilepsy. Surgical Treatment of the Epilepsies. 1987. New York, NY: Raven Press;511–540.2. Bruton CJ. The Neuropathology of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. 1988. Oxford: Oxford University Press.3. Falconer MA. Mesial temporal (Ammon's horn) sclerosis as a common cause of epilepsy: aetiology, treatment, and prevention. Lancet. 1974. 2:767–770.4. Jack CR Jr, Sharbrough FW, Cascino GD, et al. Magnetic resonance image-based hippocampal volumetry: correlation with outcome after temporal lobectomy. Ann Neurol. 1992. 31:138–146.5. Jack CR. Epilepsy: surgery and imaging. Radiology. 1993. 189:635–646.6. Bronen RA. Epilepsy: the role of MR imaging. AJR. 1992. 159:1165–1174.7. Tien RD, Felsberg GJ, Castro C, et al. Complex partial seizures and mesial temporal sclerosis: evaluation with fast spin-echo MR imaging. Radiology. 1993. 189:835–842.8. Jackson GD, Berkovic SF, Tress BM, et al. Hippocampal sclerosis can be reliably detected by magnetic resonance imaging. Neurology. 1990. 40:1869–1875.9. Jackson GD, Berkovic SF, Duncan JS, Connelly A. Optimizing the diagnosis of hippocampal sclerosis using MR imaging. AJNR. 1993. 14:753–762.10. Casino GD, Jack CR Jr, Parisi JE, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging-based volume studies in temporal lobe epilepsy: pathological correlations. Ann Neurol. 1991. 30:31–36.11. Berkovic SF, Andermann F, Oliver A, et al. Hippocampal sclerosis in temporal lobe epilepsy demonstrated by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol. 1991. 29:175–182.12. Bronen RA, Fulbright RK, Spencer DD, et al. Refractory epilepsy: comparision of MR imaging, CT, and histopathologic findings in 117 patients. Radiology. 1996. 201:97–105.13. Engel J Jr. Engel J, editor. Outcome with respect to epileptic seizures. Surgical Treatment of the Epilepsies. 1987. New York, NY: Raven Press;553–571.14. Earle KM, Baldwin M, Penfield W. Incisural sclerosis and temporal lobe seizures produced by hippocampal herniation at birth. Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1953. 69:27–42.15. Duncan R, Sagar HJ. Seizure characteristics, pathology and outcome after temporal lobectomy. Neurology. 1987. 37:405–409.16. Meldrum BS, Vigouroux RA, Brierley JB. Systemic factors and epileptic brain damage. Arch Neurol. 1973. 29:82–87.17. Kuzniecky R, Burgard S, Faught E, Morawetz R, Bartolucci A. Predictive value of magnetic resonance imaging in temporal lobe epilepsy surgery. Arch Neurol. 1993. 50:65–69.18. Garcia PA, Laxer KD, Barbaro NM, Dillon WP. Prognostic value of qualitative magnetic resonance imaging of hippocampal abnormalities in patients undergoing temporal lobectomy for medically refractory seizures. Epilepsia. 1994. 35:520–524.19. Bronen RA, Cheung G, Charles JT, et al. Imaging findings in hippocampal sclerosis: correlation with pathology. AJNR. 1991. 12:933–940.20. Nayel MH, Awad IA, Luders H. Extent of mesiobasal resection determines outcome after temporal lobectomy for intractable complex partial seizures. Neurosurgery. 1991. 29:55–61.21. Lencz T, McCarthy G, Bronen RA, et al. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging in temporal lobe epilepsy: relationship to neuropathology and neuropsychological function. Ann Neurol. 1992. 31:629–637.22. Kuzniecky R, de la Sayette V, Ethier R, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in temporal lobe epilepsy: pathologic correlations. Ann Neurol. 1987. 22:341–347.23. Van Paesschen W, Revesz T, Duncan JS, et al. Quantitative neuropathology and quantitative MRI of hippocampal sclerosis. Epilepsia. 1994. 35:S8. 19.24. Jack CR Jr, Rydberg CH, Krecke KN, et al. Mesial temporal sclerosis: diagnosis with fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery versus spin-echo MR imaging. Radiology. 1996. 199:367–373.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Significance and Limitation of MR Volumetry: Comparison between Normal Adults and the Patients with Epilepsy and Hippocampal Sclerosis
- Increased Corpora Amylacea in the Intractable Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: Case Report
- Clinical Usefulness of T2 Relaxometry in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
- Hippocampal Atrophy Pattern and Hippocampal Volume in Mesial Temporal Sclerosis: Correlation with Risk Factors and Surgical Outcome
- Usefulness of Single Voxel Pro ton MR Spectroscopy in the Evaluation of Hippocampal Sclerosis