Korean J Radiol.
2001 Dec;2(4):197-203. 10.3348/kjr.2001.2.4.197.
The Use of Contrast-Enhanced Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Differentiation of Retinal Detachment from Vitreous Membrane
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Busan Paik Hospital College of Medicine, Inje University. hancholi@chollian.net
- KMID: 754088
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2001.2.4.197
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
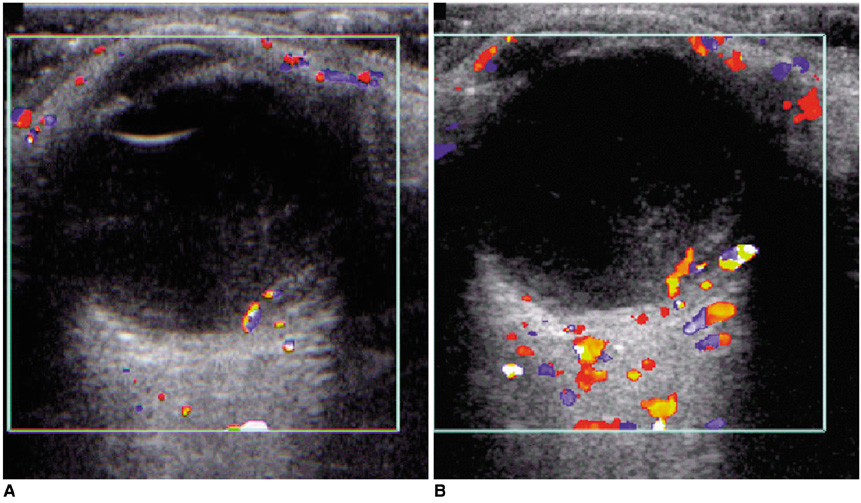
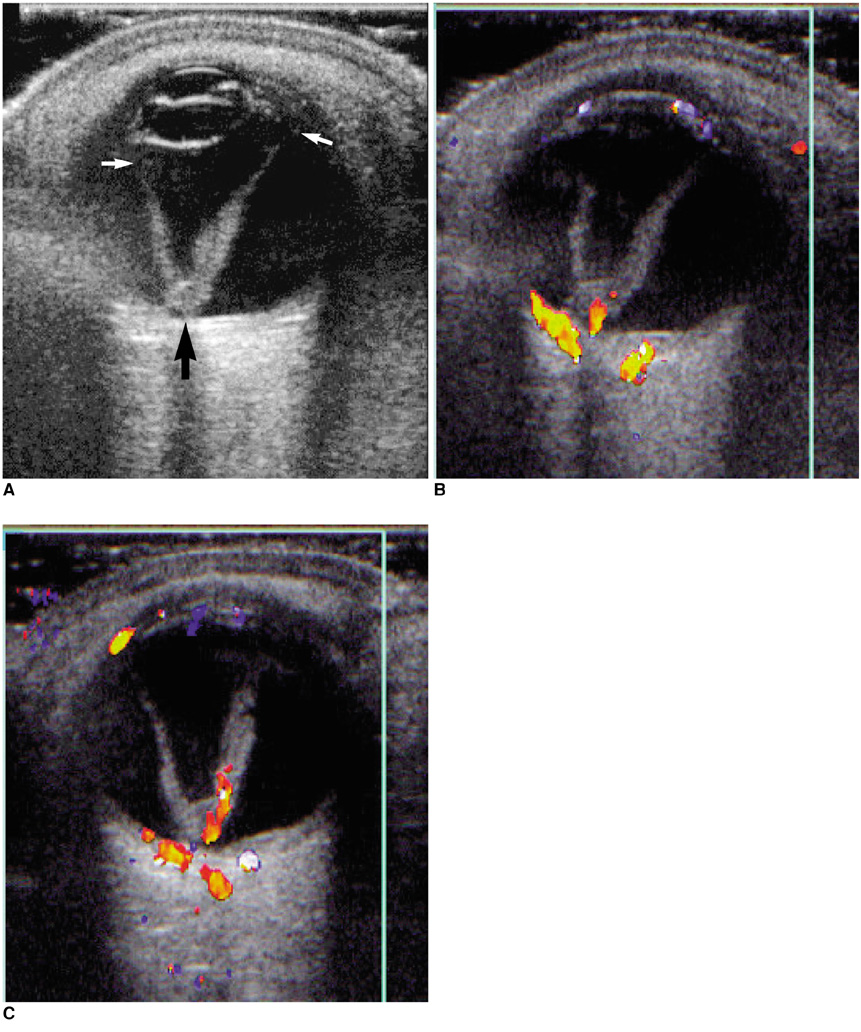
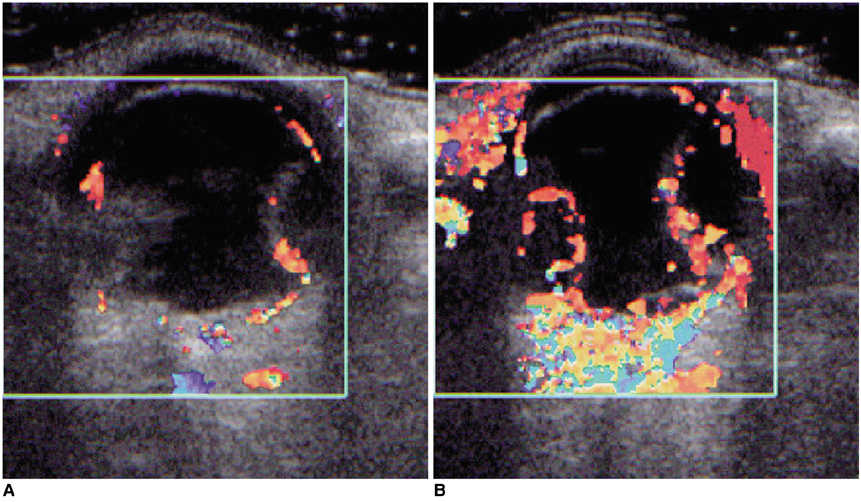
To compare the clinical utility of contrast-enhanced color Doppler US in the differentiation of retinal detachment (RD) from vitreous membrane (VM) with that of various conventional US modalities, and to analyze the enhancement patterns in cases showing an enhancement effect. MATERIALS AND METHODS: In 32 eyes examined over a recent two-year period, RD (n=14) and VM (n=18) were confirmed by surgery (n=28) or clinical follow-up (n=4). In all cases, gray-scale, color Doppler, and power Doppler US were performed prior to contrast injection, and after the intravenous injection of Levovist (Schering, Berlin) by hand for 30 seconds at a dose of 2.5 g and a concentration of 300 mg/mL via an antecubital vein, contrast-enhanced color Doppler US was performed. At Doppler US, the diagnostic criterion for RD and VM was whether or not color signals were visualized in membranous structures. RESULTS: Diagnostic accuracy was 78% at gray-scale US, 81% at color Doppler US, 59% at power Doppler US, and 97% at contrast-enhanced color Doppler US. The sensitivity of color Doppler US to color signals in RD increased from 57% to 93% after contrast enhancement. The enhancement patterns observed were signal accentuation (n=3), signal extension (n=2), signal addition (n=3), and new signal visualization (n=5). CONCLUSION: Contrast-enhanced color Doppler US was the most accurate US modality for differentiating RD from VM, showing a significantly increased signal detection rate in RD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Aged
Comparative Study
*Contrast Media/administration & dosage
Diagnosis, Differential
Female
Human
Image Enhancement
Male
Middle Age
Polysaccharides/administration & dosage/*diagnostic use
Retinal Detachment/*ultrasonography
Sensitivity and Specificity
Ultrasonography, Doppler, Color/*methods
Vitreous Detachment/*ultrasonography
Figure
Reference
-
1. Belden CJ, Abbitt PL, Beadles KA. Color Doppler US of the orbit. RadioGraphics. 1995. 15:589–608.2. Coleman DJ, Jack RL. B-scan ultrasonography in diagnosis and management of retinal detachments. Arch Ophthalmol. 1973. 90:29–34.3. Wong AD, Cooperberg PL, Ross WH, Araki DN. Differentiation of detached retina and vitreous membrane with color flow Doppler. Radiology. 1991. 178:429–431.4. Kerman BM, Coleman DJ. B-scan ultrasonography of retinal detachments. Ann Ophthalmol. 1978. 10:903–911.5. Lieb WE. Color Doppler imaging of the eye and orbit. Radiol Clin North Am. 1998. 36:1059–1071.6. Rubin JM, Bude RO, Carson PL, Bree RL, Adler RS. Power Doppler US: A potentially useful alternative to mean frequency-based color Doppler US. Radiology. 1994. 190:853–856.7. Giovagnorio F, Quaranta L. Power Doppler sonography enhances visualization of orbital vessels. J Ultrasound Med. 1995. 14:837–842.8. Wermke W, Gaβmann B. Tumour diagnostics of the liver with echo enhancers - colour atlas. 1998. Berlin: Springer-Verlag;15.9. Melany ML, Grant EG. Clinical experience with sonographic contrast agents. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 1997. 18:3–12.10. Lemke AJ, Hosten N, Richter M, et al. Contrast-enhanced color Doppler sonography of uveal melanomas. J Clin Ultrasound. 2001. 29:205–211.11. Wells RG, Miro P, Brummond R. Color-flow Doppler sonography of persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous. J Ultrasound Med. 1991. 10:405–407.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Differentiations of Retinal Detachment and Vitreous Membrane Using Color Doppler Imaging
- Differentiation of Retinal Detachment and Vitreous Membrane Formation using Color&Power Doppler Ultrasonography
- Electron Microscopic Features of Epiretinal Membrane in Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment
- The Electron Microscopic Feature of Idiopathic and Complicated Epiretinal Membrane
- A Developmental Mechanism of Spontaneous Reattachment in Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment