Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2025 May;29(2):199-204. 10.14701/ahbps.24-186.
Post-cholecystectomy total bile duct strictures: Cases for magnetic compression anastomosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Minimal Access Surgical Unit, Dr. Luís Razetti University Hospital, Barcelona, Venezuela
- 2University of Oriente, Barcelona, Venezuela
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2568269
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.24-186
Abstract
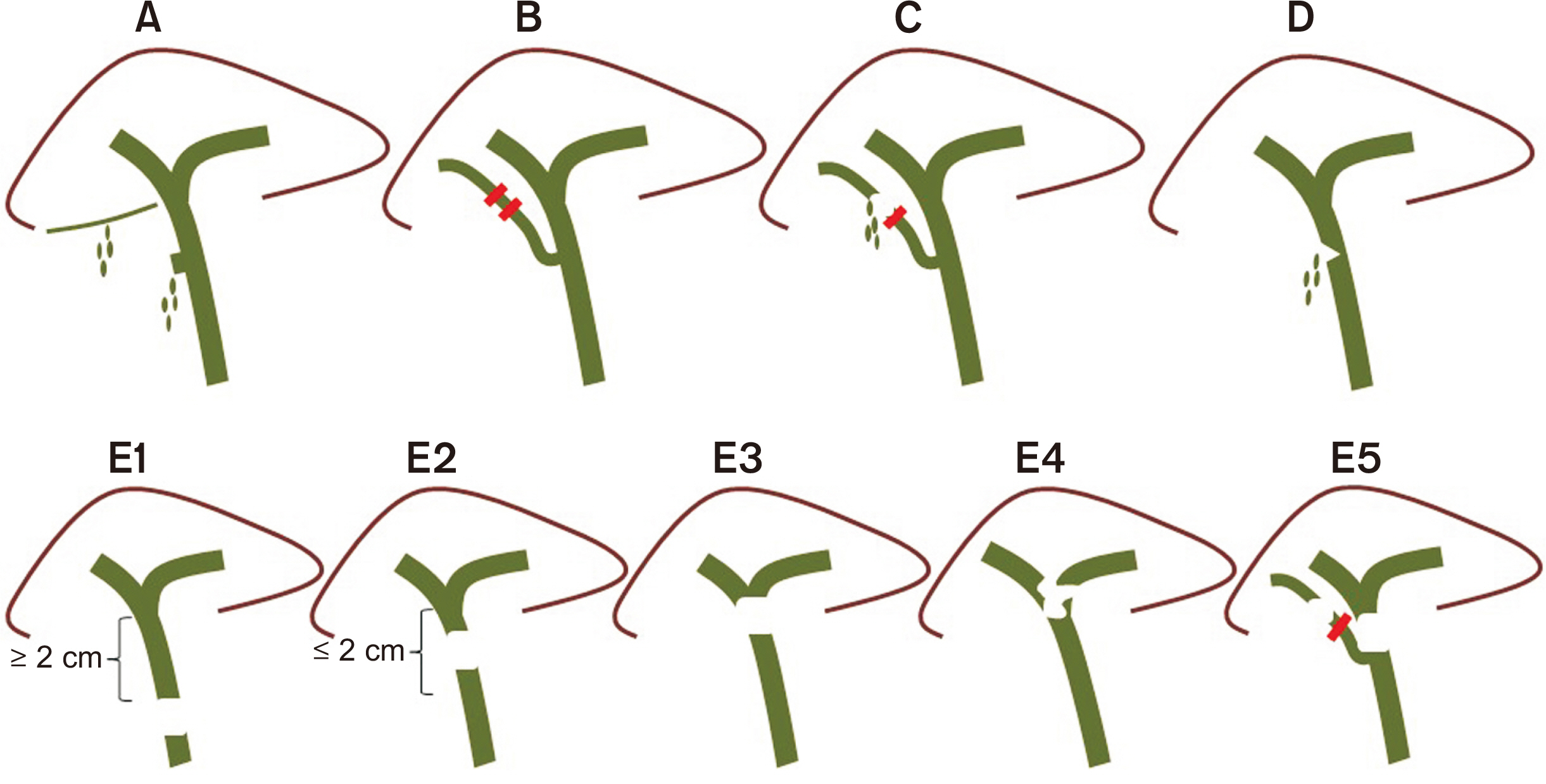
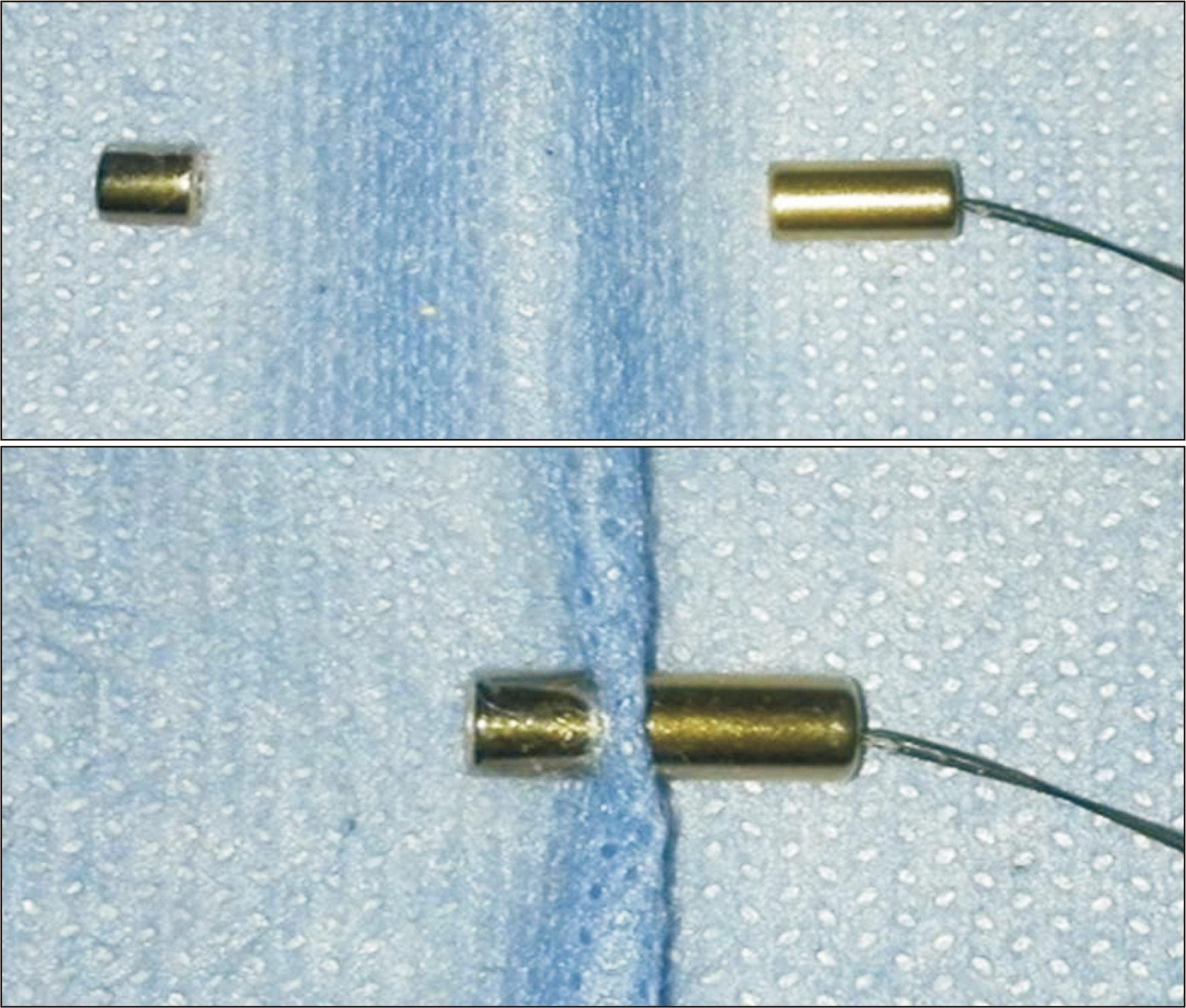
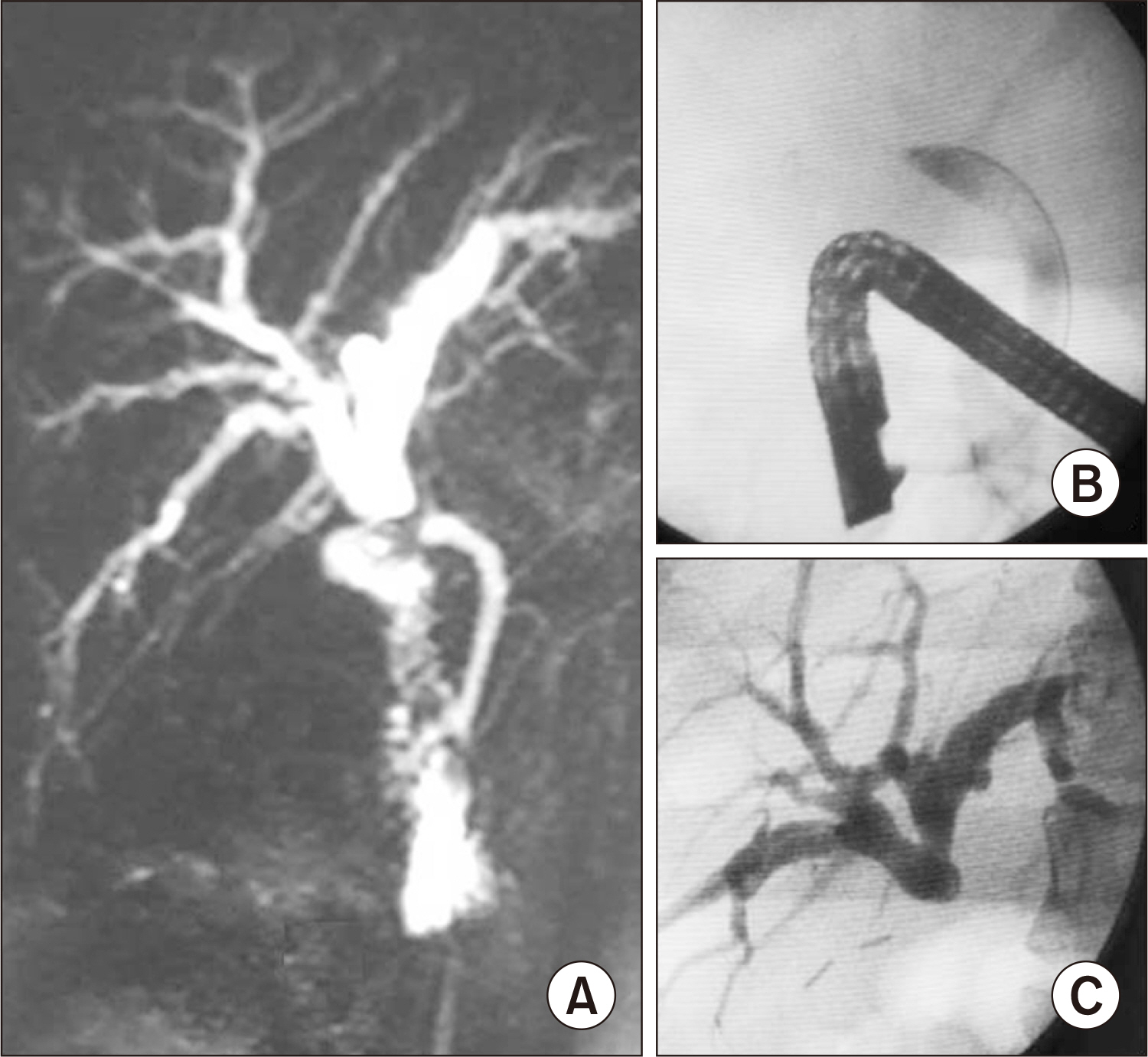
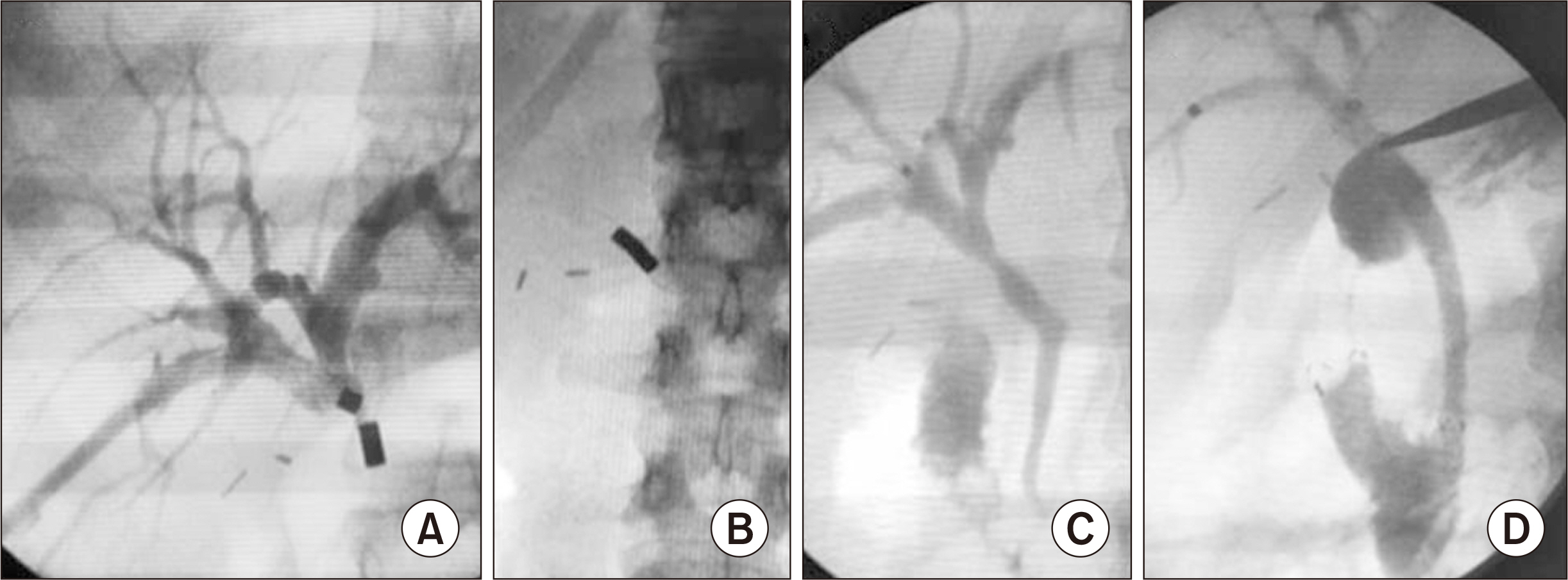
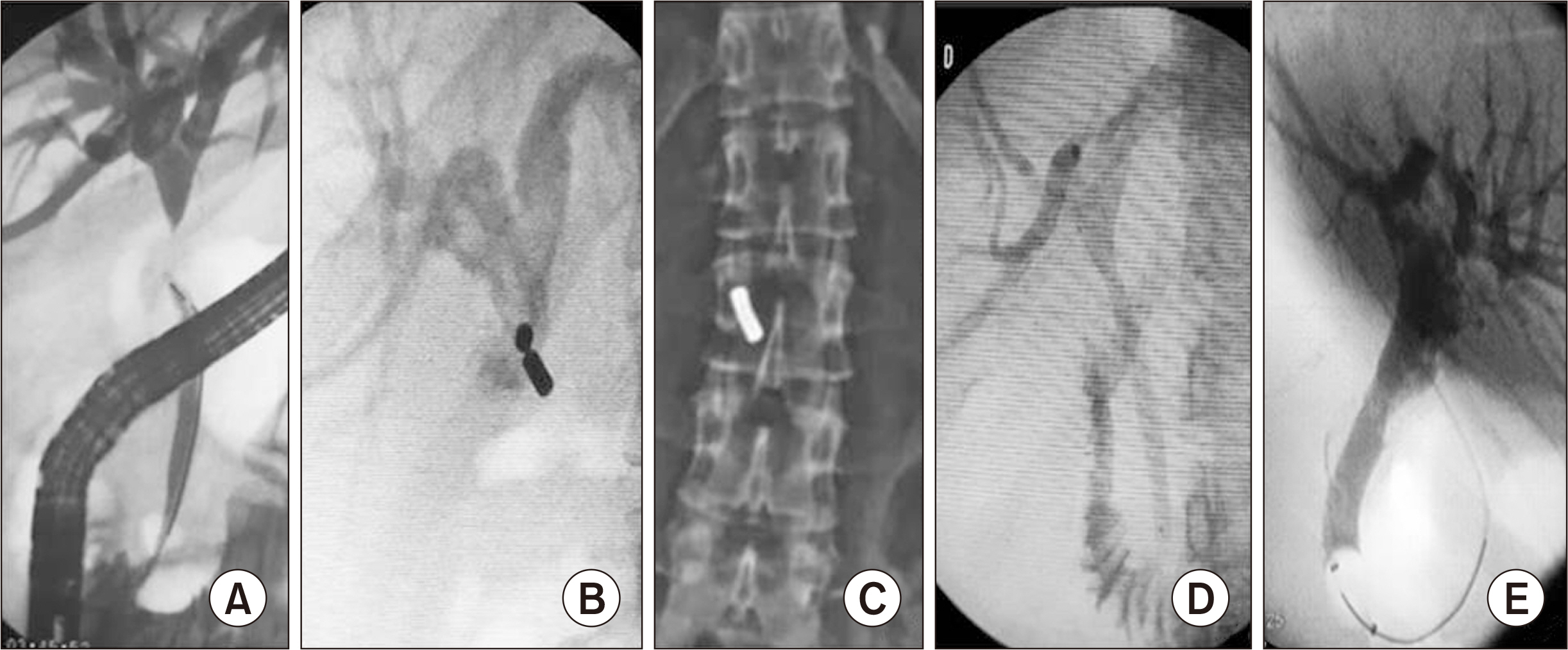
- Bile duct injuries are a serious issue, and their surgical treatment carries the risk of morbidity and mortality. In selected cases, non-surgical treatments are possible, even for total strictures. We outline the technique and results of using magnetic compression anastomosis (MCA) to treat post-cholecystectomy bile duct stricture (PCBDS), in two female patients. Initially, a bilio-cutaneous tract was established via external biliary drainage, followed by the positioning of both endoscopic and percutaneous biliary magnets. After their approximation and subsequent removal, a fully covered self-expandable metal stent (FCSEMS) was deployed across the stricture. The magnet coupling was successfully achieved within the first two weeks of placement. The FCSEMS was maintained for durations of 12 and 16 months. Follow-up durations were 28 and 15 months post-FCSEMS removal. Both patients remain asymptomatic, with normal laboratory and imaging studies, and no adverse events were reported. MCA proves to be a safe and effective method for treating selected cases of total PCBDS. However, further studies and long-term follow-up are required to fully assess the efficacy of this technique.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Schreuder AM, Busch OR, Besselink MG, Ignatavicius P, Gulbinas A, Barauskas G, et al. 2020; Long-term impact of iatrogenic bile duct injury. Dig Surg. 37:10–21. DOI: 10.1159/000496432. PMID: 30654363. PMCID: PMC7026941.
Article2. Strasberg SM, Hertl M, Soper NJ. 1995; An analysis of the problem of biliary injury during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. J Am Coll Surg. 180:101–125.3. Bismuth H, Majno PE. 2001; Biliary strictures: classification based on the principles of surgical treatment. World J Surg. 25:1241–1244. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-001-0102-8. PMID: 11596882.
Article4. Cho JY, Baron TH, Carr-Locke DL, Chapman WC, Costamagna G, de Santibanes E, et al. 2018; Proposed standards for reporting outcomes of treating biliary injuries. HPB (Oxford). 20:370–378. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2017.10.012. PMID: 29397335.
Article5. Jang SI, Cho JH, Lee DK. 2020; Magnetic compression anastomosis for the treatment of post-transplant biliary stricture. Clin Endosc. 53:266–275. DOI: 10.5946/ce.2020.095. PMID: 32506893. PMCID: PMC7280848.
Article6. Li Y, Sun H, Yan X, Wang S, Dong D, Liu X, et al. 2020; Magnetic compression anastomosis for the treatment of benign biliary strictures: a clinical study from China. Surg Endosc. 34:2541–2550. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-019-07063-8. PMID: 31399950.
Article7. Jang SI, Choi J, Lee DK. 2015; Magnetic compression anastomosis for treatment of benign biliary stricture. Dig Endosc. 27:239–249. DOI: 10.1111/den.12319. PMID: 24905938.
Article8. Way LW, Stewart L, Gantert W, Liu K, Lee CM, Whang K, et al. 2003; Causes and prevention of laparoscopic bile duct injuries: analysis of 252 cases from a human factors and cognitive psychology perspective. Ann Surg. 237:460–469. DOI: 10.1097/01.SLA.0000060680.92690.E9. PMID: 12677139. PMCID: PMC1514483.9. Costamagna G, Pandolfi M, Mutignani M, Spada C, Perri V. 2001; Long-term results of endoscopic management of postoperative bile duct strictures with increasing numbers of stents. Gastrointest Endosc. 54:162–168. DOI: 10.1067/mge.2001.116876. PMID: 11474384.
Article10. Dumonceau JM, Tringali A, Papanikolaou IS, Blero D, Mangiavillano B, Schmidt A, et al. 2018; Endoscopic biliary stenting: indications, choice of stents, and results: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline - Updated October 2017. Endoscopy. 50:910–930. DOI: 10.1055/a-0659-9864. PMID: 30086596.
Article11. Yamanouchi E, Kumano R, Kobayashi K, Hattori T, Matsumoto J, Oonishi T, et al. 2002; [Treatment for bowel or biliary obstruction by magnetic compression anastomosis development of Yamanouchi's method and its clinical evaluation]. J Nippon Med Sch. 69:471–475. Japanese. DOI: 10.1272/jnms.69.471. PMID: 12382010.
Article12. Kaidar-Person O, Rosenthal RJ, Wexner SD, Szomstein S, Person B. 2008; Compression anastomosis: history and clinical considerations. Am J Surg. 195:818–826. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.10.006. PMID: 18367149.
Article13. Itoi T, Yamanouchi E, Ikeuchi N, Kasuya K, Iwamoto H, Tsuchida A. 2010; Magnetic compression duct-to-duct anastomosis for biliary obstruction in a patient with living donor liver transplantation. Gut Liver. 4 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S96–S98. DOI: 10.5009/gnl.2010.4.S1.S96. PMID: 21103303. PMCID: PMC2989546.
Article14. Jang SI, Kim JH, Won JY, Lee KH, Kim HW, You JW, et al. 2011; Magnetic compression anastomosis is useful in biliary anastomotic strictures after living donor liver transplantation. Gastrointest Endosc. 74:1040–1048. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.06.026. PMID: 21855872.
Article15. Jang SI, Rhee K, Kim H, Kim YH, Yun J, Lee KH, et al. 2014; Recanalization of refractory benign biliary stricture using magnetic compression anastomosis. Endoscopy. 46:70–74. DOI: 10.1055/s-0033-1358907. PMID: 24254385.
Article16. Jang SI, Do MY, Lee SY, Cho JH, Joo SM, Lee KH, et al. 2024; Magnetic compression anastomosis for the treatment of complete biliary obstruction after cholecystectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 100:1053–1060.e1054. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2024.05.009. PMID: 38762041.
Article17. Do MY, Jang SI, Cho JH, Joo SM, Lee DK. 2022; Magnetic compression anastomosis for treatment of biliary stricture after cholecystectomy. VideoGIE. 7:253–255. DOI: 10.1016/j.vgie.2022.03.005. PMID: 35815159. PMCID: PMC9264143.
Article18. Ödemiş B, Başpınar B, Tola M, Torun S. 2022; Magnetic compression anastomosis is a good treatment option for patients with completely obstructed benign biliary strictures: a case series study. Dig Dis Sci. 67:4906–4918. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-022-07381-3. PMID: 35050430.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Magnetic Compression Anastomosis for the Treatment of Post-Transplant Biliary Stricture
- Foreign bodies in common bile duct in post cholecystectomy status— case series of 8 cases—A single center experience in western India
- Bile Duct Injury during Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
- Magnetic Compression Anastomosis for Treatment of Right Intrahepatic Bile Duct Injury After Cholecystectomy
- Recent classifications of the common bile duct injury