J Pathol Transl Med.
2025 Jan;59(1):68-83. 10.4132/jptm.2024.11.27.
PLUNC downregulates the expression of PD-L1 by inhibiting the interaction of DDX17/β-catenin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, The Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Reproductive and Genetic Hospital of CITIC-Xiangya, Changsha, China
- 3Department of Blood Transfusion, Children's Hospital Affiliated to Zhengzhou University, Henan Children's Hospital, Zhengzhou Children's Hospital, Zhengzhou, China
- 4The First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yatsen University, Guangzhou, China
- 5Department of Medical Laboratory Science , Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Changsha, China
- 6Hunan Key Laboratory of Nonresolving Inflammation and Cancer, Disease Genome Research Center, The Third Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China
- 7NHC Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis, Hunan Cancer Hospital and the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Changsha, China
- 8The Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Cancer Invasion of the Chinese Ministry of Education, Cancer Research Institute and School of Basic Medicine Sciences, Central South University, Changsha, China
- 9Department of Pathology, Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China
- KMID: 2563886
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2024.11.27
Abstract
- Background
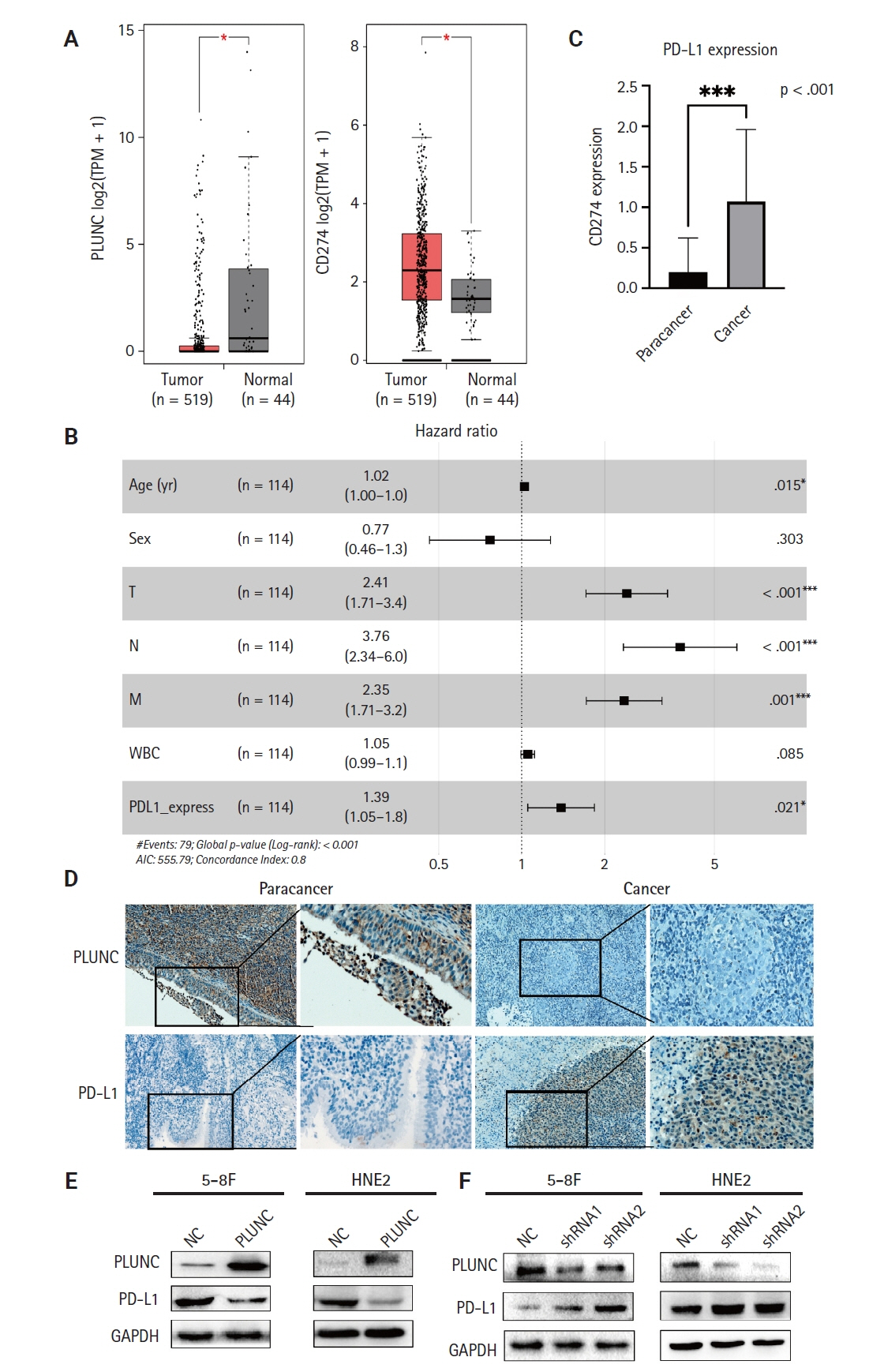
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is characterized by high programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression and abundant infiltration of non-malignant lymphocytes, which renders patients potentially suitable candidates for immune checkpoint blockade therapies. Palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone (PLUNC) inhibit the growth of NPC cells and enhance cellular apoptosis and differentiation. Currently, the relationship between PLUNC (as a tumor-suppressor) and PD-L1 in NPC is unclear.
Methods
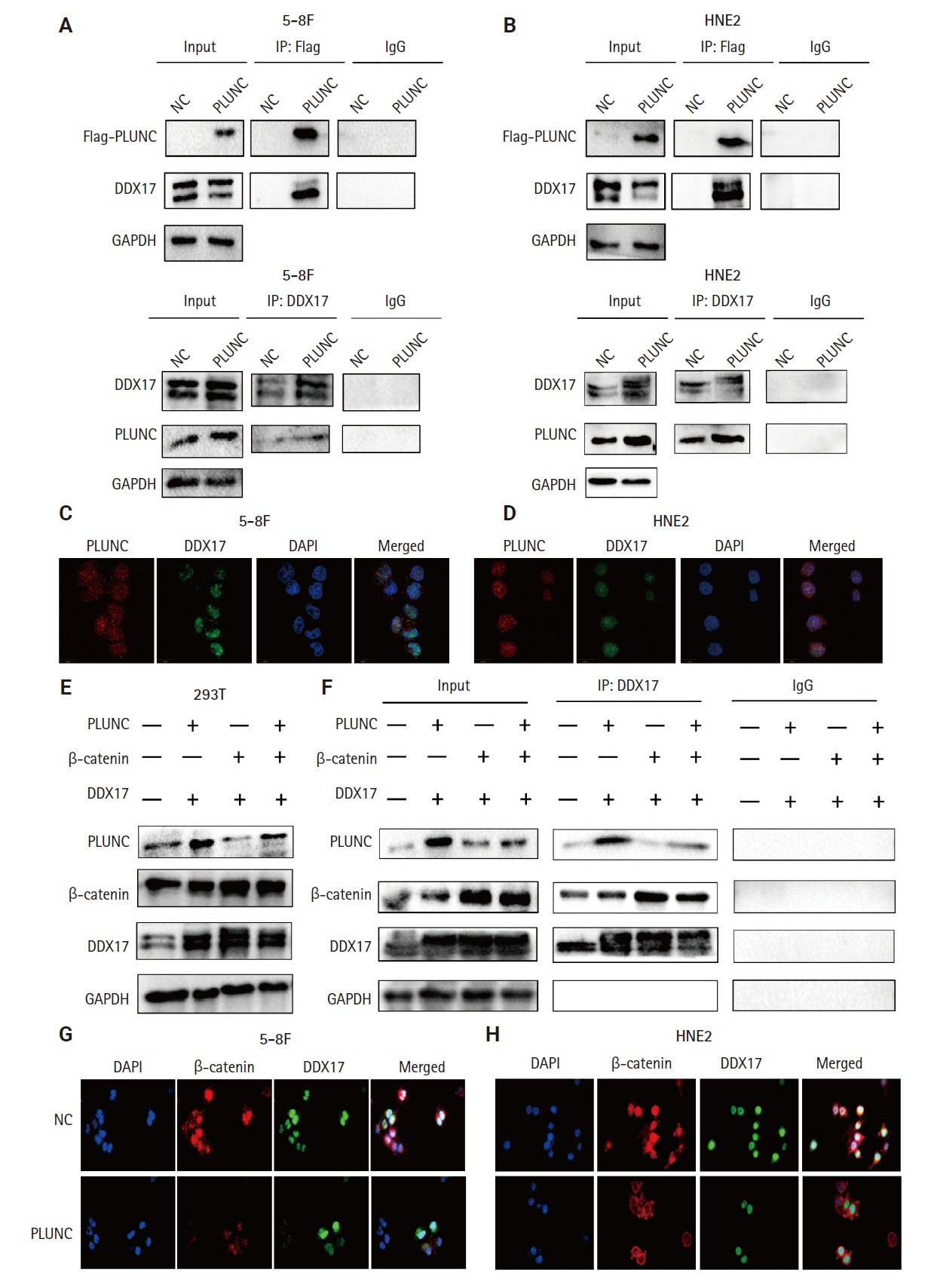
We collected clinical samples of NPC to verify the relationship between PLUNC and PD-L1. PLUNC plasmid was transfected into NPC cells, and the variation of PD-L1 was verified by western blot and immunofluorescence. In NPC cells, we verified the relationship of PD-L1, activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3), and β-catenin by western blot and immunofluorescence. Later, we further verified that PLUNC regulates PD-L1 through β-catenin. Finally, the effect of PLUNC on β-catenin was verified by co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP).
Results
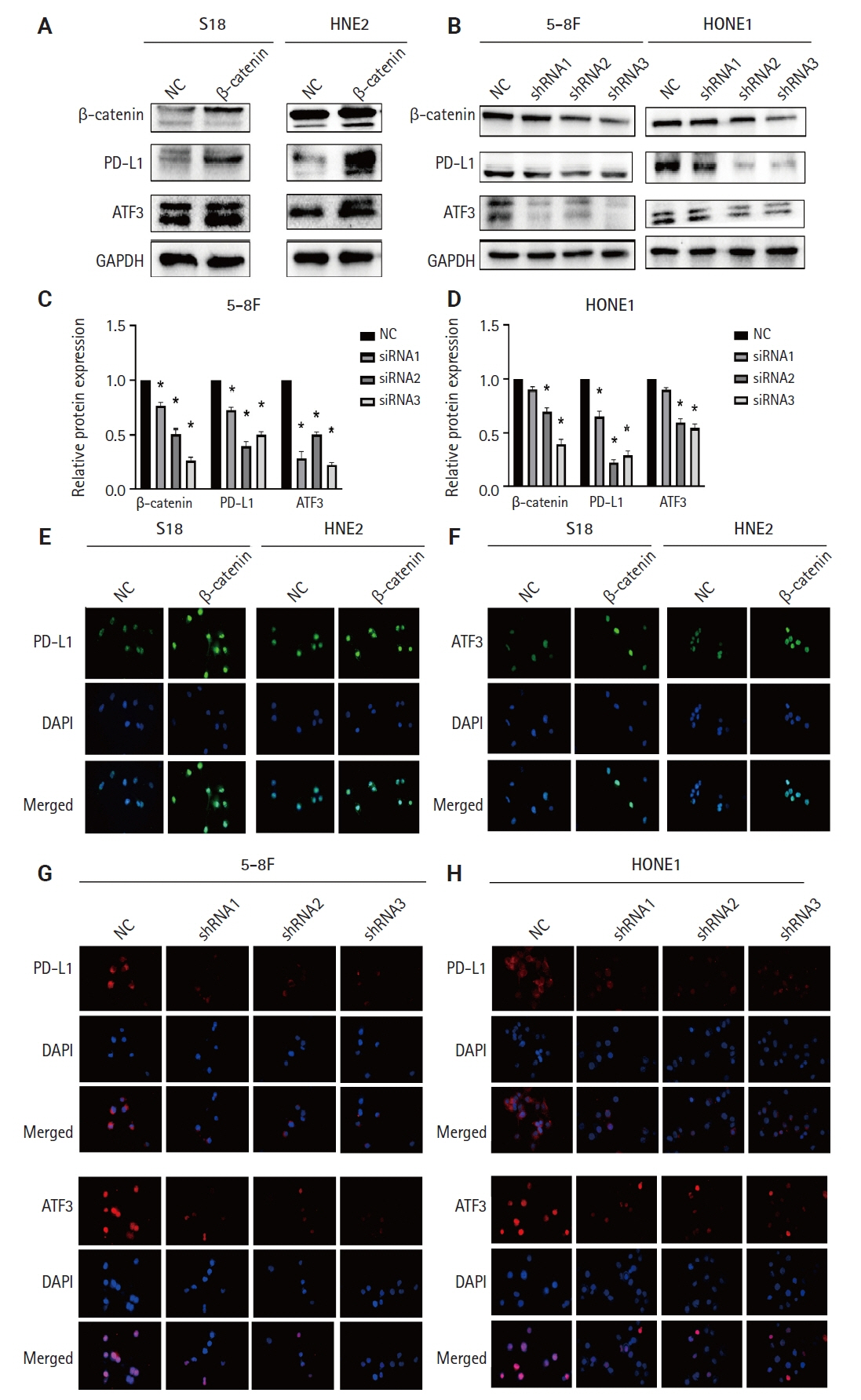
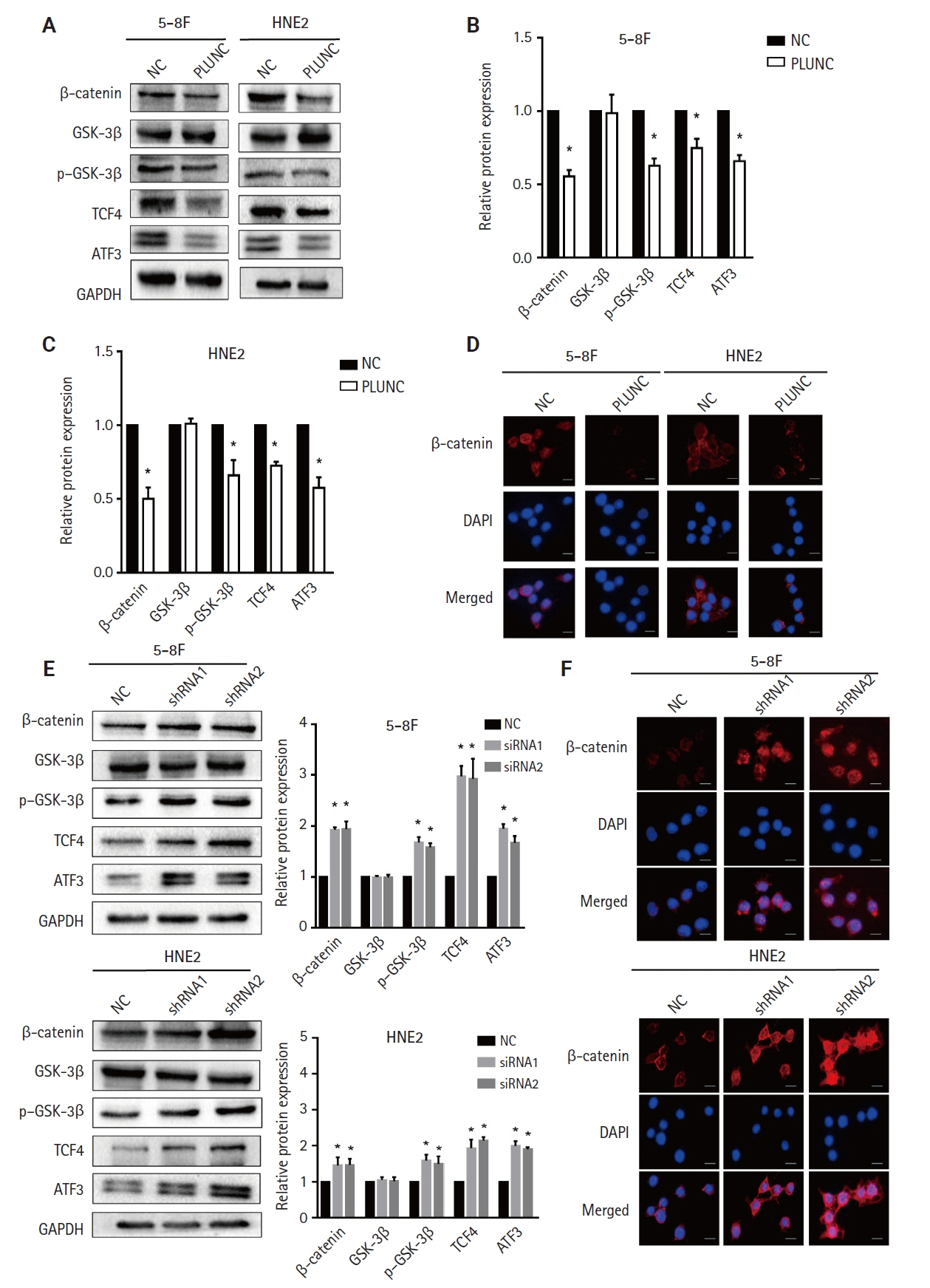
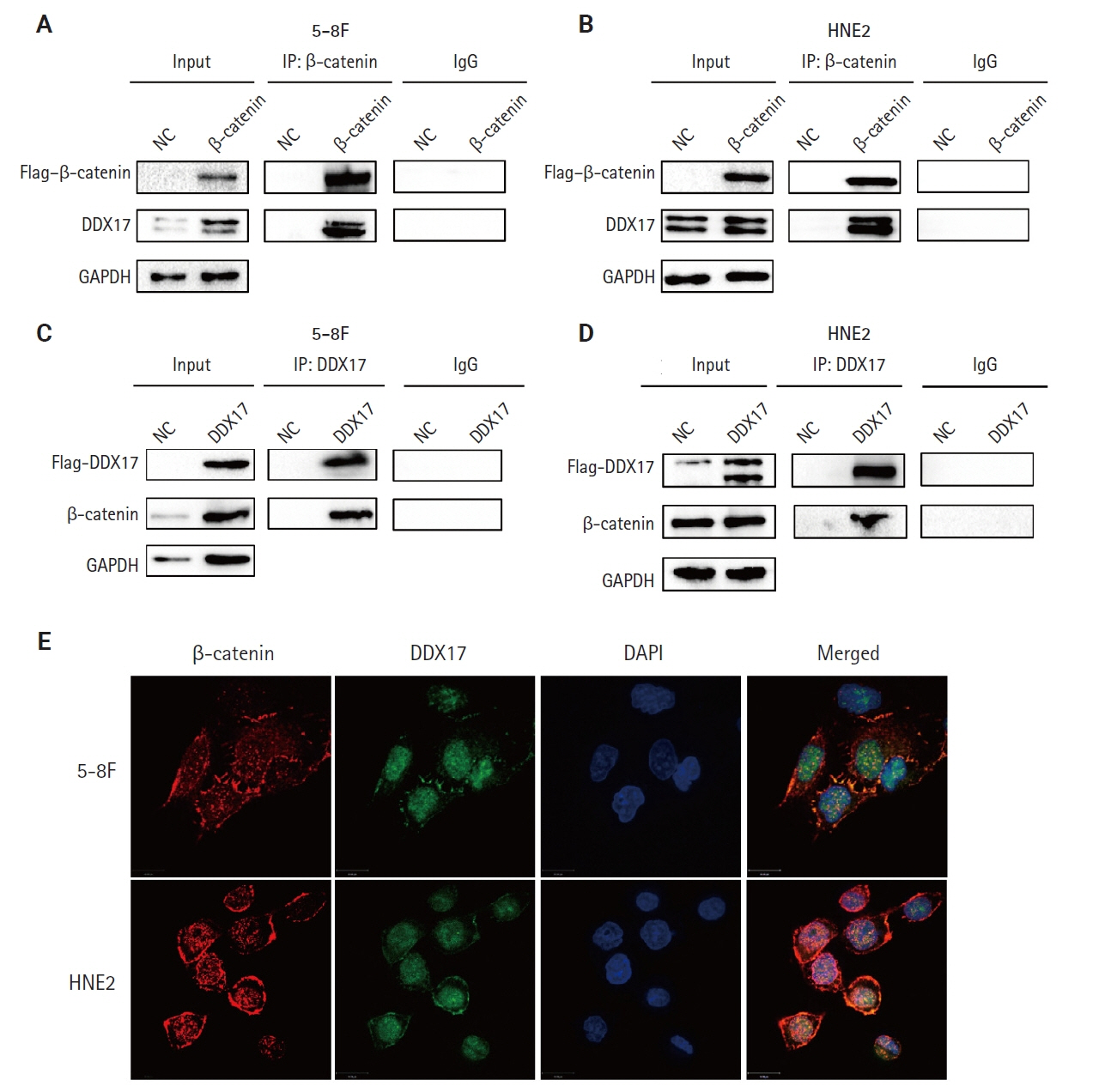
We found that PLUNC expression was lower in NPC tissues than in paracancer tissues. PD-L1 expression was opposite to that of PLUNC. Western blot and immunofluorescence showed that β-catenin could upregulate ATF3 and PD-L1, while PLUNC could downregulate ATF3/PD-L1 by inhibiting the expression of β-catenin. PLUNC inhibits the entry of β-catenin into the nucleus. Co-IP experiments demonstrated that PLUNC inhibited the interaction of DEAD-box helicase 17 (DDX17) and β-catenin.
Conclusions
PLUNC downregulates the expression of PD-L1 by inhibiting the interaction of DDX17/β-catenin in NPC.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021; 71:209–49. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. PMID: 33538338.2. Tang LQ, Li CF, Li J, et al. Establishment and validation of prognostic nomograms for endemic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016; 108:djv291. DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djv291. PMID: 26467665.3. Xu JY, Wei XL, Wang YQ, Wang FH. Current status and advances of immunotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2022; 14:17588359221096214. DOI: 10.1177/17588359221096214. PMID: 35547095.4. Chen YP, Chan AT, Le QT, Blanchard P, Sun Y, Ma J. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 2019; 394:64–80. DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(19)30956-0. PMID: 31178151.5. Adkins DR, Haddad RI. Clinical trial data of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy for recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: a review. Cancer Treat Rev. 2022; 109:102428. DOI: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2022.102428. PMID: 35753157.6. Bingle CD, Craven CJ. PLUNC: a novel family of candidate host defence proteins expressed in the upper airways and nasopharynx. Hum Mol Genet. 2002; 11:937–43. DOI: 10.1093/hmg/11.8.937. PMID: 11971875.7. Geetha C, Venkatesh SG, Bingle L, Bingle CD, Gorr SU. Design and validation of anti-inflammatory peptides from human parotid secretory protein. J Dent Res. 2005; 84:149–53. DOI: 10.1177/154405910508400208. PMID: 15668332.8. Bartlett JA, Gakhar L, Penterman J, et al. PLUNC: a multifunctional surfactant of the airways. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011; 39:1012–6. DOI: 10.1042/bst0391012. PMID: 21787339.9. Ben-Meir E, Perrem L, Shaw M, Ratjen F, Grasemann H. SPLUNC1 as a biomarker of pulmonary exacerbations in children with cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros. 2024; 23:288–92. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcf.2024.02.009. PMID: 38413298.10. Liu H, Zhang X, Wu J, French SW, He Z. New insights on the palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone (PLUNC) proteins: based on molecular and functional analysis of its homolog of YH1/SPLUNC1. Exp Mol Pathol. 2016; 100:363–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2015.12.002. PMID: 26654795.11. Tsou YA, Peng MT, Wu YF, et al. Decreased PLUNC expression in nasal polyps is associated with multibacterial colonization in chronic rhinosinusitis patients. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014; 271:299–304. DOI: 10.1007/s00405-013-2535-8. PMID: 23644997.12. Khanal S, Webster M, Niu N, et al. SPLUNC1: a novel marker of cystic fibrosis exacerbations. Eur Respir J. 2021; 58:2000507. DOI: 10.1183/13993003.00507-2020. PMID: 33958427.13. Osada M, Aishima S, Hirahashi M, et al. Combination of hepatocellular markers is useful for prognostication in gastric hepatoid adenocarcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2014; 45:1243–50. DOI: 10.1016/j.humpath.2014.02.003. PMID: 24767858.14. Zhang W, Zeng Z, Wei F, et al. SPLUNC1 is associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma prognosis and plays an important role in all-trans-retinoic acid-induced growth inhibition and differentiation in nasopharyngeal cancer cells. FEBS J. 2014; 281:4815–29. DOI: 10.1111/febs.13020. PMID: 25161098.15. Ou C, Sun Z, Zhang H, et al. SPLUNC1 reduces the inflammatory response of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells infected with the EB virus by inhibiting the TLR9/NF-kappaB pathway. Oncol Rep. 2015; 33:2779–88. DOI: 10.3892/or.2015.3913. PMID: 25891128.16. Liu H, Tang L, Gong S, et al. USP7 inhibits the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma via promoting SPLUNC1-mediated M1 macrophage polarization through TRIM24. Cell Death Dis. 2023; 14:852. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-06368-w. PMID: 38129408.17. Tang L, Peng L, Liu H, et al. SPLUNC1 regulates LPS-induced progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and proliferation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Med Oncol. 2022; 39:214. DOI: 10.1007/s12032-022-01816-7. PMID: 36175598.18. Yu F, Yu C, Li F, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cancers and targeted therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021; 6:307. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-021-00701-5. PMID: 34456337.19. Pang Q, Hu W, Zhang X, Pang M. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway-related proteins (DKK-3, beta-catenin, and c-MYC) are involved in prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2019; 34:436–43. DOI: 10.1089/cbr.2019.2771. PMID: 31025872.20. Hu Z, Meng J, Cai H, et al. KIF3A inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma proliferation, migration and invasion by interacting with beta-catenin to suppress its nuclear accumulation. Am J Cancer Res. 2022; 12:5226–40. DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-1031455/v1. PMID: 36504907.21. Ou X, Zhang Y, Xu Y, et al. PICK1 inhibits the malignancy of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and serves as a novel prognostic marker. Cell Death Dis. 2024; 15:294. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-06687-6. PMID: 38664379.22. Liu N, Yan M, Tao Q, et al. Inhibition of TCA cycle improves the anti-PD-1 immunotherapy efficacy in melanoma cells via ATF3-mediated PD-L1 expression and glycolysis. J Immunother Cancer. 2023; 11:e007146. DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007146. PMID: 37678921.23. Jin PY, Zheng ZH, Lu HJ, et al. Roles of beta-catenin, TCF-4, and survivin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: correlation with clinicopathological features and prognostic significance. Cancer Cell Int. 2019; 19:48. DOI: 10.1186/s12935-019-0764-7. PMID: 30867651.24. Du L, Lee JH, Jiang H, et al. Beta-catenin induces transcriptional expression of PD-L1 to promote glioblastoma immune evasion. J Exp Med. 2020; 217:e20191115. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20191115. PMID: 32860047.25. Xue W, Yang L, Chen C, Ashrafizadeh M, Tian Y, Sun R. Wnt/beta-catenin-driven EMT regulation in human cancers. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024; 81:79. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-023-05099-7. PMID: 38334836.26. Delgado-Bellido D, Zamudio-Martinez E, Fernandez-Cortes M, et al. VE-cadherin modulates beta-catenin/TCF-4 to enhance vasculogenic mimicry. Cell Death Dis. 2023; 14:135. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-05666-7. PMID: 36797281.27. Yang S, Winstone L, Mondal S, Wu Y. Helicases in R-loop formation and resolution. J Biol Chem. 2023; 299:105307. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105307. PMID: 37778731.28. Zhao G, Wang Q, Zhang Y, et al. DDX17 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis through the miR-149-3p/CYBRD1 pathway in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2023; 14:1. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-05508-y. PMID: 36593242.29. Wang J, Ge J, Wang Y, et al. EBV miRNAs BART11 and BART17-3p promote immune escape through the enhancer-mediated transcription of PD-L1. Nat Commun. 2022; 13:866. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28479-2. PMID: 35165282.30. Ge J, Wang J, Xiong F, et al. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded circular RNA CircBART2.2 promotes immune escape of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating PD-L1. Cancer Res. 2021; 81:5074–88. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-20-4321. PMID: 34321242.31. Kase K, Kondo S, Wakisaka N, et al. Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 induces soluble PD-L1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Microorganisms. 2021; 9:603. DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9030603. PMID: 33804064.32. Wang FH, Wei XL, Feng J, et al. Efficacy, safety, and correlative biomarkers of toripalimab in previously treated recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a phase II clinical trial (POLARIS-02). J Clin Oncol. 2021; 39:704–12. DOI: 10.1200/jco.20.02712. PMID: 33492986.33. Mai HQ, Chen QY, Chen D, et al. Toripalimab or placebo plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a multicenter randomized phase 3 trial. Nat Med. 2021; 27:1536–43. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-021-01444-0. PMID: 34341578.34. Weston WM, LeClair EE, Trzyna W, et al. Differential display identification of plunc, a novel gene expressed in embryonic palate, nasal epithelium, and adult lung. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:13698–703. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.274.19.13698. PMID: 10224143.35. Vitorino R, Lobo MJ, Ferrer-Correira AJ, et al. Identification of human whole saliva protein components using proteomics. Proteomics. 2004; 4:1109–15. DOI: 10.1002/pmic.200300638. PMID: 15048992.36. Ghafouri B, Kihlstrom E, Stahlbom B, Tagesson C, Lindahl M. PLUNC (palate, lung and nasal epithelial clone) proteins in human nasal lavage fluid. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003; 31:810–4. DOI: 10.1042/bst0310810. PMID: 12887311.37. Di YP, Harper R, Zhao Y, Pahlavan N, Finkbeiner W, Wu R. Molecular cloning and characterization of spurt, a human novel gene that is retinoic acid-inducible and encodes a secretory protein specific in upper respiratory tracts. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278:1165–73. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.m210523200. PMID: 12409287.38. Campos MA, Abreu AR, Nlend MC, Cobas MA, Conner GE, Whitney PL. Purification and characterization of PLUNC from human tracheobronchial secretions. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2004; 30:184–92. DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2003-0142oc. PMID: 12920053.39. Bartlett JA, Hicks BJ, Schlomann JM, Ramachandran S, Nauseef WM, McCray PB Jr. PLUNC is a secreted product of neutrophil granules. J Leukoc Biol. 2008; 83:1201–6. DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0507302. PMID: 18245229.40. Huang H, Yao Y, Deng X, et al. Immunotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: current status and prospects (review). Int J Oncol. 2023; 63:97. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5545. PMID: 37417358.41. Johnson D, Ma BB. Targeting the PD-1/ PD-L1 interaction in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2021; 113:105127. DOI: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.105127. PMID: 33454551.42. Liu J, Xiao Q, Xiao J, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signalling: function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022; 7:3. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-021-00762-6. PMID: 34980884.43. Wang D, Wu S, He J, et al. FAT4 overexpression promotes antitumor immunity by regulating the beta-catenin/STT3/PD-L1 axis in cervical cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023; 42:222. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-023-02758-2. PMID: 37658376.44. Wang H, Luo K, Zhan Y, Peng S, Fan S, Wang W. Role of beta-catenin in PD-L1 expression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Heliyon. 2023; 9:e18130. DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18130. PMID: 37496925.45. Moy RH, Cole BS, Yasunaga A, et al. Stem-loop recognition by DDX17 facilitates miRNA processing and antiviral defense. Cell. 2014; 158:764–77. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.023. PMID: 25126784.46. Terrone S, Valat J, Fontrodona N, et al. RNA helicase-dependent gene looping impacts messenger RNA processing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022; 50:9226–46. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkac717. PMID: 36039747.47. Suthapot P, Xiao T, Felsenfeld G, Hongeng S, Wongtrakoongate P. The RNA helicases DDX5 and DDX17 facilitate neural differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells NTERA2. Life Sci. 2022; 291:120298. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.120298. PMID: 35007564.48. Zhou HZ, Li F, Cheng ST, et al. DDX17-regulated alternative splicing that produced an oncogenic isoform of PXN-AS1 to promote HCC metastasis. Hepatology. 2022; 75:847–65. DOI: 10.1002/hep.32195. PMID: 34626132.49. Li K, Mo C, Gong D, et al. DDX17 nucleocytoplasmic shuttling promotes acquired gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells via activation of beta-catenin. Cancer Lett. 2017; 400:194–202. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.02.029. PMID: 28259822.50. Germann S, Gratadou L, Zonta E, et al. Dual role of the ddx5/ddx17 RNA helicases in the control of the pro-migratory NFAT5 transcription factor. Oncogene. 2012; 31:4536–49. DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.618. PMID: 22266867.51. Wilson BJ, Bates GJ, Nicol SM, Gregory DJ, Perkins ND, Fuller-Pace FV. The p68 and p72 DEAD box RNA helicases interact with HDAC1 and repress transcription in a promoter-specific manner. BMC Mol Biol. 2004; 5:11. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-5-11. PMID: 15298701.52. Alqahtani H, Gopal K, Gupta N, et al. DDX17 (P72), a Sox2 binding partner, promotes stem-like features conferred by Sox2 in a small cell population in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Cell Signal. 2016; 28:42–50. DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.11.004. PMID: 26569340.53. Shin S, Rossow KL, Grande JP, Janknecht R. Involvement of RNA helicases p68 and p72 in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2007; 67:7572–8. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-06-4652. PMID: 17699760.54. Liu X, Li L, Geng C, et al. DDX17 promotes the growth and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Discov. 2022; 8:425. DOI: 10.1038/s41420-022-01215-x. PMID: 36273228.55. Wortham NC, Ahamed E, Nicol SM, et al. The DEAD-box protein p72 regulates ERalpha-/oestrogen-dependent transcription and cell growth, and is associated with improved survival in ERalpha-positive breast cancer. Oncogene. 2009; 28:4053–64. DOI: 10.1038/onc.2009.261. PMID: 19718048.56. Ku HC, Cheng CF. Master regulator activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) in metabolic homeostasis and cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020; 11:556. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00556. PMID: 32922364.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of E-cadherin and a-catenin in Thyroid Carcinomas
- Immunohistochemical expression of programmed death-ligand 1 and CD8 in glioblastomas
- Immunohistochemical Expression of PD-L1 in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Its Association with Risk of Metastasis
- PD-1: A Negative Regulator of Phagocytosis by Tumour-Associated Macrophages in Colon Cancer
- The Expression of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 on Immune Cells Is Related to a Better Prognosis in Biliary Tract Cancer