Ann Lab Med.
2024 Nov;44(6):586-590. 10.3343/alm.2024.0083.
Limited Contribution of Creatine Kinase-Myocardial Band Alongside High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin in Diagnosing Acute Myocardial Infarction in an Emergency Department
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, International St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, Catholic Kwandong University, Incheon, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 3Research and Development Institute for In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2560807
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2024.0083
Abstract
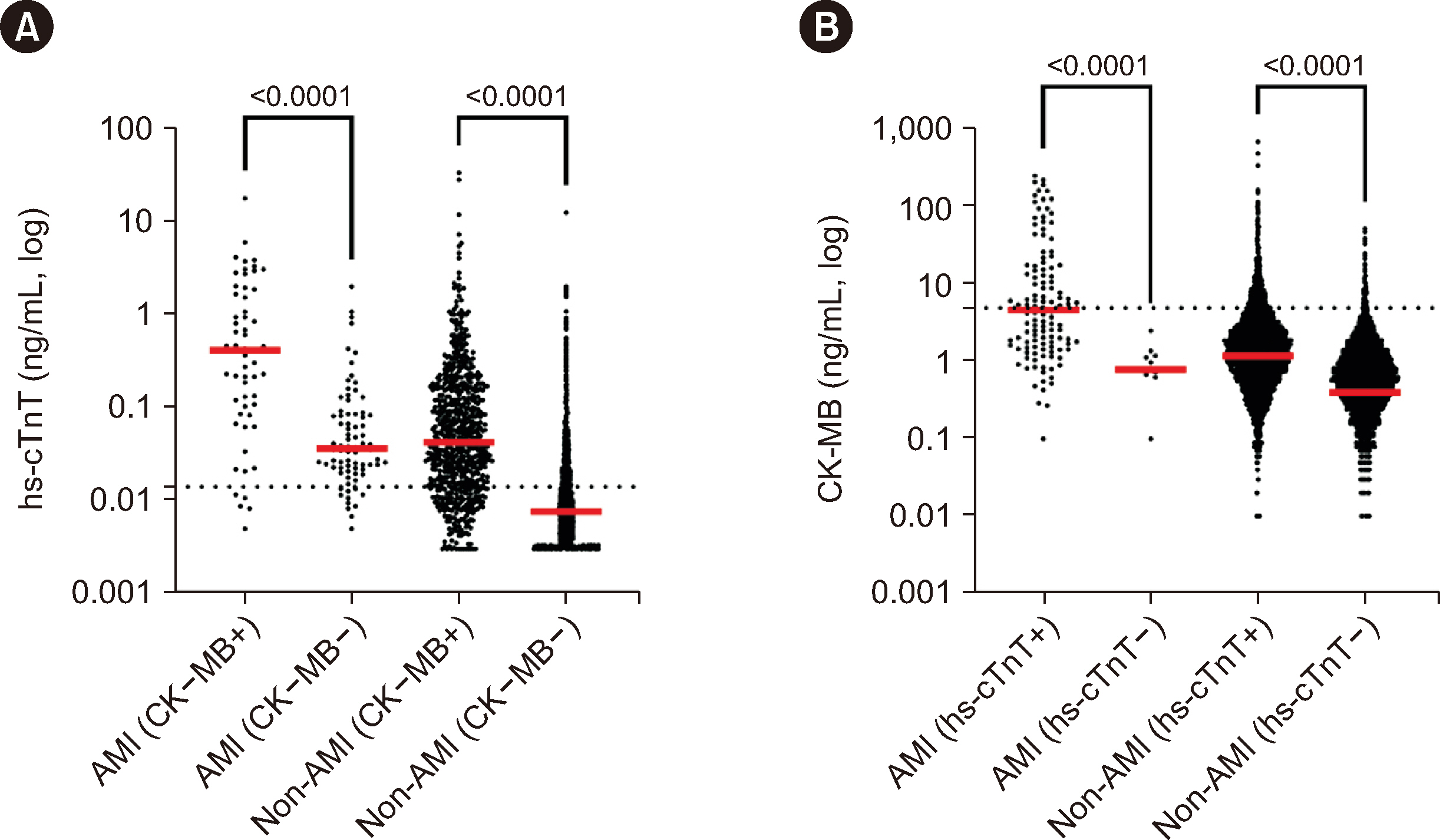
- Cardiac biomarkers, especially high-sensitivity cardiac troponin C or I (hs-cTnC or hs-cTnI, respectively), are vital for diagnosing acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Despite the specificity of hs-cTn as a biomarker, the creatine kinase-myocardial band (CK-MB) is commonly used alongside hs-cTn in emergency departments (EDs). We analyzed 23,771 simultaneous hs-cTn (hs-cTnT or hs-cTnI) and CK-MB requests for 17,185 patients in tertiary hospital ED in 2022. The objective of this study was to assess their practical value in diagnosing AMI in real-world settings. Among all 17,185 patients tested, 98.0% underwent hs-cTnT and CK-MB tests, and substantially fewer underwent hs-cTnI testing. We observed concordance between the initial hs-cTn and CK-MB results in 71.3% of patients. Of 131 AMI cases, 57 were positive for both biomarkers, 63 for hs-cTn only, and none for CK-MB alone. CK-MB positivity was often found in the absence of AMI. Discrepancies between the hscTnT and hs-cTnI results occurred in 30.0% of patients. Indiscriminate CK-MB testing for diagnosing AMI in EDs should be reconsidered. Efficient use of CK-MB is important for reducing costs and ensuring optimal patient care.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Collet JP, Thiele H, Barbato E, Barthelemy O, Bauersachs J, Bhatt DL, et al. 2021; 2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation. Eur Heart J. 42:1289–1367. DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa575. PMID: 32860058.2. Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, Casey DE Jr., Ganiats TG, Holmes DR Jr., et al. 2014; 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 130:2354–94. DOI: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000133. PMID: 25249586.3. Wiens EJ, Arbour J, Thompson K, Seifer CM. 2019; Routine creatine kinase testing does not provide clinical utility in the emergency department for diagnosis of acute coronary syndromes. BMC Emerg Med. 19:37. DOI: 10.1186/s12873-019-0251-4. PMID: 31288735. PMCID: PMC6617848. PMID: d33e1cd3926648a28fb8d8105a57c972.4. Raza S, Amaral AC, Pang J, Moussa F, Shelton D, Notario L, et al. 2020; Reducing redundant creatine kinase testing in cardiac injury. BMJ Open Qual. 9:e001182. DOI: 10.1136/bmjoq-2020-001182. PMID: 33376105. PMCID: PMC7778776. PMID: e5cf905591f746a5ab54c458922971a9.5. Baroni S, Gabrielli M, Ferrigno F, Franceschi F, Urbani A. 2020; Lack of utility of CK-MB in combination with troponin I for the diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome. Intern Emerg Med. 15:1345–6. DOI: 10.1007/s11739-020-02399-9. PMID: 32564290.6. Alvin MD, Jaffe AS, Ziegelstein RC, Trost JC. 2017; Eliminating creatine kinase-myocardial band testing in suspected acute coronary syndrome: A value-based quality improvement. JAMA Intern Med. 177:1508–12. DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.3597. PMID: 28806444.7. Le RD, Kosowsky JM, Landman AB, Bixho I, Melanson SE, Tanasijevic MJ. 2015; Clinical and financial impact of removing creatine kinase-MB from the routine testing menu in the emergency setting. Am J Emerg Med. 33:72–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajem.2014.10.017. PMID: 25455047.8. Giger RD, du Fay de Lavallaz J, Prepoudis A, Stoll T, Lopez-Ayala P, Glarner N, et al. 2020; Rhabdomyolysis: A noncardiac source of increased circulating concentrations of cardiac troponin T? J Am Coll Cardiol. 76:2685–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.08.088. PMID: 33243386.9. Gibbons RJ, Valeti US, Araoz PA, Jaffe AS. 2004; The quantification of infarct size. J Am Coll Cardiol. 44:1533–42. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.06.071. PMID: 15489082.10. Wilson G, Barkley K, Slicker K, Kowal R, Pope B, Michel J. 2017; Overuse of troponin? A comprehensive evaluation of testing in a large hospital system. J Hosp Med. 12:329–31. DOI: 10.12788/jhm.2732. PMID: 28459901.11. Eggers KM, Hammarsten O, Lindahl B. 2023; Differences between high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T and I in stable populations: underlying causes and clinical implications. Clin Chem Lab Med. 61:380–7. DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2022-0778. PMID: 36424851.12. Collinson PO, Saenger AK, Apple FS, IFCC C-CB. 2019; High sensitivity, contemporary and point-of-care cardiac troponin assays: educational aids developed by the IFCC Committee on Clinical Application of Cardiac Bio-Markers. Clin Chem Lab Med. 57:623–32. DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2018-1211. PMID: 30530880.13. Wang GM, Li Y, Wu S, Zheng W, Ma JJ, Xu F, et al. 2022; The combination of creatine kinase-myocardial band isoenzyme and point-of-care cardiac troponin/contemporary cardiac troponin for the early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. World J Emerg Med. 13:163–8. DOI: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2022.033. PMID: 35646222. PMCID: PMC9108910.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Is it Necessary to Study both Creatine Kinase MB and Troponin for an Acute Diagnosis of Myocardial Infarction?
- Diagnostic Efficiency of Lactate Dehydrogenase, Crreatine Kinase and Troponin T in Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Clinical Usefulness of the CK-MB Activity and Cardiac Troponin T as Markers for Detection of Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Performance of Copeptin for Early Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction in an Emergency Department Setting
- Diagnostic Value of Cardiac STATus(TM) for Diagnosing Acute Cardiac Ischemia in Patients with Acute Chest Pain in an Emergency Settings