Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2024;26(2):39-45. 10.14253/acn.24008.
Revisiting PD: Unraveling the brain-first and body-first perspectives
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Nowon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Neurology, Eulji University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
- KMID: 2560430
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.24008
Abstract
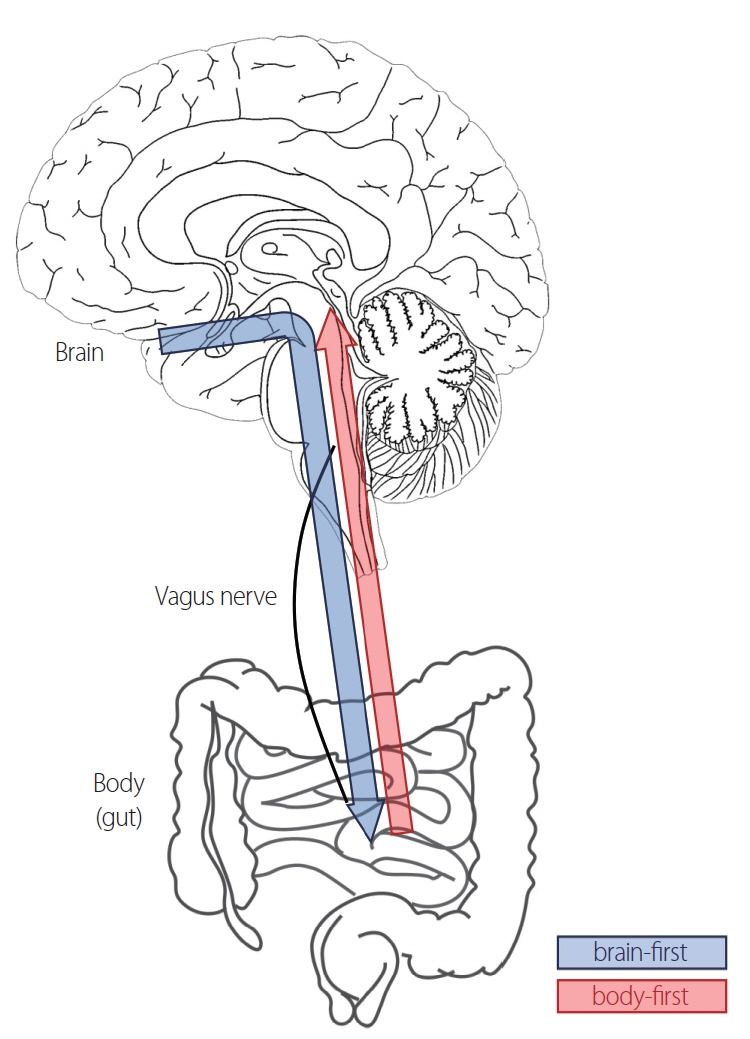
- Parkinson’s disease (PD) has undergone significant advancements in diagnosis and treatment over the past century, with apparent dopaminergic cell degeneration on dopamine transporter scans and a strong response to medication being key features. However, the etiology remains complex, involving various pathogenic mechanisms beyond alpha-synuclein accumulation. The recent brain-first versus body-first hypothesis, emerging from advances in functional imaging and clinical symptom clustering, suggests distinct starting points of alpha-synuclein pathology-either in the brain or the body, with subsequent spread via neural connections. This theory, exemplified by the alpha-synuclein origin site and connectome (SOC) model, proposes that body-first PD may originate in the enteric nervous system and spread to the brain, while brain-first PD starts within the central nervous system, such as the olfactory bulb or amygdala. While the SOC model offers valuable insights into the progression of PD, it raises several controversies. Critics argue that the model may oversimplify the disease’s complexity, failing to account for overlapping symptoms and the varying progression rates observed in different subtypes. Furthermore, there are concerns about the lack of longitudinal data and the potential for reclassification of PD subtypes over time. Despite these challenges, the ongoing development of imaging techniques that reflect in-vivo pathology holds promise for resolving these controversies and advancing the selection of patients for disease-modifying therapies.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lewis PA. James parkinson: the man behind the shaking palsy. J Parkinsons Dis. 2012; 2:181–187.
Article2. Chaudhuri KR, Jenner P. Two hundred years since James Parkinson’s essay on the shaking palsy-Have we made progress? Insights from the James Parkinson’s 200 years course held in London, March 2017. Mov Disord. 2017; 32:1311–1315.
Article3. Del Rey NL, Quiroga-Varela A, Garbayo E, Carballo-Carbajal I, Fernández-Santiago R, Monje MHG, et al. Advances in Parkinson’s disease: 200 years later. Front Neuroanat. 2018; 12:113.
Article4. Postuma RB, Berg D, Stern M, Poewe W, Olanow CW, Oertel W, et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2015; 30:1591–1601.
Article5. de la Fuente-Fernández R. Role of DaTSCAN and clinical diagnosis in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2012; 78:696–701.
Article6. Mahlknecht P, Krismer F, Poewe W, Seppi K. Meta-analysis of dorsolateral nigral hyperintensity on magnetic resonance imaging as a marker for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2017; 32:619–623.
Article7. Kim PH, Lee DH, Suh CH, Kim M, Shim WH, Kim SJ. Diagnostic performance of loss of nigral hyperintensity on susceptibility-weighted imaging in parkinsonism: an updated meta-analysis. Eur Radiol. 2021; 31:6342–6352.
Article8. Hasegawa T, Sugeno N, Kikuchi A, Baba T, Aoki M. Membrane trafficking illuminates a path to Parkinson’s disease. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2017; 242:63–76.
Article9. Espay AJ, Kepp KP, Herrup K. Lecanemab and donanemab as therapies for Alzheimer’s disease: an illustrated perspective on the data. eNeuro. 2024; 11:ENEURO.0319–23.2024.
Article10. Painous C, Fernández M, Pérez J, de Mena L, Cámara A, Compta Y. Fluid and tissue biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease: immunodetection or seed amplification? Central or peripheral? Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2024; 121:105968.
Article11. Yoo D, Bang JI, Ahn C, Nyaga VN, Kim YE, Kang MJ, et al. Diagnostic value of α-synuclein seeding amplification assays in α-synucleinopathies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2022; 104:99–109.
Article12. Postuma RB, Berg D. Advances in markers of prodromal Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016; 12:622–634.
Article13. Oliveira MAP, Balling R, Smidt MP, Fleming RMT. Embryonic development of selectively vulnerable neurons in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2017; 3:21.
Article14. Fasano A, Visanji NP, Liu LW, Lang AE, Pfeiffer RF. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015; 14:625–639.
Article15. Palma JA, Kaufmann H. Treatment of autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson disease and other synucleinopathies. Mov Disord. 2018; 33:372–390.
Article16. Connolly BS, Lang AE. Pharmacological treatment of Parkinson disease: a review. JAMA. 2014; 311:1670–1683.17. Morris JG. A review of some aspects of the pharmacology of levodopa. Clin Exp Neurol. 1978; 15:24–50.18. Poewe W, Antonini A, Zijlmans JC, Burkhard PR, Vingerhoets F. Levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease: an old drug still going strong. Clin Interv Aging. 2010; 5:229–238.19. Chou KL, Stacy M, Simuni T, Miyasaki J, Oertel WH, Sethi K, et al. The spectrum of “off” in Parkinson’s disease: what have we learned over 40 years? Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2018; 51:9–16.
Article20. Adler CH. Relevance of motor complications in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology. 2002; 58:S51–S56.
Article21. Reimer J, Grabowski M, Lindvall O, Hagell P. Use and interpretation of on/off diaries in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2004; 75:396–400.
Article22. Qualman SJ, Haupt HM, Yang P, Hamilton SR. Esophageal Lewy bodies associated with ganglion cell loss in achalasia. Similarity to Parkinson’s disease. Gastroenterology. 1984; 87:848–856.
Article23. Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H, Ohama E, Ikuta F. Parkinson’s disease: an immunohistochemical study of Lewy body-containing neurons in the enteric nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 1990; 79:581–583.
Article24. Braak H, de Vos RA, Bohl J, Del Tredici K. Gastric alpha-synuclein immunoreactive inclusions in Meissner’s and Auerbach’s plexuses in cases staged for Parkinson’s disease-related brain pathology. Neurosci Lett. 2006; 396:67–72.
Article25. Chiang HL, Lin CH. Altered gut microbiome and intestinal pathology in Parkinson’s disease. J Mov Disord. 2019; 12:67–83.
Article26. Arotcarena ML, Dovero S, Prigent A, Bourdenx M, Camus S, Porras G, et al. Bidirectional gut-to-brain and brain-to-gut propagation of synucleinopathy in non-human primates. Brain. 2020; 143:1462–1475.
Article27. Uemura N, Yagi H, Uemura MT, Hatanaka Y, Yamakado H, Takahashi R. Inoculation of α-synuclein preformed fibrils into the mouse gastrointestinal tract induces Lewy body-like aggregates in the brainstem via the vagus nerve. Mol Neurodegener. 2018; 13:21.
Article28. Kim S, Kwon SH, Kam TI, Panicker N, Karuppagounder SS, Lee S, et al. Transneuronal propagation of pathologic α-synuclein from the gut to the brain models Parkinson’s disease. Neuron. 2019; 103:627–641.e7.
Article29. Liu B, Fang F, Pedersen NL, Tillander A, Ludvigsson JF, Ekbom A, et al. Vagotomy and Parkinson disease: a Swedish register-based matched-cohort study. Neurology. 2017; 88:1996–2002.30. Svensson E, Horváth-Puhó E, Thomsen RW, Djurhuus JC, Pedersen L, Borghammer P, et al. Vagotomy and subsequent risk of Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol. 2015; 78:522–529.31. Sakakibara R, Tateno F, Kishi M, Tsuyusaki Y, Terada H, Inaoka T. MIBG myocardial scintigraphy in pre-motor Parkinson’s disease: a review. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014; 20:267–273.32. Borghammer P, Van Den Berge N. Brain-first versus gut-first Parkinson’s disease: a hypothesis. J Parkinsons Dis. 2019; 9:S281–S295.
Article33. Horsager J, Andersen KB, Knudsen K, Skjærbæk C, Fedorova TD, Okkels N, et al. Brain-first versus body-first Parkinson’s disease: a multimodal imaging case-control study. Brain. 2020; 143:3077–3088.
Article34. Borghammer P. The α-synuclein origin and connectome model (SOC Model) of Parkinson’s disease: explaining motor asymmetry, non-motor phenotypes, and cognitive decline. J Parkinsons Dis. 2021; 11:455–474.
Article35. Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2003; 24:197–211.
Article36. Raunio A, Kaivola K, Tuimala J, Kero M, Oinas M, Polvikoski T, et al. Lewy-related pathology exhibits two anatomically and genetically distinct progression patterns: a population-based study of Finns aged 85. Acta Neuropathol. 2019; 138:771–782.
Article37. Tanei ZI, Saito Y, Ito S, Matsubara T, Motoda A, Yamazaki M, et al. Lewy pathology of the esophagus correlates with the progression of Lewy body disease: a Japanese cohort study of autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol. 2021; 141:25–37.
Article38. Di Folco C, Couronné R, Arnulf I, Mangone G, Leu-Semenescu S, Dodet P, et al. Charting disease trajectories from Iiolated REM sleep behavior disorder to Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord. 2024; 39:64–75.
Article39. Chen Y, Xu Q, Wu L, Zhou M, Lin Y, Jiang Y, et al. REM sleep behavior disorder correlates with constipation in de novo Chinese Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurol Sci. 2023; 44:191–197.
Article40. Cicero CE, Luca A, Mostile G, Donzuso G, Giuliano L, Zappia M, et al. Influence of RBD onset on the clinical characteristics of Parkinson’s disease patients: a retrospective study. J Neurol. 2023; 270:3171–3178.
Article41. Bloem BR, Okun MS, Klein C. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet. 2021; 397:2284–2303.
Article42. Okuzumi A, Kurosawa M, Hatano T, Takanashi M, Nojiri S, Fukuhara T, et al. Rapid dissemination of alpha-synuclein seeds through neural circuits in an in-vivo prion-like seeding experiment. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2018; 6:96.
Article43. Pagano G, Ferrara N, Brooks DJ, Pavese N. Age at onset and Parkinson disease phenotype. Neurology. 2016; 86:1400–1407.
Article44. Cotogni M, Sacchi L, Sadikov A, Georgiev D. Asymmetry at disease onset is not a predictor of Parkinson’s disease progression. J Parkinsons Dis. 2021; 11:1689–1694.
Article45. Fearon C, Lang AE, Espay AJ. The logic and pitfalls of Parkinson’s disease as “brain-first” versus “body-first” subtypes. Mov Disord. 2021; 36:594–598.
Article46. Buchman AS, Yu L, Wilson RS, Leurgans SE, Nag S, Shulman JM, et al. Progressive parkinsonism in older adults is related to the burden of mixed brain pathologies. Neurology. 2019; 92:e1821–e1830.
Article47. Robinson JL, Lee EB, Xie SX, Rennert L, Suh E, Bredenberg C, et al. Neurodegenerative disease concomitant proteinopathies are prevalent, age-related and APOE4-associated. Brain. 2018; 141:2181–2193.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Comparative Study of how Subjects' Characteristics and Nursing Service Quality Influence on Hospital Revisiting Intent between Patients and Nurses
- The Relationships among Waiting Time, Patient's Satisfaction, and Revisiting Intention of Outpatients in General Hospital
- Cholesterol Metabolism in the Brain and Its Association with Parkinson's Disease
- Successful Treatment of Advanced Gastric Cancer with Brain Metastases through an Abscopal Effect by Radiation and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy
- Update on Parkinson’s Disease Rehabilitation