Clin Transplant Res.
2024 Sep;38(3):197-202. 10.4285/ctr.24.0028.
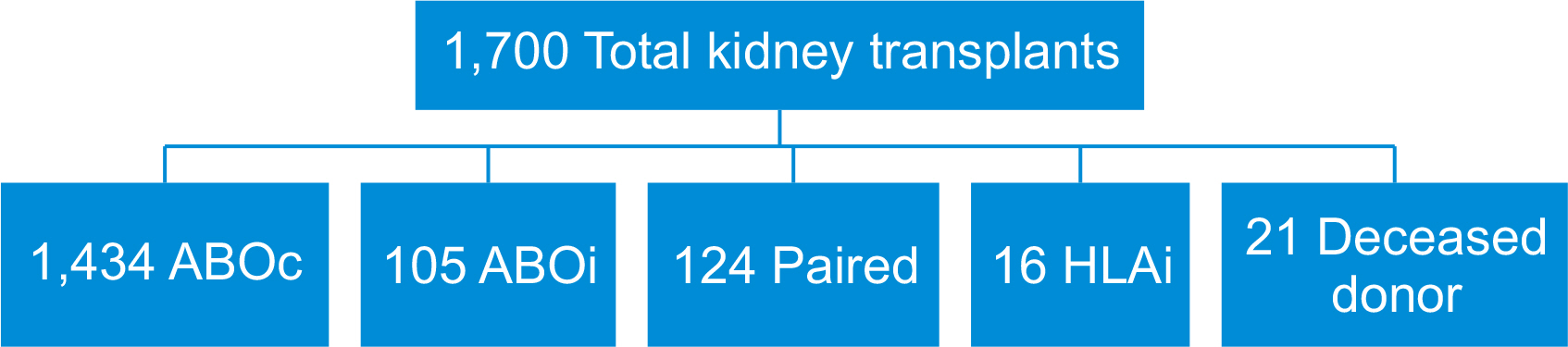
Perioperative outcomes of 105 cases of ABO-incompatible live donor kidney transplantation: a retrospective single-center observational study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anaesthesia and Critical Care, Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Hospital, Jaipur, India
- 2Department of Pathology, Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Hospital, Jaipur, India
- 3Department of Organ Transplant Anaesthesia and Critical Care, Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Hospital, Jaipur, India
- 4Division of Biostatistics, Department of Community Medicine, Mahatma Gandhi Medical College and Hospital, Jaipur, India
- KMID: 2559806
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/ctr.24.0028
Abstract
- Background
ABO-incompatible (ABOi) kidney transplantation poses significant challenges in achieving successful outcomes. This study aimed to investigate the impact of various interventions and techniques on improving the success rates of ABOi kidney transplantation.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective observational analysis of patients who underwent ABOi kidney transplantation from November 2012 to March 2023. The study included a total of 105 patients. We collected and analyzed data on patient demographics, preoperative assessments, surgical details, and postoperative outcomes.
Results
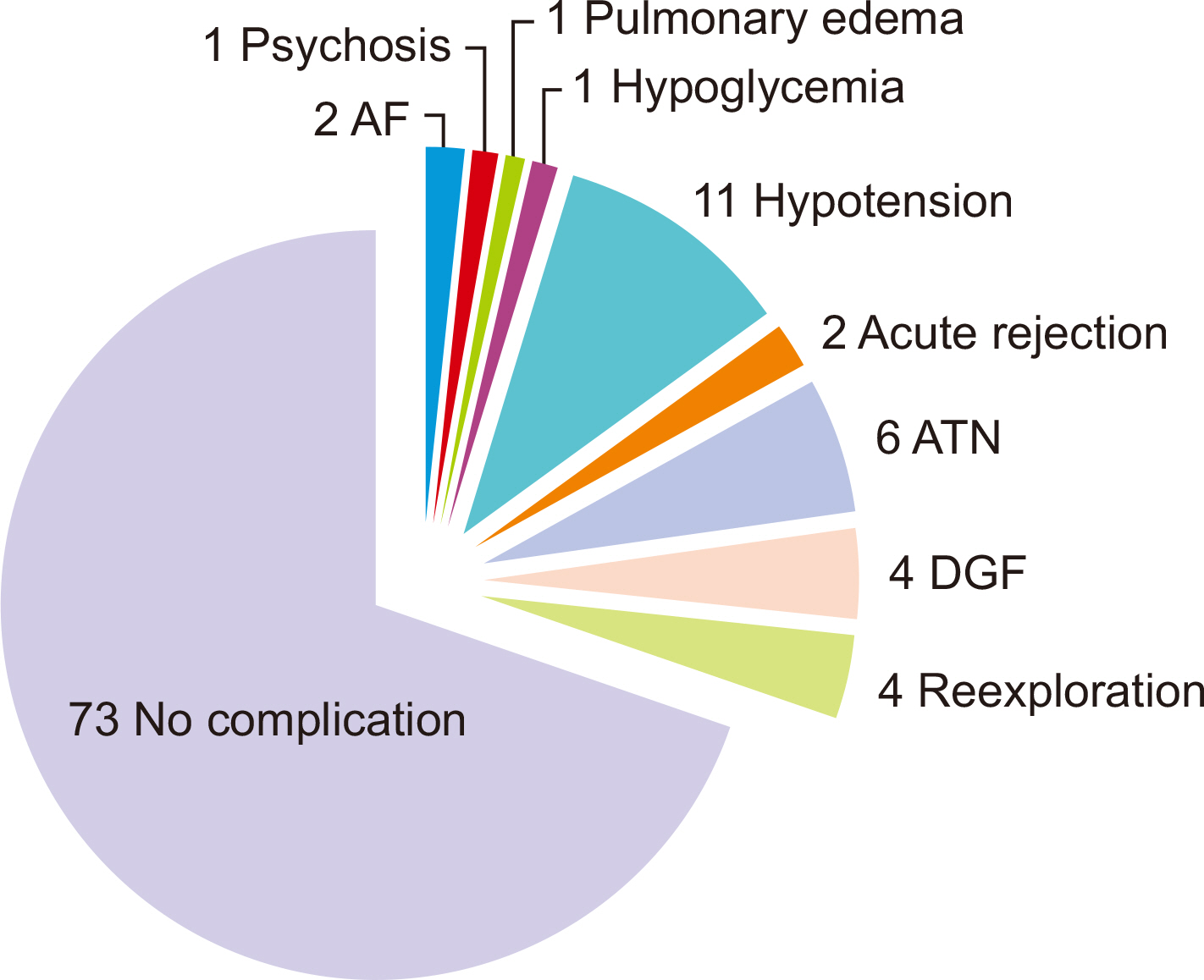
The mean ages of the donors and recipients were 50.52±10.32 and 36.63±11.61 years, respectively. The majority of recipients were male (81.9%), while most donors were female (89.5%). The most common blood group among recipients was O (69.5%), and among donors, it was B (46.7%). The median durations of chronic kidney disease and dialysis were 12 months (interquartile range [IQR], 7–28 months) and 6 months (IQR, 2–12 months), respectively. Baseline antibody titers (anti-A and anti-B) ranged from 64.0 to 256.0, while on the day of surgery, they were ≤8. Perioperative complications in-cluded hypotension (10.5%), acute tubular necrosis (5.7%), delayed graft function (3.8%), and reexploration (3.8%) due to hematoma.
Conclusions
ABOi kidney transplantation is a viable option for recipients lacking available donors with an ABO-compatible match. Perioperative concerns, including hypoalbuminemia, heightened risk of infections, coagulopathies, aseptic precautions, and immunological surveillance, must be carefully addressed.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Opelz G, Morath C, Süsal C, Tran TH, Zeier M, Döhler B. 2015; Three-year outcomes following 1420 ABO-incompatible living-donor kidney transplants performed after ABO antibody reduction: results from 101 centers. Transplantation. 99:400–4. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000312. PMID: 25050471.2. Tydén G, Donauer J, Wadström J, Kumlien G, Wilpert J, Nilsson T, et al. 2007; Implementation of a protocol for ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation - a three-center experience with 60 consecutive transplantations. Transplantation. 83:1153–5. DOI: 10.1097/01.tp.0000262570.18117.55. PMID: 17496528.3. Montgomery JR, Berger JC, Warren DS, James NT, Montgomery RA, Segev DL. 2012; Outcomes of ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation in the United States. Transplantation. 93:603–9. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318245b2af. PMID: 22290268. PMCID: PMC3299822.4. Naciri Bennani H, Abdulrahman Z, Allal A, Sallusto F, Delarche A, Game X, et al. 2016; Early post-transplant complications following ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. J Nephropathol. 5:19–27. DOI: 10.15171/jnp.2016.04. PMID: 27047806. PMCID: PMC4790183.5. Goyal VK, Solanki SL, Baj B. 2018; Pulmonary hypertension and post-operative outcome in renal transplant: a retrospective analysis of 170 patients. Indian J Anaesth. 62:131–5. DOI: 10.4103/ija.IJA_529_17. PMID: 29491519. PMCID: PMC5827480.6. Okumi M, Toki D, Nozaki T, Shimizu T, Shirakawa H, Omoto K, et al. 2016; ABO-incompatible living kidney transplants: evolution of outcomes and immunosuppressive management. Am J Transplant. 16:886–96. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.13502. PMID: 26555133.7. Shin M, Kim SJ. 2011; ABO incompatible kidney transplantation-current status and uncertainties. J Transplant. 2011:970421. DOI: 10.1155/2011/970421. PMID: 22174989. PMCID: PMC3235893.8. Donauer J, Wilpert J, Geyer M, Schwertfeger E, Kirste G, Drognitz O, et al. 2006; ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation using antigen-specific immunoadsorption and rituximab: a single center experience. Xenotransplantation. 13:108–10. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-3089.2006.00293.x. PMID: 16623802.9. de Weerd AE, Betjes MG. 2018; ABO-incompatible kidney transplant outcomes: a meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 13:1234–43. DOI: 10.2215/CJN.00540118. PMID: 30012630. PMCID: PMC6086717.10. Scurt FG, Ewert L, Mertens PR, Haller H, Schmidt BM, Chatzikyrkou C. 2019; Clinical outcomes after ABO-incompatible renal transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 393:2059–72. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32091-9. PMID: 31006573.11. Habicht A, Bröker V, Blume C, Lorenzen J, Schiffer M, Richter N, et al. 2011; Increase of infectious complications in ABO-incompatible kidney transplant recipients--a single centre experience. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 26:4124–31. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfr215. PMID: 21622990.12. Zöllner S, Pablik E, Druml W, Derfler K, Rees A, Biesenbach P. 2014; Fibrinogen reduction and bleeding complications in plasma exchange, immunoadsorption and a combination of the two. Blood Purif. 38:160–6. DOI: 10.1159/000367682. PMID: 25501972.13. Chung Y, Ko DH, Lim J, Kim KH, Kim H. 2022; Choice of ABO group for blood component transfusion in ABO-incompatible solid organ transplantation: a questionnaire survey in Korea and guideline proposal. Ann Lab Med. 42:105–9. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.1.105. PMID: 34374356. PMCID: PMC8368232.14. Goyal VK, Mandal S, Nimje GR, Shekhrajka P, Rana PS, Mittal S. 2023; Acute pain management after kidney transplantation: a current review of literature. Indian J Transpl. 17:402–9. DOI: 10.4103/ijot.ijot_49_23.15. Mittal S, Goyal VK, Shekhrajka P, Bhardwaj M, Nimje GR, Singh P, et al. 2023; Role of intrathecal morphine for acute postoperative pain management in patients undergoing kidney transplant: a randomized controlled study. Exp Clin Transplant. 21:939–45. DOI: 10.6002/ect.2023.0063. PMID: 38263780.16. Baj BB, Goyal VK, Shekhrajka P, Nimje GR, Mittal S. 2023; Perioperative management of a severely thrombocytopenic kidney transplant recipient using thromboelastography. Med J Armed Forces India. 79:718–21. DOI: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2023.01.011. PMID: 37981936. PMCID: PMC10654360.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation
- Analysis of the Results of ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplantation: In Comparison with ABO-Compatible Kidney Transplantation
- Desensitization in HLA Incompatible Transplantation
- ABO-Incompatible Living Donor Liver Transplantation
- Pretransplant mycophenolate mofetil reduces intrahepatic cholangiopathy related to laparoscopic donor hepatectomy in ABO-incompatible liver transplantation