J Korean Med Sci.
2024 Sep;39(37):e247. 10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e247.
Validity of the Tablet-Based Digital Cognitive Test (SCST) in Identifying Different Degrees of Cognitive Impairment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Happymind Clinic, Seoul, Korea
- 2Beaubrain Healthcare Co., LTD., Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Neurology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Neuroscience Center, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 5Samsung Alzheimer’s Convergence Research Center, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2559778
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e247
Abstract
- Background
As society ages, the incidence of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias has surged, highlighting the importance of early dementia diagnosis. The Seoul Cognitive Status Test (SCST), a digital neuropsychological test, is designed for the early detection of cognitive impairment and has been standardized to establish reliability and validity. This study aims to verify whether the SCST effectively discriminates between groups based on three cognitive statuses (subjective cognitive decline [SCD], mild cognitive impairment [MCI], Dementia) in a large sample. We also seek to determine whether the SCST discriminates between individuals with three different cognitive statuses as defined by the Cognitive Dementia Rating (CDR).
Methods
We enrolled 254 participants from a dementia clinic who underwent a comprehensive neuropsychological battery (Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery-II) during the dementia evaluation by experienced neurologists (55 with SCD, 126 with MCI, 73 with dementia). In addition, the degree of cognitive decline in participants was classified by CDR level (186 with CDR 0.5, 52 with CDR 1, 15 with CDR 2). One-way analysis of variance was used to compare SCST scores according to each of the three cognitive status groups and CDR levels.
Results
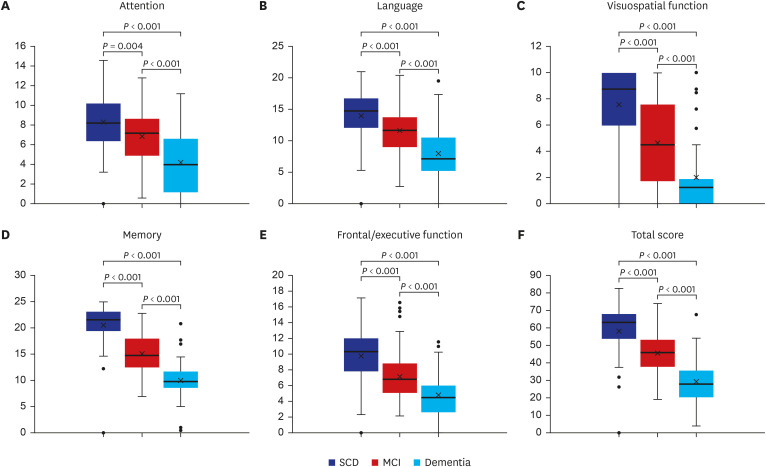
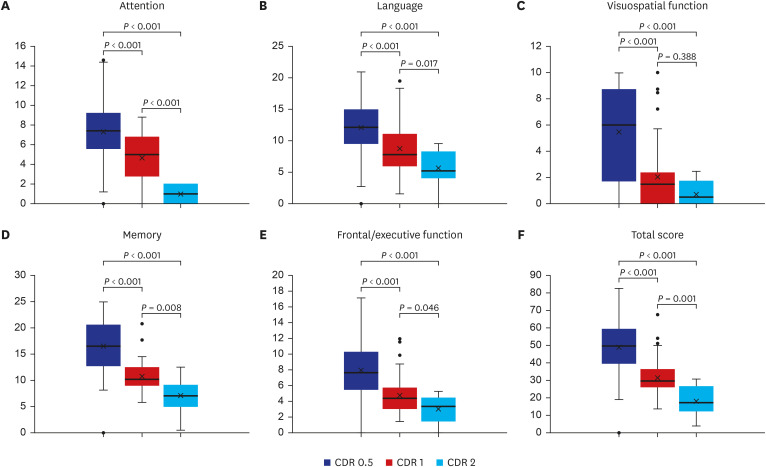
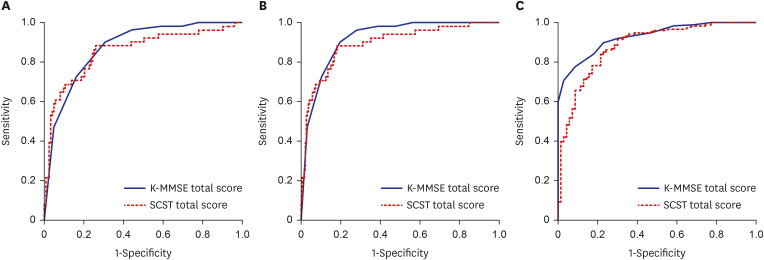
The SCST total score, cognitive domain scores (attention, language, visuospatial function, memory, executive function), and most of the subtest scores decreased significantly in the order of SCD, MCI and dementia. Likewise, the differences in SCST scores between CDR levels were significant, particularly in distinguishing between CDR 0.5 and CDR 1.
Conclusion
This study reaffirmed that the SCST can significantly discriminate between groups of individuals with SCD, MCI, and dementia based on a large sample. Furthermore, differences in SCT scores were found across the levels of CDR, confirming the clinical utility of the SCST. These findings suggest that the SCST is an efficient and useful neuropsychological test for the sensitive detection of early cognitive impairment.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Statistics Korea. Updated 2023. Accessed May 30, 2024. http://kosis.kr/visual/populationKorea/PopulationDashBoardMain.do .2. Jung YS, Kim YE, Ock M, Yoon SJ. Measuring the burden of disease in Korea using disability-adjusted life years (2008-2020). J Korean Med Sci. 2024; 39(7):e67. PMID: 38412612.3. Alzheimer’s Disease International. World Alzheimer report 2015: the global impact of dementia. Updated 2015. Accessed May 13, 2024. http://www.alz.co.uk/research/WorldAlzheimerReport2015.pdf .4. Kang Y, Jahng S, Na DL. Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery. 2nd ed. Seoul, Korea: Human Brain Research & Consulting Co.;2012.5. Lee JH, Lee KU, Lee DY, Kim KW, Jhoo JH, Kim JH, et al. Development of the Korean version of the Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Packet (CERAD-K): clinical and neuropsychological assessment batteries. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci. 2002; 57(1):47–53.6. Chan JY, Yau ST, Kwok TC, Tsoi KK. Diagnostic performance of digital cognitive tests for the identification of MCI and dementia: a systematic review. Ageing Res Rev. 2021; 72:101506. PMID: 34744026.7. Bauer RM, Iverson GL, Cernich AN, Binder LM, Ruff RM, Naugle RI. Computerized neuropsychological assessment devices: joint position paper of the American Academy of Clinical Neuropsychology and the National Academy of Neuropsychology. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2012; 27(3):362–373. PMID: 22382386.8. Wild K, Howieson D, Webbe F, Seelye A, Kaye J. Status of computerized cognitive testing in aging: a systematic review. Alzheimers Dement. 2008; 4(6):428–437. PMID: 19012868.9. Chin J, Kim DE, Lee H, Yun J, Lee BH, Park J, et al. A validation study of the Inbrain CST: a tablet computer-based cognitive screening test for elderly people with cognitive impairment. J Korean Med Sci. 2020; 35(34):e292. PMID: 32864906.10. Na S, Seo SW, Kim YJ, Yoo H, Lee ES. Correlation analysis between subtest scores of CERAD-K and a newly developed tablet computer-based digital cognitive test (Inbrain CST). Front Aging Neurosci. 2023; 15:1178324. PMID: 37455932.11. Na S, Lee ES, Lee TK. Diagnostic performance of a tablet computer-based cognitive screening test for identification of amnestic mild cognitive impairment. J Korean Med Sci. 2023; 38(17):e131. PMID: 37128875.12. Morris JC. The Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology. 1993; 43(11):2412–2414.13. Molinuevo JL, Rabin LA, Amariglio R, Buckley R, Dubois B, Ellis KA, et al. Implementation of subjective cognitive decline criteria in research studies. Alzheimers Dement. 2017; 13(3):296–311. PMID: 27825022.14. Petersen RC. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J Intern Med. 2004; 256(3):183–194. PMID: 15324362.15. McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology. 1984; 34(7):939–944. PMID: 6610841.16. Park HK, Na DL, Han SH, Kim JY, Cheong HK, Kim SY, et al. Clinical characteristics of a nationwide hospital-based registry of mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease patients in Korea: a CREDOS (Clinical Research Center for Dementia of South Korea) study. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26(9):1219–1226. PMID: 21935279.17. Ahn HJ, Chin J, Park A, Lee BH, Suh MK, Seo SW, et al. Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery-dementia version (SNSB-D): a useful tool for assessing and monitoring cognitive impairments in dementia patients. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25(7):1071–1076. PMID: 20592901.18. Murphy KJ, Rich JB, Troyer AK. Verbal fluency patterns in amnestic mild cognitive impairment are characteristic of Alzheimer’s type dementia. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2006; 12(4):570–574. PMID: 16981610.19. Troyer AK, Moscovitch M, Winocur G, Alexander MP, Stuss D. Clustering and switching on verbal fluency: the effects of focal frontal- and temporal-lobe lesions. Neuropsychologia. 1998; 36(6):499–504. PMID: 9705059.20. Kang SH, Park YH, Lee D, Kim JP, Chin J, Ahn Y, et al. The cortical neuroanatomy related to specific neuropsychological deficits in Alzheimer’s continuum. Dement Neurocogn Disord. 2019; 18(3):77–95. PMID: 31681443.21. Henry JD, Crawford JR, Phillips LH. Verbal fluency performance in dementia of the Alzheimer’s type: a meta-analysis. Neuropsychologia. 2004; 42(9):1212–1222. PMID: 15178173.22. Jang JW, Kim K, Baek MJ, Kim S. A comparison of five types of Trail Making Test in Korean elderly. Dement Neurocogn Disord. 2016; 15(4):135–141. PMID: 30906355.23. Hafiz NJ, Lohse A, Haas R, Reiche S, Sedlaczek L, Brandl EJ, et al. Trail making test error analysis in subjective cognitive decline, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s dementia with and without depression. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 2023; 38(1):25–36. PMID: 35901514.24. Haaksma ML, Calderón-Larrañaga A, Olde Rikkert MG, Melis RJ, Leoutsakos JS. Cognitive and functional progression in Alzheimer disease: a prediction model of latent classes. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018; 33(8):1057–1064. PMID: 29761569.25. Quiroz YT, Sperling RA, Norton DJ, Baena A, Arboleda-Velasquez JF, Cosio D, et al. Association between Amyloid and Tau accumulation in young adults with autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease. JAMA Neurol. 2018; 75(5):548–556. PMID: 29435558.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Discriminative Power of Seoul Cognitive Status Test in Differentiating Subjective Cognitive Decline, Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Dementia Based on CERAD-K Standards
- Development of the Diagnostic Matrix of the Seoul Cognitive Status Test, Compared to Traditional Paper-andPencil Neuropsychological Tests
- Effect of Tablet-based Cognitive Intervention on Cognition in Patients With Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Pilot Study
- Cognitive Assessment in Traumatic Brain Injury
- Relationship between Social Participation and Cognitive Impairment in Low-Educated Older Adults Based on Indonesian Family Life Survey-5