Clin Endosc.
2024 Sep;57(5):666-674. 10.5946/ce.2023.272.
Safety and efficacy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic duct drainage using a drill dilator: a retrospective study in Japan
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Helwan University, Cairo, Egypt
- 2Department of Gastroenterology, Aichi Cancer Center Hospital, Nagoya, Japan
- 3Department of Medicine and Therapeutics, University of Ghana Medical School, Korle Bu Teaching Hospital, Accra, Ghana
- KMID: 2559218
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2023.272
Abstract
- Background/Aims
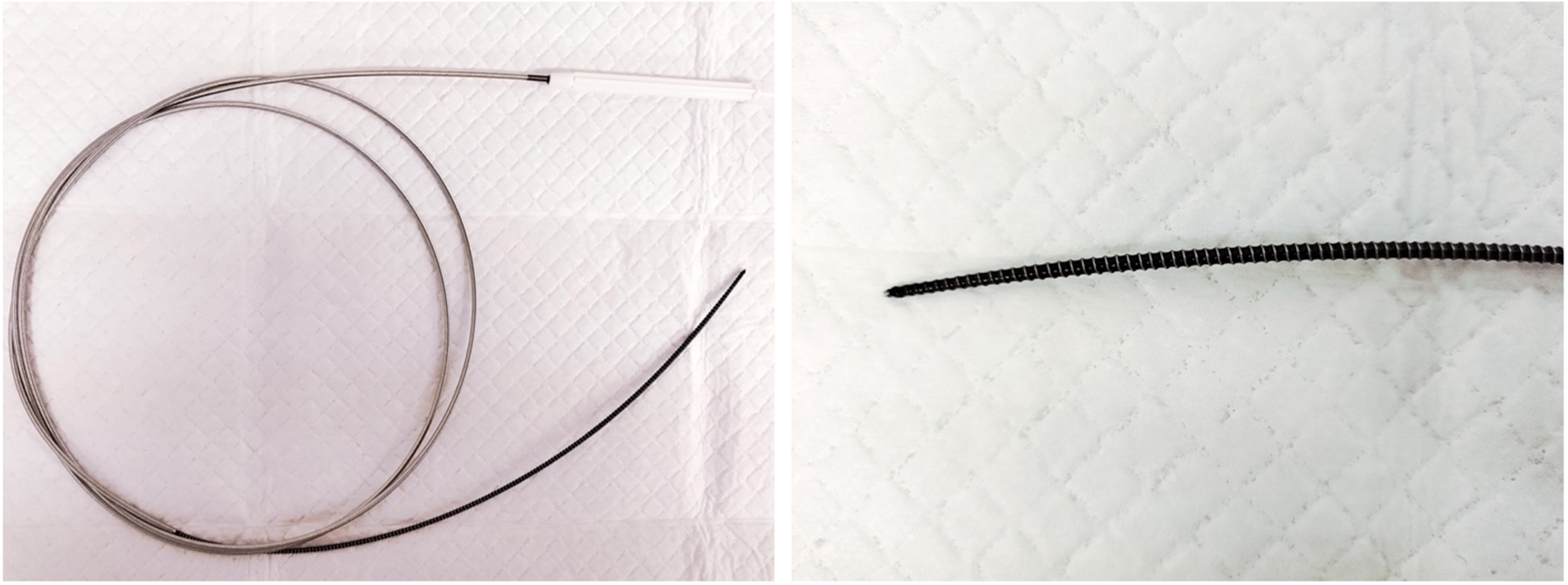
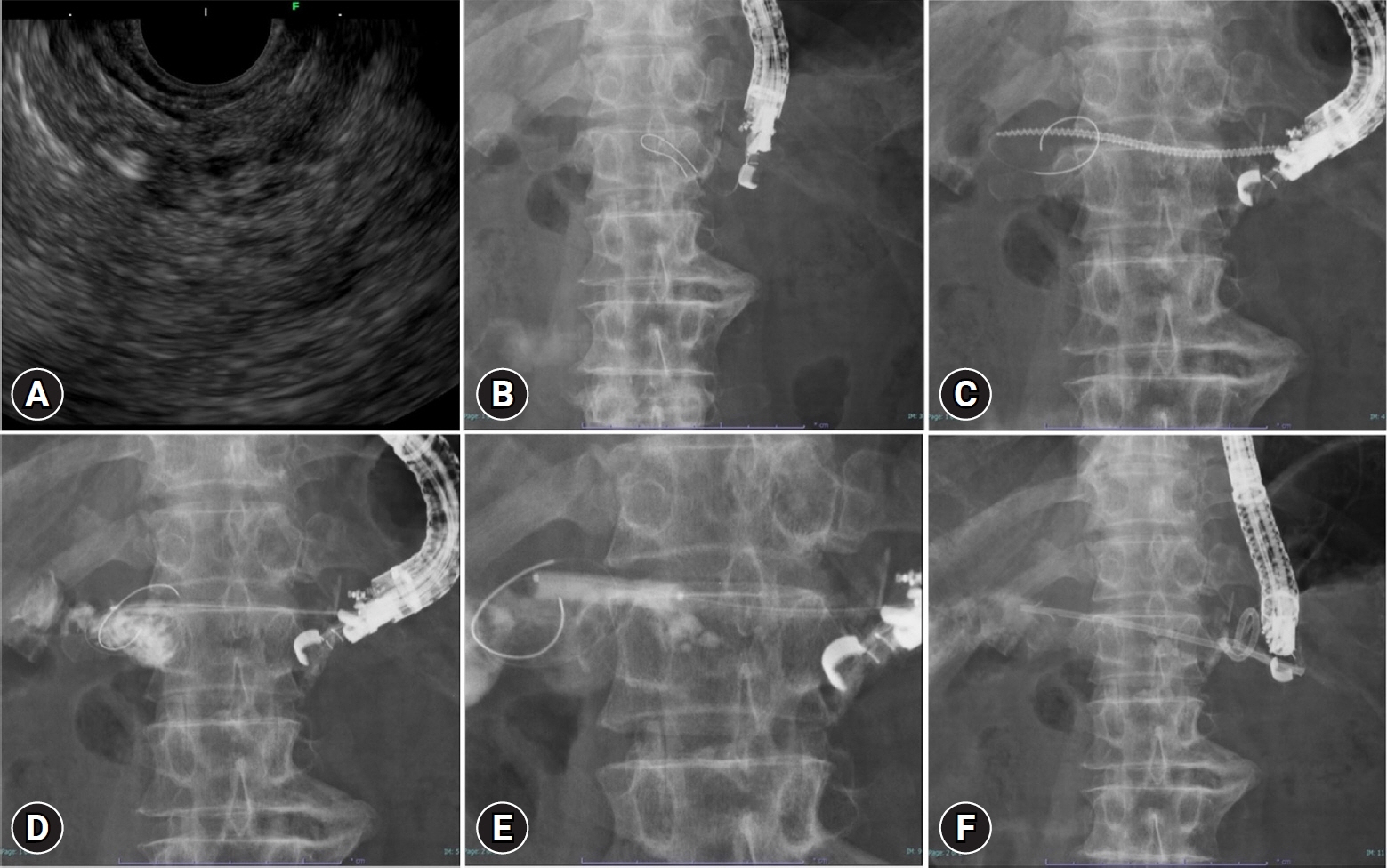
Dilation of the tract before stent deployment is a challenging step in endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic duct drainage (EUS-PDD). In this study, we examined the effectiveness and safety of a novel spiral dilator, Tornus ES (Asahi Intec), for EUS-PDD.
Methods
This was a retrospective, single-arm, observational study at Aichi Cancer Center Hospital. The punctured tract was dilated using a Tornus ES dilator in all EUS-PDD cases. Our primary endpoint was the technical success rate of initial tract dilation. Technical success was defined as successful fistula dilation using a Tornus ES followed by successful stent insertion. Secondary endpoints were procedure times and early adverse events.
Results
A total of 12 patients were included between December 2021 and March 2023. EUS-PDD was performed in 11 patients for post-pancreaticoduodenectomy anastomotic strictures and one patient with pancreatitis with duodenal perforation. The technical success rates of stent insertion and fistula dilation using a Tornus ES dilator was 100%. The median procedure time was 24 minutes. No remarkable adverse events related to the procedure were observed, apart from fever, which occurred in 2 patients.
Conclusions
Tract dilation in EUS-PDD using a Tornus ES is effective and safe.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bataille L, Deprez P. A new application for therapeutic EUS: main pancreatic duct drainage with a “pancreatic rendezvous technique”. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:740–743.2. Rösch T, Daniel S, Scholz M, et al. Endoscopic treatment of chronic pancreatitis: a multicenter study of 1000 patients with long-term follow-up. Endoscopy. 2002; 34:765–771.3. Itoi T, Kasuya K, Sofuni A, et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided pancreatic duct access: techniques and literature review of pancreatography, transmural drainage and rendezvous techniques. Dig Endosc. 2013; 25:241–252.4. Nakai Y, Kogure H, Isayama H, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic duct drainage. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2019; 25:210–217.5. Imoto A, Ogura T, Higuchi K. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic duct drainage: techniques and literature review of transmural stenting. Clin Endosc. 2020; 53:525–534.6. Yasuda T, Hara K, Haba S. Dilation of pancreatic duct stenosis using a newly designed drill dilator. Dig Endosc. 2022; 34:e73–e74.7. Hara K, Okuno N, Haba S, et al. Utility of a novel drill dilator for easier EUS-guided pancreatic duct drainage. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2022; 29:e91–e92.8. Okuno N, Hara K, Haba S, et al. Novel drill dilator facilitates endoscopic ultrasound-guided hepaticogastrostomy. Dig Endosc. 2023; 35:389–393.9. Cotton PB, Eisen GM, Aabakken L, et al. A lexicon for endoscopic adverse events: report of an ASGE workshop. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:446–454.10. Chandan S, Mohan BP, Khan SR, et al. Efficacy and safety of endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic duct drainage (EUS-PDD): a systematic review and meta-analysis of 714 patients. Endosc Int Open. 2020; 8:E1664–E1672.11. Itoi T, Yasuda I, Kurihara T, et al. Technique of endoscopic ultrasonography-guided pancreatic duct intervention (with videos). J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014; 21:E4–E9.12. Matsunami Y, Itoi T, Sofuni A, et al. Evaluation of a new stent for EUS-guided pancreatic duct drainage: long-term follow-up outcome. Endosc Int Open. 2018; 6:E505–E512.13. Nakai Y. Technical tips for endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic duct access and drainage. Int J Gastrointest Interv. 2020; 9:154–159.14. Honjo M, Itoi T, Tsuchiya T, et al. Safety and efficacy of ultra-tapered mechanical dilator for EUS-guided hepaticogastrostomy and pancreatic duct drainage compared with electrocautery dilator (with video). Endosc Ultrasound. 2018; 7:376–382.15. Park DH, Jang JW, Lee SS, et al. EUS-guided biliary drainage with transluminal stenting after failed ERCP: predictors of adverse events and long-term results. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:1276–1284.16. Ogawa T, Kanno Y, Koshita S, et al. Prospective feasibility study on the efficacy and safety of a novel spiral dilator for endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage. DEN Open. 2022; 3:e170.17. Krafft MR, Nasr JY. Anterograde endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic duct drainage: a technical review. Dig Dis Sci. 2019; 64:1770–1781.18. Dalal A, Patil G, Maydeo A. Six-year retrospective analysis of endoscopic ultrasonography-guided pancreatic ductal interventions at a tertiary referral center. Dig Endosc. 2020; 32:409–416.19. Ogura T, Ohama H, Higuchi K. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic transmural stenting and transmural intervention. Clin Endosc. 2020; 53:429–435.20. Oh D, Park DH, Song TJ, et al. Long-term outcome of endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic duct drainage using a fully covered self-expandable metal stent for pancreaticojejunal anastomosis stricture. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020; 35:994–1001.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Technical tips for endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreatic duct access and drainage
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Drainage of Pancreatic Fluid Collections (with Video)
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Pancreatic Duct Intervention
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Pancreatic Transmural Stenting and Transmural Intervention
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Drainage in Pancreatobiliary Diseases