Diabetes Metab J.
2024 Sep;48(5):949-959. 10.4093/dmj.2023.0166.
A New Tool to Identify Pediatric Patients with Atypical Diabetes Associated with Gene Polymorphisms
- Affiliations
-
- 1Pediatrics Unit, Institute for Experimental and Clinical Research, UCLouvain, Brussels, Belgium
- 2Pediatric Endocrinology Unit, Saint-Luc University Clinics, Brussels, Belgium
- 3Louvain Institute of Biomolecular Science and Technology (IBST) Unit, UCLouvain, Brussels, Belgium
- 4Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology Unit, CHU-UCL Namur sites Saint-Elisabeth and Mont-Godinne, Namur, Belgium
- 5Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetology Unit, Clinique CHC MontLégia (CHC MontLégia Clinic), Liège, Belgium
- 6Pediatric Endocrinology Unit, CHU of Liège site ND-des Bruyères, Liège, Belgium
- 7Human Molecular Genetics, de Duve Institute, UCLouvain, Brussels, Belgium
- KMID: 2559004
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0166
Abstract
- Background
Recent diabetes subclassifications have improved the differentiation between patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus despite several overlapping features, yet without considering genetic forms of diabetes. We sought to facilitate the identification of monogenic diabetes by creating a new tool that we validated in a pediatric maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) cohort.
Methods
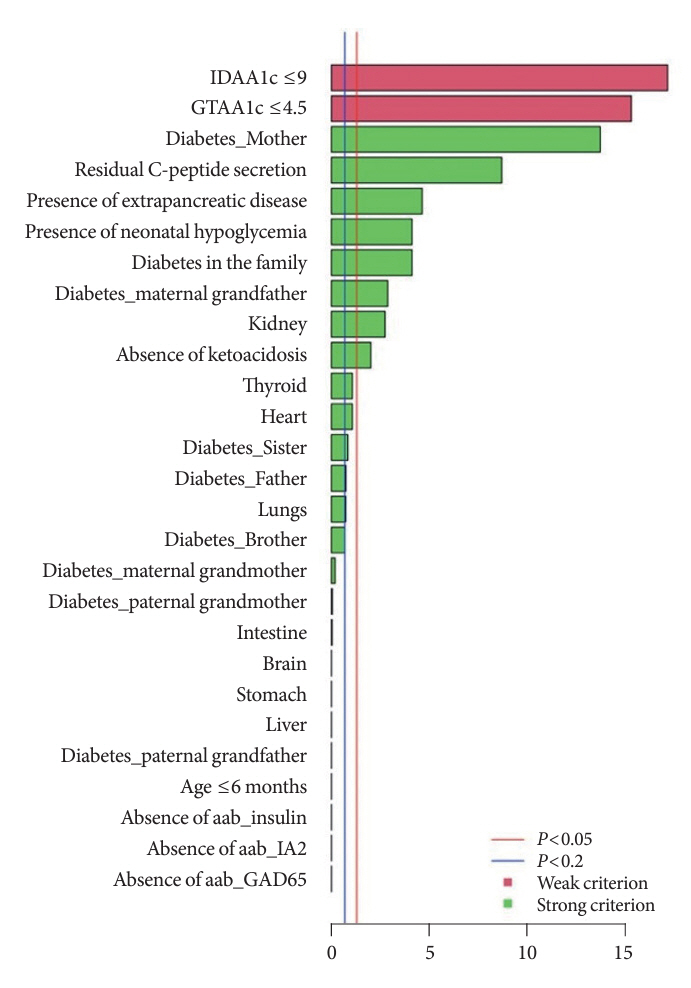
We first created the DIAgnose MOnogenic DIAbetes (DIAMODIA) criteria based on the pre-existing, but incomplete, MODY calculator. This new score is composed of four strong and five weak criteria, with patients having to display at least one weak and one strong criterion.
Results
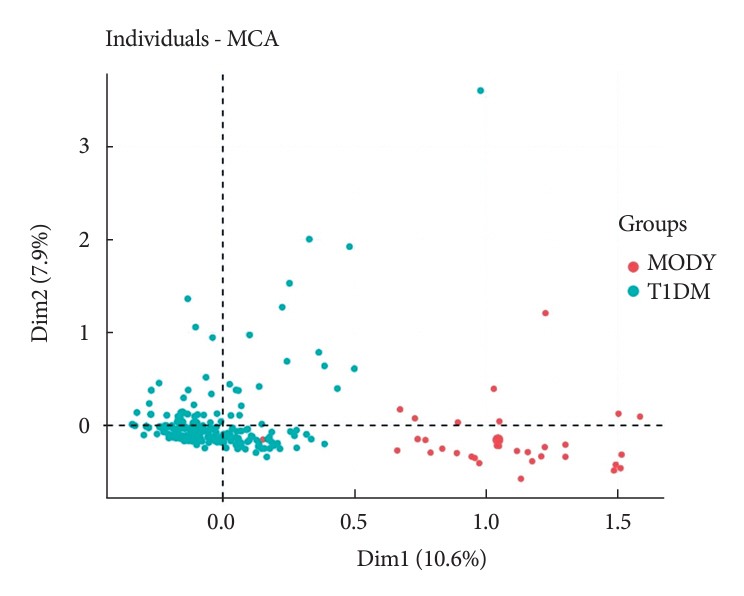
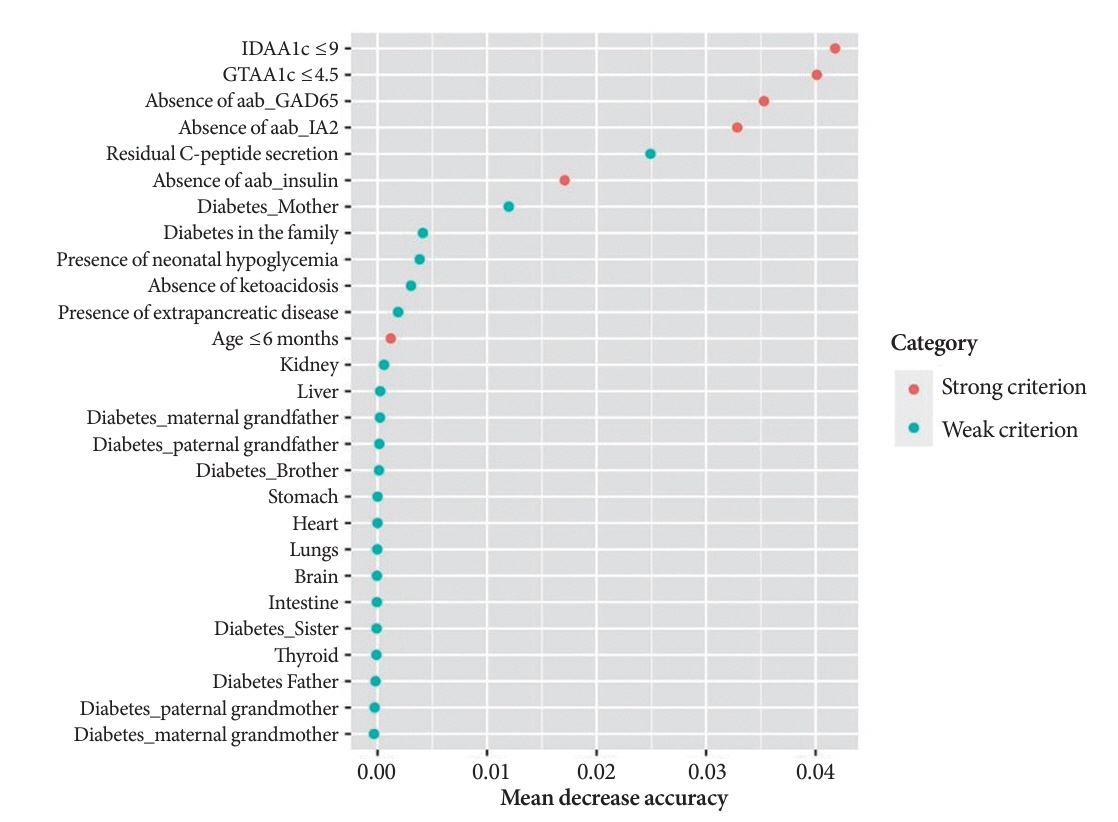
The effectiveness of the DIAMODIA criteria was evaluated in two patient cohorts, the first consisting of patients with confirmed MODY diabetes (n=34) and the second of patients with T1DM (n=390). These DIAMODIA criteria successfully detected 100% of MODY patients. Multiple correspondence analysis performed on the MODY and T1DM cohorts enabled us to differentiate MODY patients from T1DM. The three most relevant variables to distinguish a MODY from T1DM profile were: lower insulin-dose adjusted A1c score ≤9, glycemic target-adjusted A1c score ≤4.5, and absence of three anti-islet cell autoantibodies.
Conclusion
We validated the DIAMODIA criteria, as it effectively identified all monogenic diabetes patients (MODY cohort) and succeeded to differentiate T1DM from MODY patients. The creation of this new and effective tool is likely to facilitate the characterization and therapeutic management of patients with atypical diabetes, and promptly referring them for genetic testing which would markedly improve clinical care and counseling, as well.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022; 45(Suppl 1):S17–38.2. Watkins RA, Evans-Molina C, Blum JS, DiMeglio LA. Established and emerging biomarkers for the prediction of type 1 diabetes: a systematic review. Transl Res. 2014; 164:110–21.
Article3. Ahlqvist E, Storm P, Karajamaki A, Martinell M, Dorkhan M, Carlsson A, et al. Novel subgroups of adult-onset diabetes and their association with outcomes: a data-driven cluster analysis of six variables. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018; 6:361–9.
Article4. Møller AM, Dalgaard LT, Pociot F, Nerup J, Hansen T, Pedersen O. Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha gene in Caucasian families originally classified as having type I diabetes. Diabetologia. 1998; 41:1528–31.
Article5. Lambert AP, Ellard S, Allen LI, Gallen IW, Gillespie KM, Bingley PJ, et al. Identifying hepatic nuclear factor 1alpha mutations in children and young adults with a clinical diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:333–7.6. Awa WL, Schober E, Wiegand S, Herwig J, Meissner T, Schmidt F, et al. Reclassification of diabetes type in pediatric patients initially classified as type 2 diabetes mellitus: 15 years follow-up using routine data from the German/Austrian DPV database. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011; 94:463–7.
Article7. Kleinberger JW, Copeland KC, Gandica RG, Haymond MW, Levitsky LL, Linder B, et al. Monogenic diabetes in overweight and obese youth diagnosed with type 2 diabetes: the TODAY clinical trial. Genet Med. 2018; 20:583–90.
Article8. Kleinberger JW, Pollin TI. Undiagnosed MODY: time for action. Curr Diab Rep. 2015; 15:110.
Article9. Shields BM, Hicks S, Shepherd MH, Colclough K, Hattersley AT, Ellard S. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY): how many cases are we missing? Diabetologia. 2010; 53:2504–8.
Article10. Hattersley AT, Patel KA. Precision diabetes: learning from monogenic diabetes. Diabetologia. 2017; 60:769–77.
Article11. Nkonge KM, Nkonge DK, Nkonge TN. The epidemiology, molecular pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY). Clin Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020; 6:20.
Article12. Shields BM, McDonald TJ, Ellard S, Campbell MJ, Hyde C, Hattersley AT. The development and validation of a clinical prediction model to determine the probability of MODY in patients with young-onset diabetes. Diabetologia. 2012; 55:1265–72.
Article13. Harris PA, Taylor R, Minor BL, Elliott V, Fernandez M, O’Neal L, et al. The REDCap consortium: building an international community of software platform partners. J Biomed Inform. 2019; 95:103208.
Article14. Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research electronic data capture (REDCap): a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009; 42:377–81.15. Dunger DB, Sperling MA, Acerini CL, Bohn DJ, Daneman D, Danne TP, et al. European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology/Lawson Wilkins Pediatric Endocrine Society consensus statement on diabetic ketoacidosis in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2004; 113:e133–40.
Article16. Roelants M, Hauspie R, Hoppenbrouwers K. References for growth and pubertal development from birth to 21 years in Flanders, Belgium. Ann Hum Biol. 2009; 36:680–94.
Article17. Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ. 2000; 320:1240–3.
Article18. Mortensen HB, Hougaard P, Swift P, Hansen L, Holl RW, Hoey H, et al. New definition for the partial remission period in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:1384–90.
Article19. Nielens N, Polle O, Robert A, Lysy PA. Integration of routine parameters of glycemic variability in a simple screening method for partial remission in children with type 1 diabetes. J Diabetes Res. 2018; 2018:5936360.
Article20. R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing;2013.21. Le S, Josse J, Husson F. FactoMineR: an R package for multivariate analysis. J Stat Softw. 2008; 25:1–18.22. Liaw A, Wiener M. Classification and regression by randomForest. R News. 2002; 2:18–22.23. Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R. Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J Stat Softw. 2010; 33:1–22.
Article24. Kowarik A, Templ M. Imputation with the R package VIM. J Stat Softw. 2016; 74:1–16.25. Libman I, Haynes A, Lyons S, Pradeep P, Rwagasor E, Tung JY, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2022: definition, epidemiology, and classification of diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatr Diabetes. 2022; 23:1160–74.26. Besser RE, Bell KJ, Couper JJ, Ziegler AG, Wherrett DK, Knip M, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2022: stages of type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatr Diabetes. 2022; 23:1175–87.27. Greeley SA, Polak M, Njolstad PR, Barbetti F, Williams R, Castano L, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2022: the diagnosis and management of monogenic diabetes in children and adolescents. Pediatr Diabetes. 2022; 23:1188–211.
Article28. Fu J, Ping F, Wang T, Liu Y, Wang X, Yu J, et al. A clinical prediction model to distinguish maturity-onset diabetes of the young from type 1 and type 2 diabetes in the Chinese population. Endocr Pract. 2021; 27:776–82.
Article29. McDonald TJ, Colclough K, Brown R, Shields B, Shepherd M, Bingley P, et al. Islet autoantibodies can discriminate maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) from type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2011; 28:1028–33.30. Carrera P, Marzinotto I, Bonfanti R, Massimino L, Calzavara S, Favellato Μ, et al. Genetic determinants of type 1 diabetes in individuals with weak evidence of islet autoimmunity at disease onset. Diabetologia. 2023; 66:695–708.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficient Strategy to Identify Gene-Gene Interactions and Its Application to Type 2 Diabetes
- Calpain-10 and Adiponectin Gene Polymorphisms in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Patients
- Insulin Gene Polymorphisms in non-insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus ( NIDDM ) in Korean
- Association of HLA Class II and Non-HLA Gene Polymorphisms with Disease Susceptibility in Korean Children with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Polymorphisms of Kir6.2 Gene are Associated with Type 2 Diabetes and Blood Pressure in the Korean Population