Diabetes Metab J.
2024 Sep;48(5):837-846. 10.4093/dmj.2024.0317.
Benefit and Safety of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- KMID: 2558995
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2024.0317
Abstract
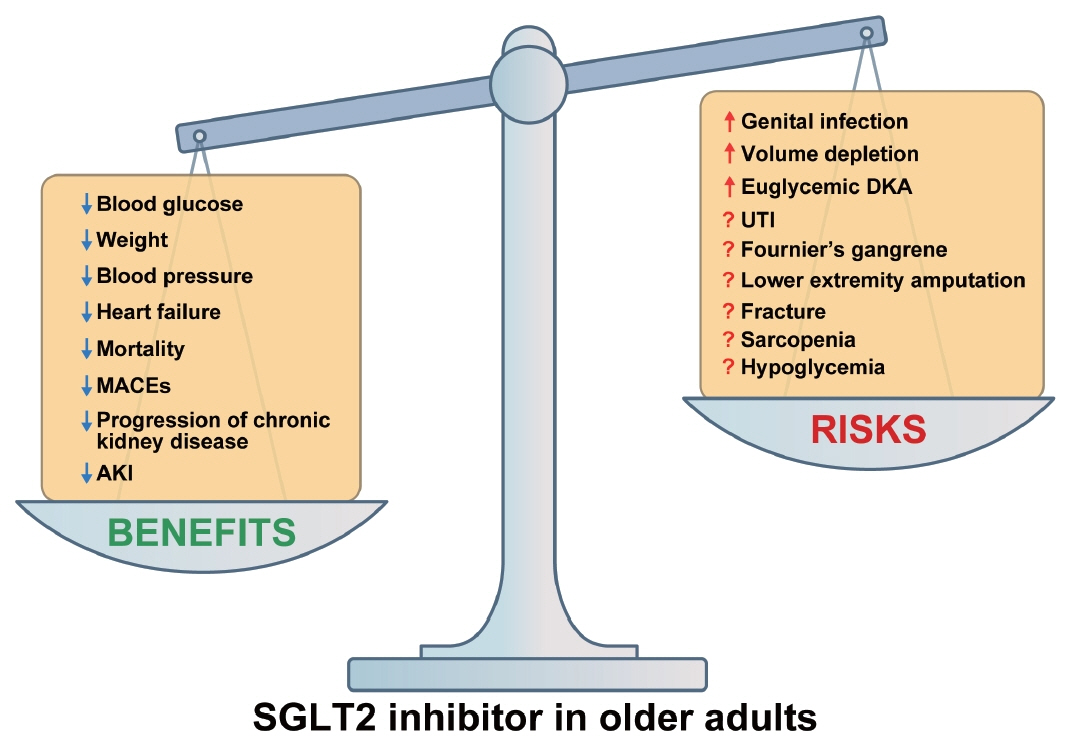
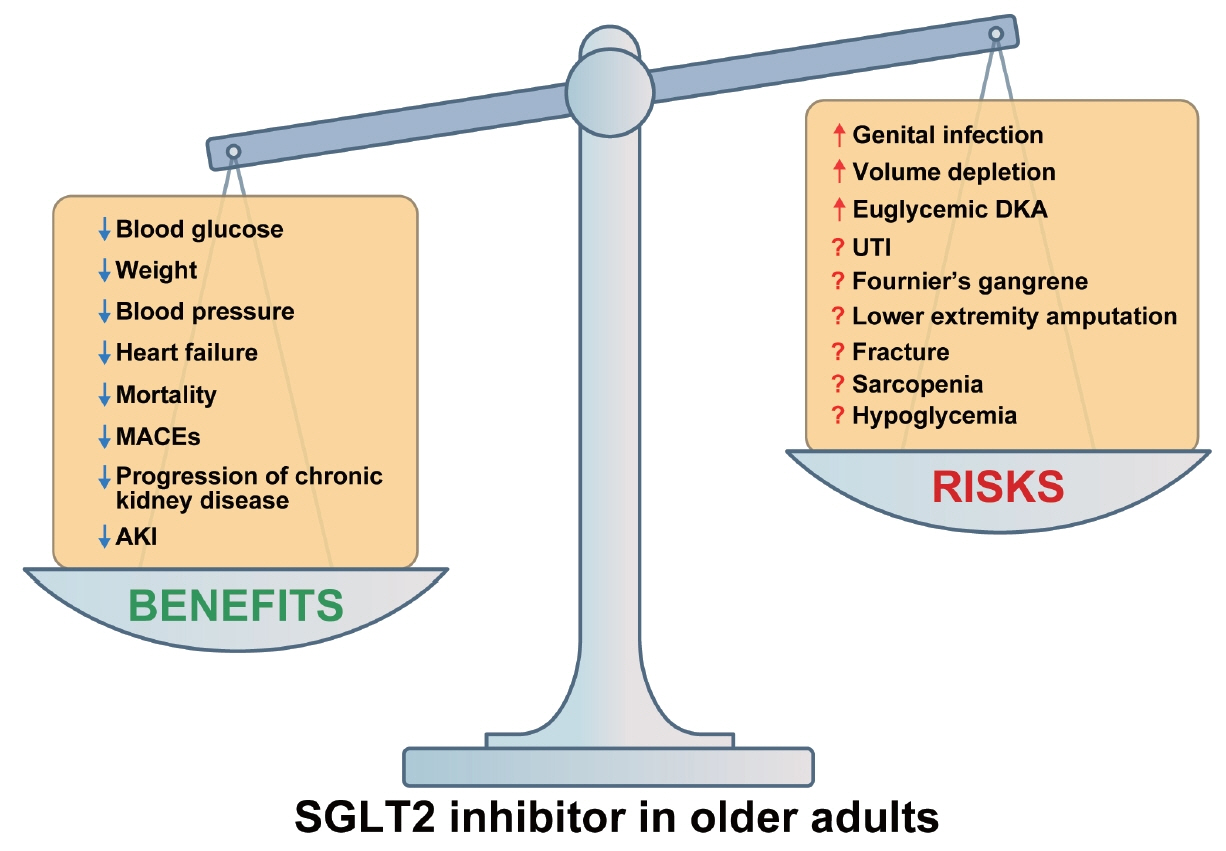
- People with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are at higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease, heart failure, chronic kidney disease, and premature death than people without diabetes. Therefore, treatment of diabetes aims to reduce these complications. Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have shown beneficial effects on cardiorenal and metabolic health beyond glucose control, making them a promising class of drugs for achieving the ultimate goals of diabetes treatment. However, despite their proven benefits, the use of SGLT2 inhibitors in eligible patients with T2DM remains suboptimal due to reports of adverse events. The use of SGLT2 inhibitors is particularly limited in older patients with T2DM because of the lack of treatment experience and insufficient long-term safety data. This article comprehensively reviews the risk-benefit profile of SGLT2 inhibitors in older patients with T2DM, drawing on data from prospective randomized controlled trials of cardiorenal outcomes, original studies, subgroup analyses across different age groups, and observational cohort studies.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Pharmacological management of diabetes in older adults
Junghyun Noh
Cardiovasc Prev Pharmacother. 2025;7(1):13-20. doi: 10.36011/cpp.2025.7.e1.
Reference
-
1. International Diabetes Federation. The IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th ed. Brussels: IDF;2021.2. Ko SH, Han KD, Park YM, Yun JS, Kim K, Bae JH, et al. Diabetes mellitus in the elderly adults in Korea: based on data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019 to 2020. Diabetes Metab J. 2023; 47:643–52.
Article3. Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:347–57.
Article4. McMurray JJ, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, Kober L, Kosiborod MN, Martinez FA, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019; 381:1995–2008.5. Solomon SD, McMurray JJ, Claggett B, de Boer RA, DeMets D, Hernandez AF, et al. Dapagliflozin in heart failure with mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2022; 387:1089–98.6. Packer M, Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Pocock SJ, Carson P, et al. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with empagliflozin in heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383:1413–24.7. Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Ferreira JP, Bocchi E, Bohm M, et al. Empagliflozin in heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2021; 385:1451–61.8. Bhatt DL, Szarek M, Pitt B, Cannon CP, Leiter LA, McGuire DK, et al. Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384:129–39.
Article9. Bhatt DL, Szarek M, Steg PG, Cannon CP, Leiter LA, McGuire DK, et al. Sotagliflozin in patients with diabetes and recent worsening heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384:117–28.
Article10. Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJ, Charytan DM, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2295–306.
Article11. Heerspink HJ, Stefansson BV, Correa-Rotter R, Chertow GM, Greene T, Hou FF, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383:1436–46.
Article12. The EMPA-KIDNEY Collaborative Group, Herrington WG, Staplin N, Wanner C, Green JB, Hauske SJ, et al. Empagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2023; 388:117–27.
Article13. Theodorakopoulou MP, Alexandrou ME, Tsitouridis A, Kamperidis V, Pella E, Xanthopoulos A, et al. Effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors on heart failure events in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2024; 10:329–41.
Article14. Baek JH, Yang YS, Ko SH, Han KD, Kim JH, Moon MK, et al. Real-world prescription patterns and barriers related to the use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors among Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Metab J. 2022; 46:701–12.
Article15. Bellary S, Barnett AH. SGLT2 inhibitors in older adults: overcoming the age barrier. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2023; 4:e127–8.
Article16. Scheen AJ. Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with SGLT2 inhibitors: real-life observational studies in older patients with type 2 diabetes: SGLT2 inhibitors in elderly and real life. Diabet Epidemiol Manag. 2023; 10:100235.17. Ozaki AF, Ko DT, Chong A, Fang J, Atzema CL, Austin PC, et al. Prescribing patterns and factors associated with sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor prescribing in patients with diabetes mellitus and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. CMAJ Open. 2023; 11:E494–503.
Article18. Schernthaner G, Shehadeh N, Ametov AS, Bazarova AV, Ebrahimi F, Fasching P, et al. Worldwide inertia to the use of cardiorenal protective glucose-lowering drugs (SGLT2i and GLP-1 RA) in high-risk patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2020; 19:185.
Article19. Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:644–57.
Article20. Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:2117–28.
Article21. Monteiro P, Bergenstal RM, Toural E, Inzucchi SE, Zinman B, Hantel S, et al. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin in older patients in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME ® trial. Age Ageing. 2019; 48:859–66.22. Cannon CP, Pratley R, Dagogo-Jack S, Mancuso J, Huyck S, Masiukiewicz U, et al. Cardiovascular outcomes with ertugliflozin in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383:1425–35.
Article23. Giugliano D, Longo M, Maiorino MI, Bellastella G, Chiodini P, Solerte SB, et al. Efficacy of SGLT-2 inhibitors in older adults with diabetes: systematic review with meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020; 162:108114.
Article24. Bhattarai M, Salih M, Regmi M, Al-Akchar M, Deshpande R, Niaz Z, et al. Association of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors with cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and other risk factors for cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2022; 5:e2142078.25. Heerspink HJ, Karasik A, Thuresson M, Melzer-Cohen C, Chodick G, Khunti K, et al. Kidney outcomes associated with use of SGLT2 inhibitors in real-world clinical practice (CVD-REAL 3): a multinational observational cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020; 8:27–35.
Article26. Birkeland KI, Jorgensen ME, Carstensen B, Persson F, Gulseth HL, Thuresson M, et al. Cardiovascular mortality and morbidity in patients with type 2 diabetes following initiation of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors versus other glucose-lowering drugs (CVD-REAL Nordic): a multinational observational analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017; 5:709–17.
Article27. Seino Y, Kim DJ, Yabe D, Tan EC, Chung WJ, Ha KH, et al. Cardiovascular and renal effectiveness of empagliflozin in routine care in East Asia: results from the EMPRISE East Asia study. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2021; 4:e00183.
Article28. Patorno E, Pawar A, Wexler DJ, Glynn RJ, Bessette LG, Paik JM, et al. Effectiveness and safety of empagliflozin in routine care patients: results from the EMPagliflozin compaRative effectIveness and SafEty (EMPRISE) study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022; 24:442–54.29. Nakai M, Iwanaga Y, Kanaoka K, Sumita Y, Nishioka Y, Myojin T, et al. Contemporary use of SGLT2 inhibitors in heart failure patients with diabetes mellitus: a comparison of DPP4 inhibitors in a nationwide electric health database of the superaged society. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022; 21:157.
Article30. Htoo PT, Tesfaye H, Schneeweiss S, Wexler DJ, Everett BM, Glynn RJ, et al. Comparative effectiveness of empagliflozin vs liraglutide or sitagliptin in older adults with diverse patient characteristics. JAMA Netw Open. 2022; 5:e2237606.
Article31. Dawwas GK, Smith SM, Park H. Cardiovascular outcomes of sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019; 21:28–36.
Article32. Yang CT, Peng ZY, Chen YC, Ou HT, Kuo S. Cardiovascular benefits with favorable renal, amputation and hypoglycemic outcomes of SGLT-2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes from the Asian perspective: a population-based cohort study and systematic review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022; 13:836365.
Article33. Gautam S, Agiro A, Barron J, Power T, Weisman H, White J. Heart failure hospitalization risk associated with use of two classes of oral antidiabetic medications: an observational, realworld analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017; 16:93.
Article34. Pasternak B, Ueda P, Eliasson B, Svensson AM, Franzen S, Gudbjornsdottir S, et al. Use of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and risk of major cardiovascular events and heart failure: Scandinavian register based cohort study. BMJ. 2019; 366:l4772.
Article35. Han SJ, Ha KH, Lee N, Kim DJ. Effectiveness and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors compared with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in older adults with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide population-based study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021; 23:682–91.
Article36. Aldafas R, Crabtree T, Alkharaiji M, Vinogradova Y, Idris I. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2) in frail or older people with type 2 diabetes and heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing. 2024; 53:afad254.
Article37. Liu Y, An C, Liu P, Yang F, Zhao Q. Comparative safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ren Fail. 2023; 45:2217287.
Article38. Kaze AD, Zhuo M, Kim SC, Patorno E, Paik JM. Association of SGLT2 inhibitors with cardiovascular, kidney, and safety outcomes among patients with diabetic kidney disease: a meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022; 21:47.
Article39. McGuire DK, Shih WJ, Cosentino F, Charbonnel B, Cherney DZ, Dagogo-Jack S, et al. Association of SGLT2 inhibitors with cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. JAMA Cardiol. 2021; 6:148–58.
Article40. Koh ES, Han K, Nam YS, Wittbrodt ET, Fenici P, Kosiborod MN, et al. Renal outcomes and all-cause death associated with sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors versus other glucose-lowering drugs (CVD-REAL 3 Korea). Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021; 23:455–66.41. Nagasu H, Yano Y, Kanegae H, Heerspink HJL, Nangaku M, Hirakawa Y, et al. Kidney outcomes associated with SGLT2 inhibitors versus other glucose-lowering drugs in real-world clinical practice: the Japan Chronic Kidney Disease Database. Diabetes Care. 2021; 44:2542–51.
Article42. Pasternak B, Wintzell V, Melbye M, Eliasson B, Svensson AM, Franzen S, et al. Use of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors and risk of serious renal events: Scandinavian cohort study. BMJ. 2020; 369:m1186.
Article43. Lui DT, Au IC, Tang EH, Cheung CL, Lee CH, Woo YC, et al. Kidney outcomes associated with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors versus glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: a real-world population-based analysis. EClinicalMedicine. 2022; 50:101510.
Article44. Neuen BL, Young T, Heerspink HJ, Neal B, Perkovic V, Billot L, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for the prevention of kidney failure in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019; 7:845–54.
Article45. Lin DS, Lee JK, Chen WJ. Clinical adverse events associated with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: a meta-analysis involving 10 randomized clinical trials and 71 553 individuals. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021; 106:2133–45.
Article46. Chung MC, Hung PH, Hsiao PJ, Wu LY, Chang CH, Hsiao KY, et al. Sodium-glucose transport protein 2 inhibitor use for type 2 diabetes and the incidence of acute kidney injury in Taiwan. JAMA Netw Open. 2023; 6:e230453.
Article47. Zhuo M, Paik JM, Wexler DJ, Bonventre JV, Kim SC, Patorno E. SGLT2 inhibitors and the risk of acute kidney injury in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Am J Kidney Dis. 2022; 79:858–67.
Article48. Li D, Wang T, Shen S, Fang Z, Dong Y, Tang H. Urinary tract and genital infections in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017; 19:348–55.
Article49. Fioretto P, Mansfield TA, Ptaszynska A, Yavin Y, Johnsson E, Parikh S. Long-term safety of dapagliflozin in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a pooled analysis of phase IIb/III studies. Drugs Aging. 2016; 33:511–22.
Article50. Cahn A, Mosenzon O, Wiviott SD, Rozenberg A, Yanuv I, Goodrich EL, et al. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in the elderly: analysis from the DECLARE-TIMI 58 study. Diabetes Care. 2020; 43:468–75.
Article51. Sinclair AJ, Bode B, Harris S, Vijapurkar U, Shaw W, Desai M, et al. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in individuals aged 75 and older with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a pooled analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2016; 64:543–52.
Article52. Pratley R, Dagogo-Jack S, Charbonnel B, Patel S, Hickman A, Liu J, et al. Efficacy and safety of ertugliflozin in older patients with type 2 diabetes: a pooled analysis of phase III studies. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020; 22:2276–86.53. Kinduryte Schorling O, Clark D, Zwiener I, Kaspers S, Lee J, Iliev H. Pooled safety and tolerability analysis of empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Adv Ther. 2020; 37:3463–84.
Article54. Ueda P, Svanstrom H, Melbye M, Eliasson B, Svensson AM, Franzen S, et al. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and risk of serious adverse events: nationwide register based cohort study. BMJ. 2018; 363:k4365.
Article55. Matthews DR, Li Q, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, et al. Effects of canagliflozin on amputation risk in type 2 diabetes: the CANVAS Program. Diabetologia. 2019; 62:926–38.
Article56. Zhou Z, Jardine M, Perkovic V, Matthews DR, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, et al. Canagliflozin and fracture risk in individuals with type 2 diabetes: results from the CANVAS Program. Diabetologia. 2019; 62:1854–67.
Article57. Ha KH, Kim DJ, Choi YJ. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors do not increase the risk of fractures in real-world clinical practice in Korea: a national observational cohort study. J Diabetes Investig. 2022; 13:986–96.58. Ha KH, Kim DJ. Effectiveness and safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in Asian populations. J Diabetes Investig. 2024; 15:285–7.59. Afsar B, Afsar RE. Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors and Sarcopenia: a controversy that must be solved. Clin Nutr. 2023; 42:2338–52.60. Zhang S, Qi Z, Wang Y, Song D, Zhu D. Effect of sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors on sarcopenia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023; 14:1203666.
Article61. Yabe D, Shiki K, Suzaki K, Meinicke T, Kotobuki Y, Nishida K, et al. Rationale and design of the EMPA-ELDERLY trial: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 52-week clinical trial of the efficacy and safety of the sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor empagliflozin in elderly Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. BMJ Open. 2021; 11:e045844.
Article62. Al-Hindi B, Mohammed MA, Mangantig E, Martini ND. Prevalence of sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitor-associated diabetic ketoacidosis in real-world data: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2024; 64:9–26.
Article63. Morace C, Lorello G, Bellone F, Quartarone C, Ruggeri D, Giandalia A, et al. Ketoacidosis and SGLT2 inhibitors: a narrative review. Metabolites. 2024; 14:264.
Article64. Tang H, Li D, Wang T, Zhai S, Song Y. Effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on diabetic ketoacidosis among patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Care. 2016; 39:e123–4.
Article65. Colacci M, Fralick J, Odutayo A, Fralick M. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and risk of diabetic ketoacidosis among adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Can J Diabetes. 2022; 46:10–5.
Article66. Rigato M, Fadini GP, Avogaro A. Safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023; 25:2963–9.
Article67. Sacks DB, Arnold M, Bakris GL, Bruns DE, Horvath AR, Lernmark A, et al. Guidelines and recommendations for laboratory analysis in the diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2023; 46:e151–99.
Article68. Choi JH, Lee KA, Moon JH, Chon S, Kim DJ, Kim HJ, et al. 2023 Clinical practice guidelines for diabetes mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J. 2023; 47:575–94.
Article69. Davies MJ, Aroda VR, Collins BS, Gabbay RA, Green J, Maruthur NM, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. a consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2022; 45:2753–86.
Article70. Zhang Y, He Y, Liu S, Deng L, Zuo Y, Huang K, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors in aging-related cardiovascular disease: a review of potential mechanisms. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2023; 23:641–62.
Article71. Evans M, Morgan AR, Davies S, Beba H, Strain WD. The role of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors in frail older adults with or without type 2 diabetes mellitus. Age Ageing. 2022; 51:afac201.
Article72. Chen K, Nie Z, Shi R, Yu D, Wang Q, Shao F, et al. Time to benefit of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors among patients with heart failure. JAMA Netw Open. 2023; 6:e2330754.
Article73. Lee DH, Oh JH, Jeon HJ, Oh TK. The efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors in real-world clinical practice: potential cautionary use in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D). Diabetes Ther. 2024; 15:1615–26.
Article74. Gudemann LM, Young KG, Thomas NJ, Hopkins R, Challen R, Jones AG, et al. Safety and effectiveness of SGLT2 inhibitors in a UK population with type 2 diabetes and aged over 70 years: an instrumental variable approach. Diabetologia. 2024; Jun. 5. [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-024-06190-9.
Article75. Scheen AJ, Bonnet F. Efficacy and safety profile of SGLT2 inhibitors in the elderly: how is the benefit/risk balance? Diabetes Metab. 2023; 49:101419.
Article76. Fralick M, Colacci M, Thiruchelvam D, Gomes T, Redelmeier DA. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors versus dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and the risk of heart failure: a nationwide cohort study of older adults with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2021; 23:950–60.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Response: Predictors of the Therapeutic Efficacy and Consideration of the Best Combination Therapy of Sodium-Glucose Co-transporter 2 Inhibitors (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:158–73)
- Letter: Predictors of the Therapeutic Efficacy and Consideration of the Best Combination Therapy of Sodium-Glucose Co-transporter 2 Inhibitors (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:158–73)
- Emerging Safety Issues of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: How to Interpret and Apply in Clinical Practice
- Glucose Lowering Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Review of Clinical Studies
- Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitor