J Yeungnam Med Sci.
2024 Jul;41(3):207-212. 10.12701/jyms.2024.00276.
Enhancing ketamine anesthesia with midazolam and fentanyl for children’s ear surgery: a prospective randomized study
- Affiliations
-
- 1St. Mary's H Pain Clinic, Seongnam, Korea
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, St. Vincent’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2558145
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2024.00276
Abstract
- Background
Myringotomy with tympanostomy tube insertion (MTI) is a superficial surgical procedure used to prevent hearing loss in children with serous otitis media. Intravenous anesthesia, often ketamine, is preferred for this procedure because of its ability to induce sedation without compromising airway reflexes. However, ketamine alone may be insufficient and potentially lead to spontaneous movement during surgery. This study evaluated the effectiveness of midazolam and fentanyl as adjuvants to ketamine in reducing spontaneous movement during MTI and enhancing the quality of recovery.
Methods
This study involved two groups of 30 patients each: one group received intravenous ketamine (1.5 mg/kg) with an equal volume of normal saline (K group), while the other received a combination of midazolam, fentanyl, and ketamine (0.05 mg/kg, 1 μg/kg, and 1.5 mg/kg, respectively; MFK group). We assessed side effects, intraoperative patient movement, surgeon satisfaction, and emergence agitation scores.
Results
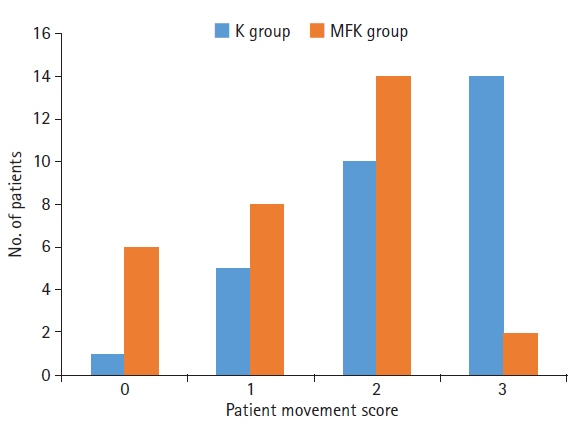
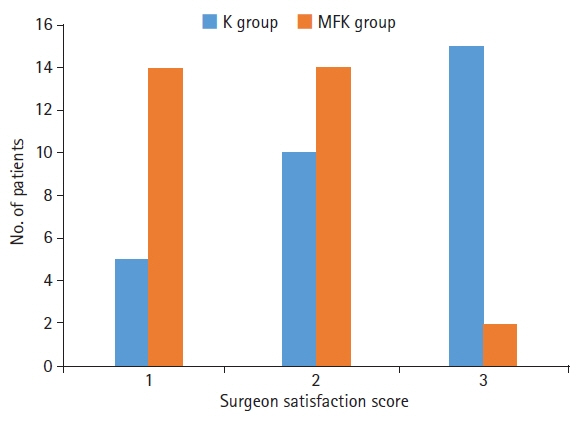
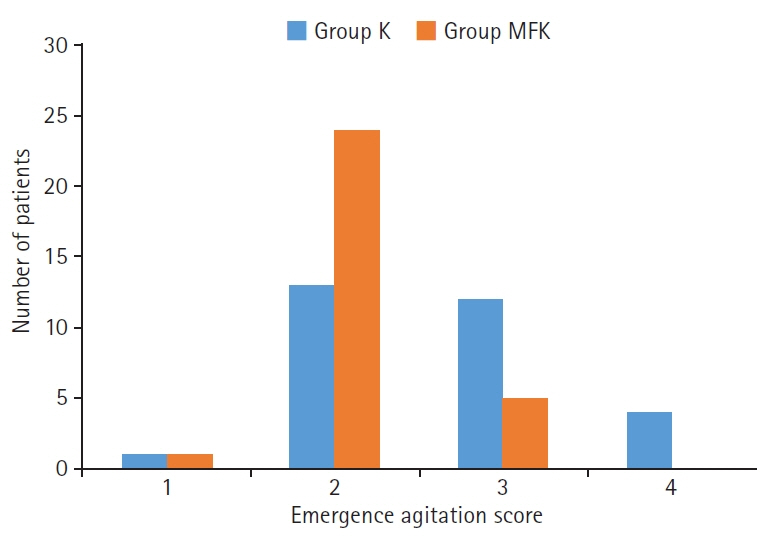
The MFK group exhibited significantly lower scores for patient movement (p<0.01) and emergence agitation (p<0.01) and markedly higher surgeon satisfaction scores (p<0.01) than the K group.
Conclusion
Administering a midazolam-fentanyl-ketamine combination effectively reduced spontaneous movement during surgery and emergence agitation during recovery without prolonging discharge times in children undergoing MTI.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Harmes KM, Blackwood RA, Burrows HL, Cooke JM, Harrison RV, Passamani PP. Otitis media: diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2013; 88:435–40.2. Al-Hussaini A, Owens D, Tomkinson A. Have two UK national guidelines had any effect on grommets day-case utilisation and rate over the last 10 years? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; 269:2053–6.3. Butterworth JF, Mackey DC, Wasnick JD. Morgan & Mikhail’s clinical anesthesiology. 5th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;2013.4. Gilger MA, Spearman RS, Dietrich CL, Spearman G, Wilsey MJ, Zayat MN. Safety and effectiveness of ketamine as a sedative agent for pediatric GI endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 59:659–63.5. Green SM, Johnson NE. Ketamine sedation for pediatric procedures: part 2, review and implications. Ann Emerg Med. 1990; 19:1033–46.6. Sussman DR. A comparative evaluation of ketamine anesthesia in children and adults. Anesthesiology. 1974; 40:459–64.7. Dalsasso M, Tresin P, Innocente F, Veronese S, Ori C. Low-dose ketamine with clonidine and midazolam for adult day care surgery. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2005; 22:67–8.8. Tobias JD. Dexmedetomidine: applications in pediatric critical care and pediatric anesthesiology. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2007; 8:115–31.9. Viitanen H, Annila P, Viitanen M, Tarkkila P. Premedication with midazolam delays recovery after ambulatory sevoflurane anesthesia in children. Anesth Analg. 1999; 89:75–9.10. Momeni M, Crucitti M, De Kock M. Patient-controlled analgesia in the management of postoperative pain. Drugs. 2006; 66:2321–37.11. Grass JA. Patient-controlled analgesia. Anesth Analg. 2005; 101(5 Suppl):S44–61.12. Lee YK, Kim H. Clinial analysis of outpatient anesthesia in children with middle ear ventilation tube insertion. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2005; 49:183–7.13. Aldrete JA, Kroulik D. A postanesthetic recovery score. Anesth Analg. 1970; 49:924–34.14. Green SM, Roback MG, Kennedy RM, Krauss B. Clinical practice guideline for emergency department ketamine dissociative sedation: 2011 update. Ann Emerg Med. 2011; 57:449–61.15. Davis PJ, Greenberg JA, Gendelman M, Fertal K. Recovery characteristics of sevoflurane and halothane in preschool-aged children undergoing bilateral myringotomy and pressure equalization tube insertion. Anesth Analg. 1999; 88:34–8.16. Knox JW, Bovill JG, Clarke RS, Dundee JW. Clinical studies of induction agents. XXXVI: ketamine. Br J Anaesth. 1970; 42:875–85.17. Green SM, Nakamura R, Johnson NE. Ketamine sedation for pediatric procedures: part 1, a prospective series. Ann Emerg Med. 1990; 19:1024–32.18. Holloway VJ, Husain HM, Saetta JP, Gautam V. Accident and emergency department led implementation of ketamine sedation in paediatric practice and parental response. J Accid Emerg Med. 2000; 17:25–8.19. Lauven PM. Pharmacology of drugs for conscious sedation. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1990; 179:1–6.20. Krauss B, Green SM. Sedation and analgesia for procedures in children. N Engl J Med. 2000; 342:938–45.21. Gloor A, Dillier C, Gerber A. Ketamine for short ambulatory procedures in children: an audit. Paediatr Anaesth. 2001; 11:533–9.22. Reich DL, Silvay G. Ketamine: an update on the first twenty-five years of clinical experience. Can J Anaesth. 1989; 36:186–97.23. White PF, Ham J, Way WL, Trevor AJ. Pharmacology of ketamine isomers in surgical patients. Anesthesiology. 1980; 52:231–9.24. Somaini M, Engelhardt T, Fumagalli R, Ingelmo PM. Emergence delirium or pain after anaesthesia: how to distinguish between the two in young children. A retrospective analysis of observational studies. Br J Anaesth. 2016; 116:377–83.25. Green SM, Rothrock SG, Harris T, Hopkins GA, Garrett W, Sherwin T. Intravenous ketamine for pediatric sedation in the emergency department: safety profile with 156 cases. Acad Emerg Med. 1998; 5:971–6.26. Sener S, Eken C, Schultz CH, Serinken M, Ozsarac M. Ketamine with and without midazolam for emergency department sedation in adults: a randomized controlled trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2011; 57:109–14.27. Sherwin TS, Green SM, Khan A, Chapman DS, Dannenberg B. Does adjunctive midazolam reduce recovery agitation after ketamine sedation for pediatric procedures? A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2000; 35:229–38.28. Finkel JC, Cohen IT, Hannallah RS, Patel KM, Kim MS, Hummer KA, et al. The effect of intranasal fentanyl on the emergence characteristics after sevoflurane anesthesia in children undergoing surgery for bilateral myringotomy tube placement. Anesth Analg. 2001; 92:1164–8.29. Cohen IT, Hannallah RS, Hummer KA. The incidence of emergence agitation associated with desflurane anesthesia in children is reduced by fentanyl. Anesth Analg. 2001; 93:88–91.30. Green SM, Kuppermann N, Rothrock SG, Hummel CB, Ho M. Predictors of adverse events with intramuscular ketamine sedation in children. Ann Emerg Med. 2000; 35:35–42.31. Short B, Fong J, Galvez V, Shelker W, Loo CK. Side-effects associated with ketamine use in depression: a systematic review. Lancet Psychiatry. 2018; 5:65–78.32. Cvrcek P. Side effects of ketamine in the long-term treatment of neuropathic pain. Pain Med. 2008; 9:253–7.33. Lonjaret L, Bataille B, Gris C, Fourcade O, Minville V. Ketamine and postoperative nausea and vomiting: role of the morphine-sparing effect. J Clin Anesth. 2012; 24:601–2.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of fentanyl and midazolam on emergence agitation following ketamine anesthesia in children
- Effect of supplemental intravenous anesthesia in plastic surgery under local anesthesia
- Influence of Ketamine and Midazolam on the Analgesic Effect of Epidural Bupivacaine and Fentanyl after Low Abdominal Surgery
- Low-dose Ketamine or Fentanyl as Analgesic Adjuvants for Intravenous Anesthesia with Propofol
- The Effect of Fentayl and Midazolam on the Incidence of Emergence Agitation in Children Following Sevoflurane Anesthesia for Tonsillectomy