J Yeungnam Med Sci.
2024 Jul;41(3):179-187. 10.12701/jyms.2024.00416.
Ultrasound imaging and guidance in the management of myofascial pain syndrome: a narrative review
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, National Taiwan University Hospital, Bei-Hu Branch, Taipei, Taiwan
- 2Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, National Taiwan University College of Medicine, Taipei, Taiwan
- 3Center for Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, Wang-Fang Hospital, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan
- 4Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine Unit, Luigi Sacco University Hospital, ASST Fatebenefratelli-Sacco, Milan, Italy
- 5Department of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, Hacettepe University Medical School, Ankara, Turkey
- KMID: 2558142
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/jyms.2024.00416
Abstract
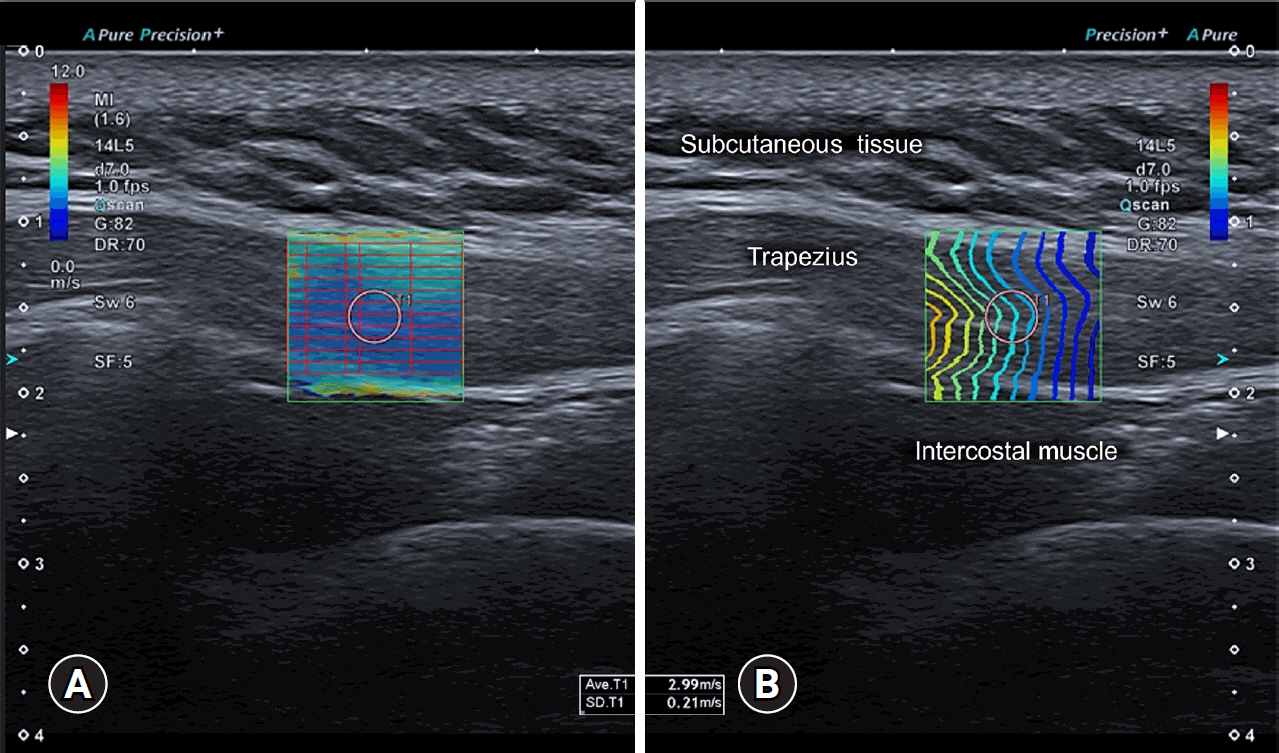
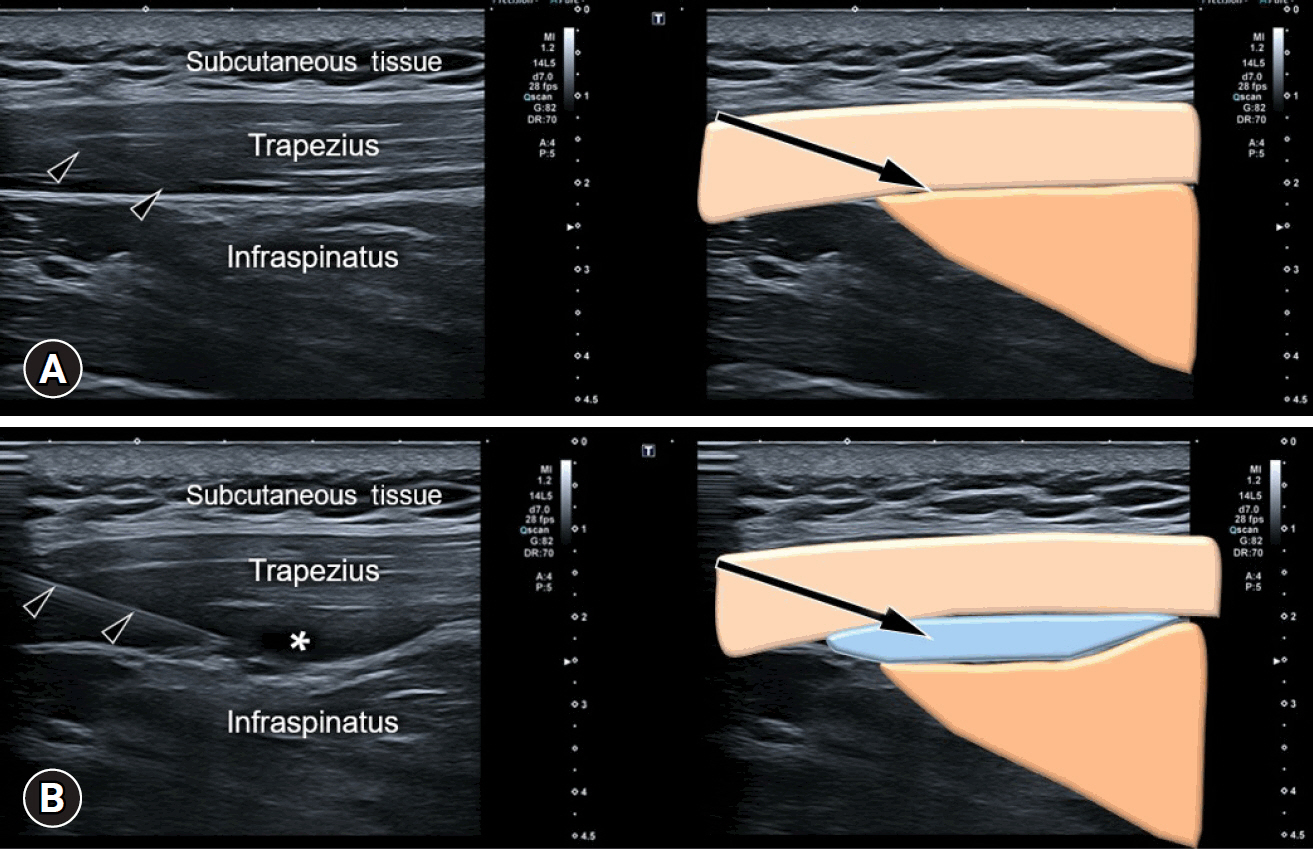
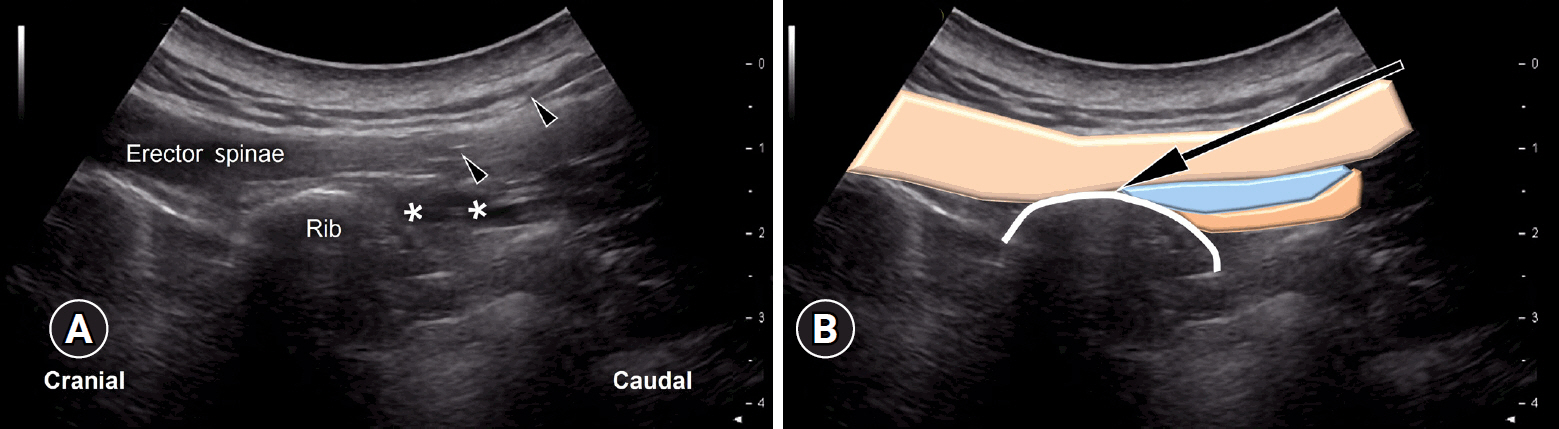
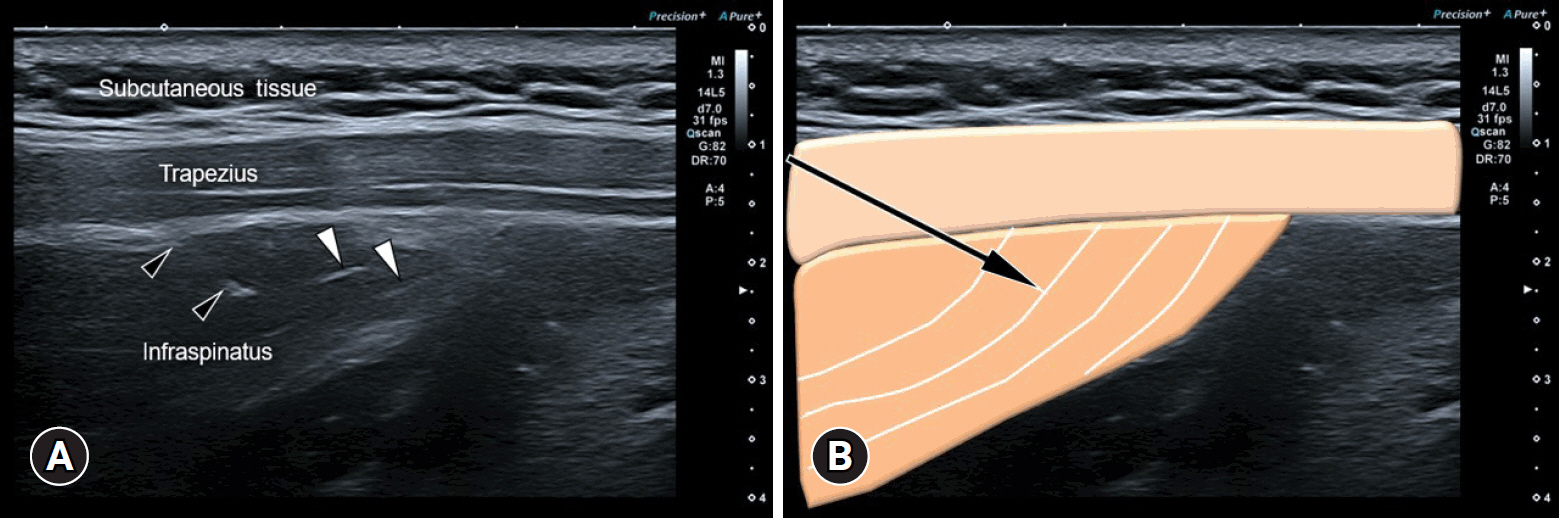
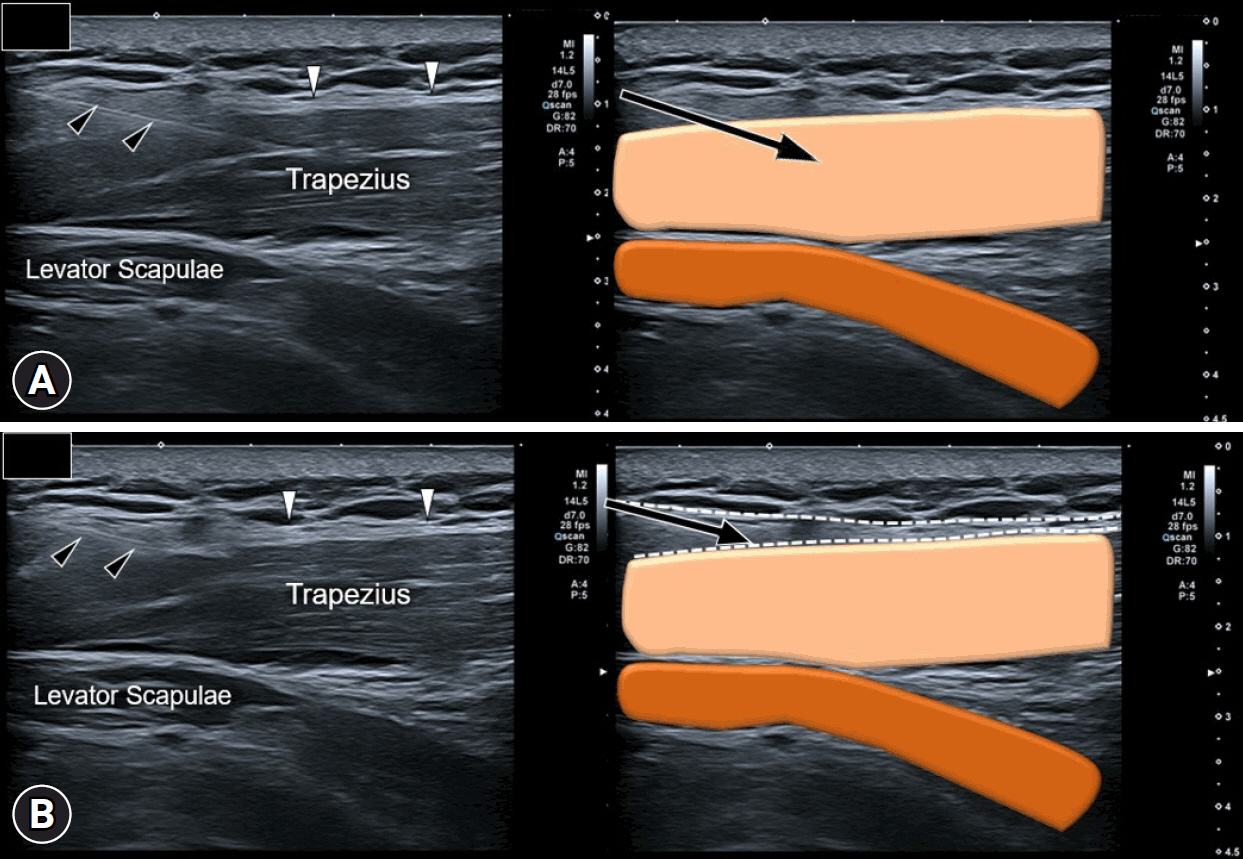
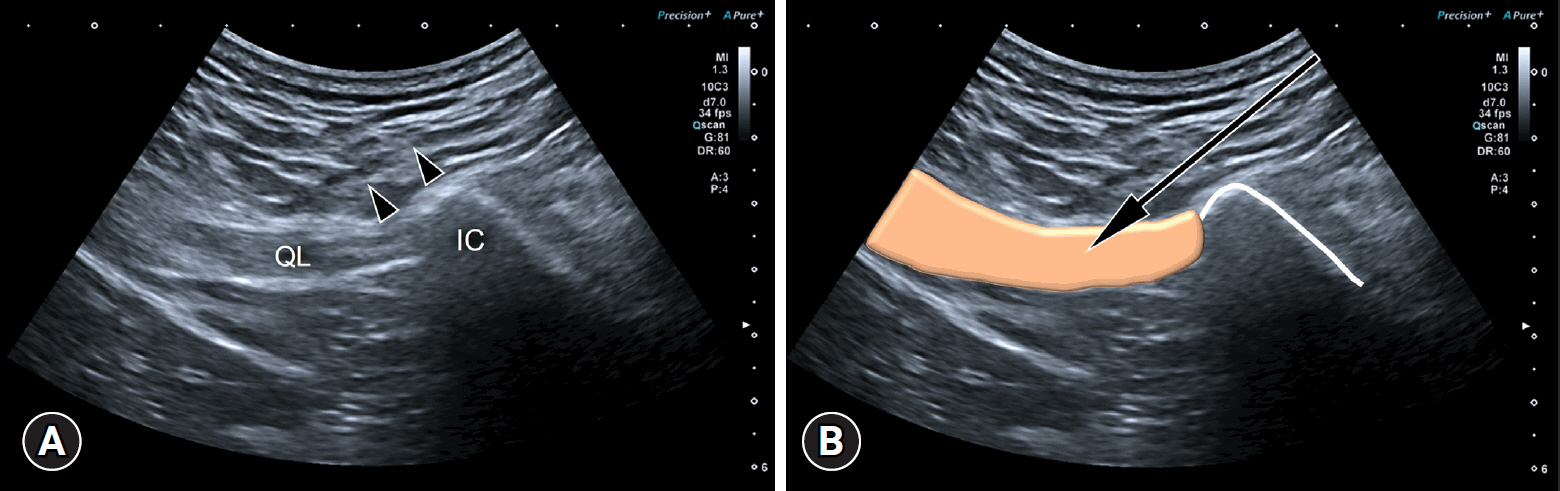
- Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) is a common musculoskeletal disorder characterized by muscle pain, tenderness, and trigger points. Ultrasonography has emerged as a key tool for diagnosing and treating MPS owing to its ability to provide precise, minimally invasive guidance. This review discusses the use of ultrasonography in various approaches to evaluate and manage MPS. Studies have shown that shear-wave sonoelastography can effectively assess muscle elasticity and offer insights into trapezius stiffness in patients with MPS. Ultrasound-guided interfascial hydrodissection, especially with visual feedback, has demonstrated effectiveness in treating trapezius MPS. Similarly, ultrasound-guided rhomboid interfascial plane blocks and perimysium dissection for posterior shoulder MPS have significantly reduced pain and improved quality of life. The combination of extracorporeal shockwave therapy with ultrasound-guided lidocaine injections has been particularly successful in reducing pain and stiffness in trapezius MPS. Research regarding various guided injections, including dry needling, interfascial plane blocks, and fascial hydrodissection, emphasizes the importance of ultrasonography for accuracy and safety. Additionally, ultrasound-guided delivery of local anesthetics and steroids to the quadratus lumborum muscle has shown lasting pain relief over a 6-month period. Overall, these findings highlight the pivotal role of ultrasonography in the assessment and treatment of MPS.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Tantanatip A, Chang KV. Myofascial pain syndrome. Updated 2023 Jul 4. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing;2024. [cited 2024 May 1]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499882/.2. Fleckenstein J, Zaps D, Rüger LJ, Lehmeyer L, Freiberg F, Lang PM, et al. Discrepancy between prevalence and perceived effectiveness of treatment methods in myofascial pain syndrome: results of a cross-sectional, nationwide survey. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010; 11:32.3. Shah JP, Danoff JV, Desai MJ, Parikh S, Nakamura LY, Phillips TM, et al. Biochemicals associated with pain and inflammation are elevated in sites near to and remote from active myofascial trigger points. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008; 89:16–23.4. Rubin D. Myofascial trigger point syndromes: an approach to management. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1981; 62:107–10.5. Hao CJ, Kang XY, Kang CS, Li TT, Huo JZ, Xu Q, et al. Upper trapezius muscle elasticity in cervical myofascial pain syndrome measured using real-time ultrasound shear-wave elastography. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023; 13:5168–81.6. Hung CY, Wang B, Chang HC, Wu WT, Liu PT, Chang KV, et al. Pictorial essay on ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging of paraspinal muscles for myofascial pain syndrome. Life (Basel). 2024; 14:499.7. Ricci V, Mezian K, Chang KV, Tarantino D, Güvener O, Gervasoni F, et al. Ultrasound imaging and guidance for cervical myofascial pain: a narrative review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023; 20:3838.8. Suarez-Ramos C, Gonzalez-Suarez C, Gomez IN, Gonzalez MK, Co PH, Llamas JA. Effectiveness of ultrasound guided interfascial hydrodissection with the use of saline anesthetic solution for myofascial pain syndrome of the upper trapezius: a single blind randomized controlled trial. Front Rehabil Sci. 2023; 4:1281813.9. Hasuo H, Oomori H, Yoshida K, Fukunaga M. Effect of visual feedback during ultrasound-guided hydrodissection for myofascial pain syndrome: an exploratory, prospective, observational clinical trial on the expectations for treatment. Front Psychiatry. 2022; 13:794425.10. Ozyemisci Taskiran O, Albayrak H, Topaloglu M, Manici M, Ketenci A, Gurkan Y. Effect of ultrasound-guided rhomboid interfascial plane block on pain severity, disability, and quality of life in myofascial pain syndrome: a case series with one-year follow-up. Pain Physician. 2023; 26:E815–22.11. Lai YC, Tsai SH, Chiou HJ. Ultrasound-guided dextrose solution perimysium dissection for posterior shoulder myofascial pain. J Chin Med Assoc. 2021; 84:650–4.12. Anwar N, Li S, Long L, Zhou L, Fan M, Zhou Y, et al. Combined effectiveness of extracorporeal radial shockwave therapy and ultrasound-guided trigger point injection of lidocaine in upper trapezius myofascial pain syndrome. Am J Transl Res. 2022; 14:182–96.13. Chang KV, Lin CP, Lin CS, Wu WT, Karmakar MK, Özçakar L. Sonographic tracking of trunk nerves: essential for ultrasound-guided pain management and research. J Pain Res. 2017; 10:79–88.14. Barreto Silva A, Malheiro N, Oliveira B, Pereira D, Antunes F, Borges J, et al. Efficacy of ultrasound-guided infiltration with levobupivacaine and triamcinolone for myofascial pain syndrome of the quadratus lumborum: a retrospective observational study. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2023; 73:718–24.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound Guided Thoracic Paravertebral Space Block for Chronic Intractable Upper Back Pain
- Botulinum Toxin-Type A in Cervical Myofascial Pain Syndrome: A report of 3 cases
- Treatment Experience of Pulsed Radiofrequency Under Ultrasound Guided to the Trapezius Muscle at Myofascial Pain Syndrome: A Case Report
- Fibromyalgia Syndrome
- Psychological Investigation in Myofascial Pain Syndrome Patients