Diabetes Metab J.
2024 Jul;48(4):531-545. 10.4093/dmj.2024.0310.
Holistic and Personalized Strategies for Managing in Elderly Type 2 Diabetes Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Statistics and Actuarial Science, Soongsil University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2558035
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2024.0310
Abstract
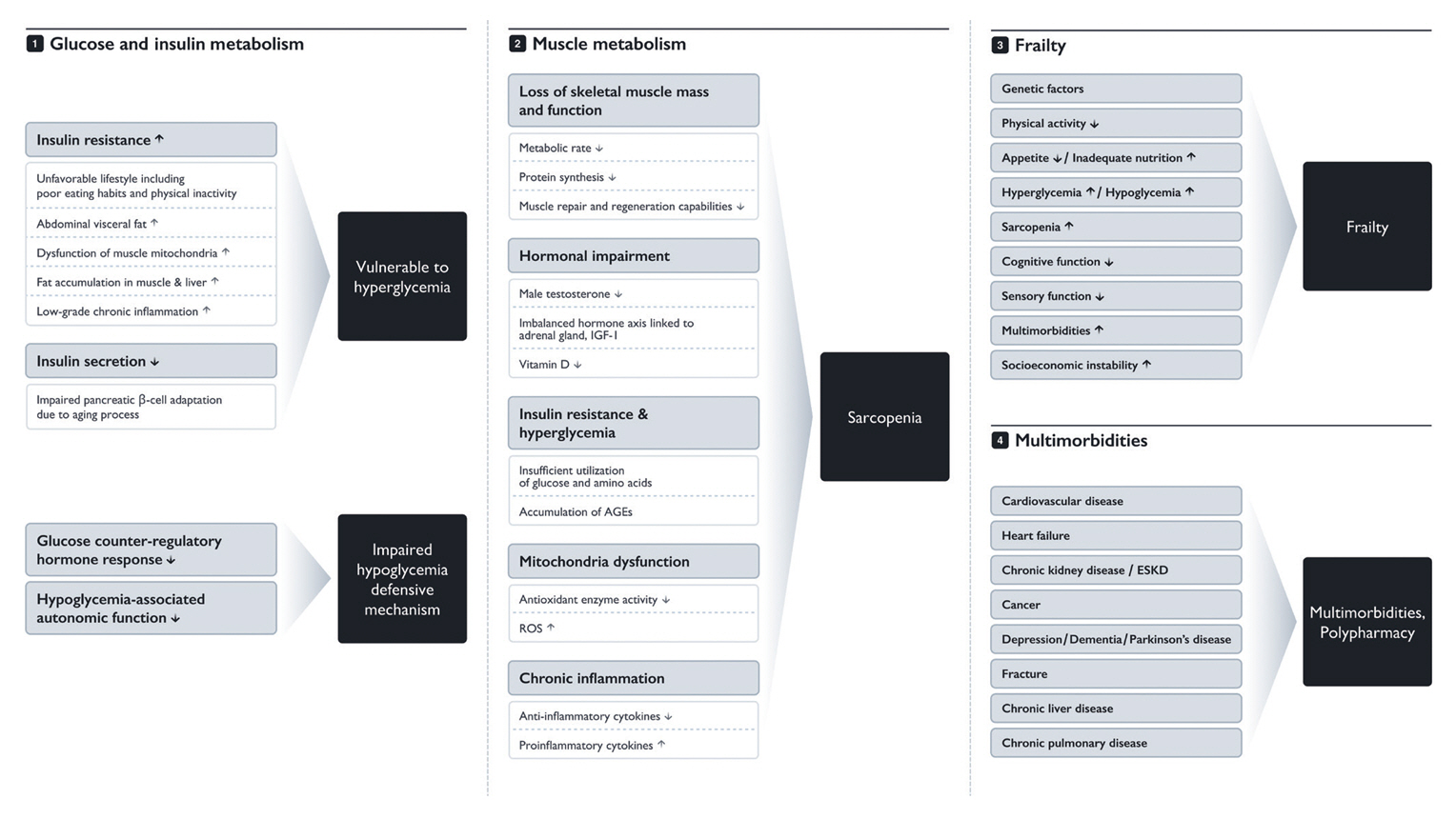
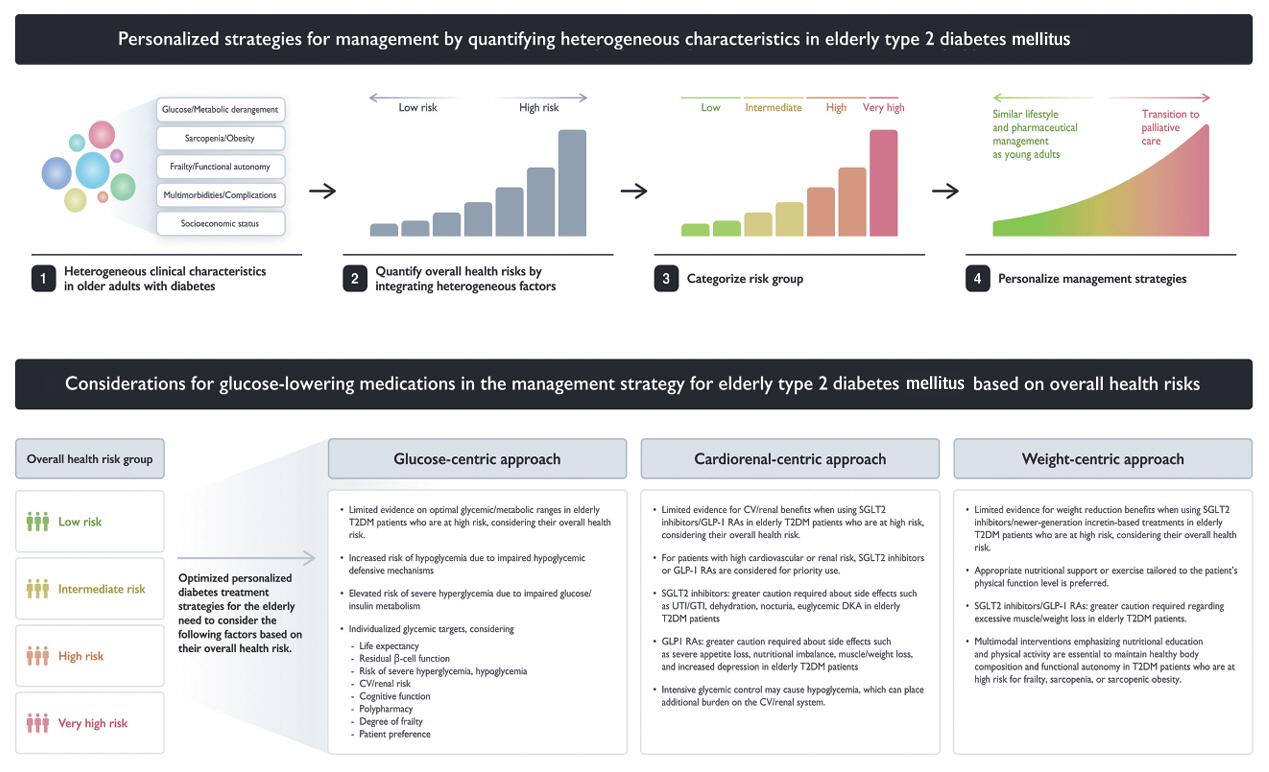
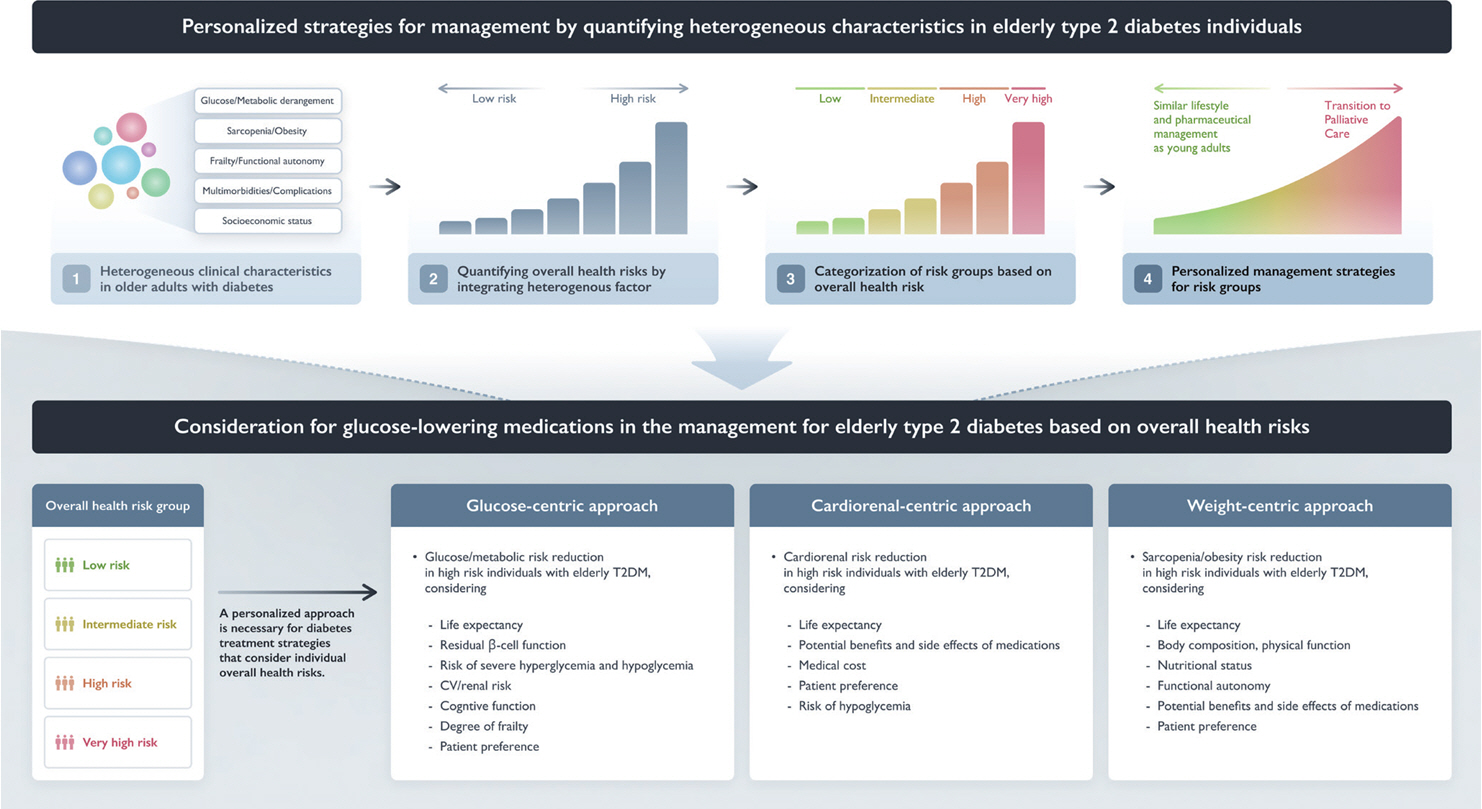
- Due to increased life expectancy and lifestyle changes, the prevalence of diabetes among the elderly in Korea is continuously rising, as is the associated public health burden. Diabetes management in elderly patients is complicated by age-related physiological changes, sarcopenia characterized by loss of muscle mass and function, comorbidities, and varying levels of functional, cognitive, and mobility abilities that lead to frailty. Moreover, elderly patients with diabetes frequently face multiple chronic conditions that elevate their risk of cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and mortality; they are also prone to complications such as hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state, diabetic ketoacidosis, and severe hypoglycemia. This review examines the characteristics of and management approaches for diabetes in the elderly, and advocates for a comprehensive yet personalized strategy.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea 2024
Se Eun Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ji Yoon Kim, Kyuho Kim, Joon Ho Moon, Nam Hoon Kim, Kyung Do Han, Sung Hee Choi, Bong Soo Cha
Diabetes Metab J. 2025;49(1):24-33. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0818.Older Adults with Diabetes in Korea: Latest Clinical and Epidemiologic Trends
Kyuho Kim, Bongseong Kim, Kyuna Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko, Sung Hee Choi, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Diabetes Metab J. 2025;49(2):183-193. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0836.
Reference
-
1. Kontis V, Bennett JE, Mathers CD, Li G, Foreman K, Ezzati M. Future life expectancy in 35 industrialised countries: projections with a Bayesian model ensemble. Lancet. 2017; 389:1323–35.
Article2. Statistics Korea. 2024 Statistics Korea. Available from: http://kostat.go.kr (cited 2024 Jul 11).3. GBD 2019 viewpoint collaborators. Five insights from the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet. 2020; 396:1135–59.4. Bae JH, Han KD, Ko SH, Yang YS, Choi JH, Choi KM, et al. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea 2021. Diabetes Metab J. 2022; 46:417–26.
Article5. Jeong SM, Jung JH, Yang YS, Kim W, Cho IY, Lee YB, et al. 2023 Obesity fact sheet: prevalence of obesity and abdominal obesity in adults, adolescents, and children in Korea from 2012 to 2021. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2024; 33:27–35.
Article6. Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018; 138:271–81.
Article7. Bellary S, Kyrou I, Brown JE, Bailey CJ. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in older adults: clinical considerations and management. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021; 17:534–48.8. Miklavcic JJ, Fraser KD, Ploeg J, Markle-Reid M, Fisher K, Gafni A, et al. Effectiveness of a community program for older adults with type 2 diabetes and multimorbidity: a pragmatic randomized controlled trial. BMC Geriatr. 2020; 20:174.
Article9. Huang ES, Laiteerapong N, Liu JY, John PM, Moffet HH, Karter AJ. Rates of complications and mortality in older patients with diabetes mellitus: the diabetes and aging study. JAMA Intern Med. 2014; 174:251–8.
Article10. Sebastian MJ, Khan SK, Pappachan JM, Jeeyavudeen MS. Diabetes and cognitive function: an evidence-based current perspective. World J Diabetes. 2023; 14:92–109.
Article11. Batsis JA, Villareal DT. Sarcopenic obesity in older adults: aetiology, epidemiology and treatment strategies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018; 14:513–37.
Article12. Remelli F, Ceresini MG, Trevisan C, Noale M, Volpato S. Prevalence and impact of polypharmacy in older patients with type 2 diabetes. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022; 34:1969–83.13. Basu R, Breda E, Oberg AL, Powell CC, Dalla Man C, Basu A, et al. Mechanisms of the age-associated deterioration in glucose tolerance: contribution of alterations in insulin secretion, action, and clearance. Diabetes. 2003; 52:1738–48.14. Meneilly GS, Elahi D. Metabolic alterations in middle-aged and elderly lean patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:1498–9.
Article15. Kanaya AM, Harris T, Goodpaster BH, Tylavsky F, Cummings SR; Health, Aging, and Body Composition (ABC) Study. Adipocytokines attenuate the association between visceral adiposity and diabetes in older adults. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:1375–80.
Article16. Ferriolli E, Pessanha FP, Marchesi JC. Diabetes and exercise in the elderly. Med Sport Sci. 2014; 60:122–9.
Article17. Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature. 2006; 444:860–7.18. Matyka K, Evans M, Lomas J, Cranston I, Macdonald I, Amiel SA. Altered hierarchy of protective responses against severe hypoglycemia in normal aging in healthy men. Diabetes Care. 1997; 20:135–41.
Article19. Hope SV, Taylor PJ, Shields BM, Hattersley AT, Hamilton W. Are we missing hypoglycaemia?: elderly patients with insulin-treated diabetes present to primary care frequently with nonspecific symptoms associated with hypoglycaemia. Prim Care Diabetes. 2018; 12:139–46.
Article20. Vellas B, Fielding R, Bhasin S, Cerreta F, Goodpaster B, Guralnik JM, et al. Sarcopenia trials in specific diseases: report by the International Conference on Frailty and Sarcopenia Research Task Force. J Frailty Aging. 2016; 5:194–200.
Article21. Kalyani RR, Corriere M, Ferrucci L. Age-related and disease-related muscle loss: the effect of diabetes, obesity, and other diseases. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014; 2:819–29.
Article22. Rolland Y, Czerwinski S, Abellan Van Kan G, Morley JE, Cesari M, Onder G, et al. Sarcopenia: its assessment, etiology, pathogenesis, consequences and future perspectives. J Nutr Health Aging. 2008; 12:433–50.23. Chung SM, Moon JS, Chang MC. Prevalence of sarcopenia and its association with diabetes: a meta-analysis of community-dwelling Asian population. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021; 8:681232.
Article24. Anagnostis P, Gkekas NK, Achilla C, Pananastasiou G, Taouxidou P, Mitsiou M, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with increased risk of sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2020; 107:453–63.
Article25. Sinclair AJ, Rodriguez-Manas L. Diabetes and frailty: two converging conditions? Can J Diabetes. 2016; 40:77–83.
Article26. Wilson D, Jackson T, Sapey E, Lord JM. Frailty and sarcopenia: the potential role of an aged immune system. Ageing Res Rev. 2017; 36:1–10.
Article27. Sanz-Canovas J, Lopez-Sampalo A, Cobos-Palacios L, Ricci M, Hernandez-Negrin H, Mancebo-Sevilla JJ, et al. Management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in elderly patients with frailty and/or sarcopenia. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022; 19:8677.28. Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman AB, Hirsch C, Gottdiener J, et al. Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001; 56:M146–56.
Article29. Ida S, Kaneko R, Imataka K, Murata K. Relationship between frailty and mortality, hospitalization, and cardiovascular diseases in diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019; 18:81.30. Nishikawa H, Fukunishi S, Asai A, Yokohama K, Ohama H, Nishiguchi S, et al. Sarcopenia, frailty and type 2 diabetes mellitus (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2021; 24:854.31. Hopman P, de Bruin SR, Forjaz MJ, Rodriguez-Blazquez C, Tonnara G, Lemmens LC, et al. Effectiveness of comprehensive care programs for patients with multiple chronic conditions or frailty: a systematic literature review. Health Policy. 2016; 120:818–32.
Article32. Hoogendijk EO. How effective is integrated care for community-dwelling frail older people?: the case of the Netherlands. Age Ageing. 2016; 45:585–8.33. Bernabei R, Landi F, Calvani R, Cesari M, Del Signore S, Anker SD, et al. Multicomponent intervention to prevent mobility disability in frail older adults: randomised controlled trial (SPRINTT project). BMJ. 2022; 377:e068788.
Article34. Melis R, Marengoni A, Angleman S, Fratiglioni L. Incidence and predictors of multimorbidity in the elderly: a populationbased longitudinal study. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e103120.
Article35. Wolff JL, Starfield B, Anderson G. Prevalence, expenditures, and complications of multiple chronic conditions in the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 2002; 162:2269–76.
Article36. Mazziotti G, Gazzaruso C, Giustina A. Diabetes in Cushing syndrome: basic and clinical aspects. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 22:499–506.
Article37. Fried LP, Bandeen-Roche K, Kasper JD, Guralnik JM. Association of comorbidity with disability in older women: the Women’s Health and Aging Study. J Clin Epidemiol. 1999; 52:27–37.38. Magnan EM, Palta M, Mahoney JE, Pandhi N, Bolt DM, Fink J, et al. The relationship of individual comorbid chronic conditions to diabetes care quality. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2015; 3:e000080.
Article39. Griffith KN, Prentice JC, Mohr DC, Conlin PR. Predicting 5- and 10-year mortality risk in older adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2020; 43:1724–31.
Article40. Yun JS, Han K, Ko SH. Trends of severe hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes in Korea: a longitudinal nationwide cohort study. J Diabetes Investig. 2022; 13:1438–43.41. Yun JS, Ko SH. Risk factors and adverse outcomes of severe hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab J. 2016; 40:423–32.
Article42. Holstein A, Plaschke A, Egberts EH. Clinical characterisation of severe hypoglycaemia: a prospective population-based study. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2003; 111:364–9.43. Cryer PE. Mechanisms of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure in diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:362–72.
Article44. Yun JS, Ko SH. Avoiding or coping with severe hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. Korean J Intern Med. 2015; 30:6–16.
Article45. Bonora BM, Avogaro A, Fadini GP. Euglycemic ketoacidosis. Curr Diab Rep. 2020; 20:25.
Article46. Ko SH, Han KD, Park YM, Yun JS, Kim K, Bae JH, et al. Diabetes mellitus in the elderly adults in Korea: based on data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019 to 2020. Diabetes Metab J. 2023; 47:643–52.
Article47. Strain WD, Hope SV, Green A, Kar P, Valabhji J, Sinclair AJ. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in older people: a brief statement of key principles of modern day management including the assessment of frailty: a national collaborative stakeholder initiative. Diabet Med. 2018; 35:838–45.48. Sinclair A, Morley JE, Rodriguez-Manas L, Paolisso G, Bayer T, Zeyfang A, et al. Diabetes mellitus in older people: position statement on behalf of the International Association of Gerontology and Geriatrics (IAGG), the European Diabetes Working Party for Older People (EDWPOP), and the International Task Force of Experts in Diabetes. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2012; 13:497–502.
Article49. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 13. Older adults: standards of care in diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care. 2024; 47(Suppl 1):S244–57.50. Korean Diabetes Association. Clinical practice guidelines for diabetes 2023. 8th ed. Seoul: KDA;2023.51. Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, Blonde L, Bloomgarden ZT, Bush MA, et al. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm: 2019 executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2019; 25:69–100.52. LeRoith D, Biessels GJ, Braithwaite SS, Casanueva FF, Draznin B, Halter JB, et al. Treatment of diabetes in older adults: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019; 104:1520–74.
Article53. Bourdel-Marchasson I, Maggi S, Abdelhafiz A, Bellary S, Demurtas J, Forbes A, et al. Essential steps in primary care management of older people with type 2 diabetes: an executive summary on behalf of the European Geriatric Medicine Society (EuGMS) and the European Diabetes Working Party for Older People (EDWPOP) collaboration. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2023; 35:2279–91.
Article54. Araki E, Goto A, Kondo T, Noda M, Noto H, Origasa H, et al. Japanese clinical practice guideline for diabetes 2019. J Diabetes Investig. 2020; 11:1020–76.55. Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee, Meneilly GS, Knip A, Miller DB, Sherifali D, Tessier D, et al. Diabetes in older people. Can J Diabetes. 2018; 42 Suppl 1:S283–95.
Article56. Lee AK, Diaz-Ramirez LG, Boscardin WJ, Smith AK, Lee SJ. A comprehensive prognostic tool for older adults: predicting death, ADL disability, and walking disability simultaneously. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2022; 70:2884–94.57. Deardorff WJ, Barnes DE, Jeon SY, Boscardin WJ, Langa KM, Covinsky KE, et al. Development and external validation of a mortality prediction model for community-dwelling older adults with dementia. JAMA Intern Med. 2022; 182:1161–70.
Article58. Deardorff WJ, Jeon SY, Barnes DE, Boscardin WJ, Langa KM, Covinsky KE, et al. Development and external validation of models to predict need for nursing home level of care in community-dwelling older adults with dementia. JAMA Intern Med. 2024; 184:81–91.
Article59. Karter AJ, Parker MM, Moffet HH, Lipska KJ, Laiteerapong N, Grant RW, et al. Development and validation of the Life Expectancy Estimator for Older Adults with Diabetes (LEAD): the diabetes and aging study. J Gen Intern Med. 2023; 38:2860–9.60. Yun JS, Park YM, Han K, Cha SA, Ahn YB, Ko SH. Severe hypoglycemia and the risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality in type 2 diabetes: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019; 18:103.
Article61. Yun JS, Park YM, Han K, Kim HW, Cha SA, Ahn YB, et al. Severe hypoglycemia and the risk of end stage renal disease in type 2 diabetes. Sci Rep. 2021; 11:4305.
Article62. Karagiannis T, Tsapas A, Athanasiadou E, Avgerinos I, Liakos A, Matthews DR, et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors for older people with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2021; 174:108737.
Article63. Custodio JS Jr, Roriz-Filho J, Cavalcanti CA, Martins A, Salles JE. Use of SGLT2 inhibitors in older adults: scientific evidence and practical aspects. Drugs Aging. 2020; 37:399–409.
Article64. Kim SY, Bang W, Kim MS, Park B, Kim JH, Choi HG. Nocturia is associated with slipping and falling. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e016–9690.65. Handelsman Y, Henry RR, Bloomgarden ZT, Dagogo-Jack S, DeFronzo RA, Einhorn D, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology position statement on the association of SGLT-2 inhibitors and diabetic ketoacidosis. Endocr Pract. 2016; 22:753–62.
Article66. Rigato M, Fadini GP, Avogaro A. Safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023; 25:2963–9.
Article67. Frias JP, Davies MJ, Rosenstock J, Perez Manghi FC, Fernandez Lando L, Bergman BK, et al. Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2021; 385:503–15.
Article68. Wang Y, Wang J, Gong Q, Wu H, Yang S, He J, et al. Efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the elderly versus non-elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: insights from a systematic review. Endocr J. 2024; 71:571–82.
Article69. Lincoff AM, Brown-Frandsen K, Colhoun HM, Deanfield J, Emerson SS, Esbjerg S, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in obesity without diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2023; 389:2221–32.70. Kosiborod MN, Petrie MC, Borlaug BA, Butler J, Davies MJ, Hovingh GK, et al. Semaglutide in patients with obesity-related heart failure and type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2024; 390:1394–407.
Article71. Kiyosue A, Dunn JP, Cui X, Hickey A, Hirase T, Imaoka T, et al. Safety and efficacy analyses across age and body mass index subgroups in East Asian participants with type 2 diabetes in the phase 3 tirzepatide studies (SURPASS programme). Diabetes Obes Metab. 2023; 25:1056–67.72. Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. Obesity fact sheet in Korea 2023. https://www.kosso.or.kr/popup/obesity_fact_sheet.html (cited 2024 Jul 12).73. Linnebjerg H, Kothare PA, Seger M, Wolka AM, Mitchell MI. Exenatide: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety and tolerability in patients ≥ 75 years of age with type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 49:99–108.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Managing high‑risk atrial fibrillation patients with multiple comorbidities
- What is the Most Appropriate Hypoglycemic Agent for Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus?
- Recent Advances in the Treatment of Diabetes in the Elderly
- Care Tips for Self-Care among Older Diabetic Patients
- Microbiome and Diabetes