Ann Lab Med.
2024 Jul;44(4):307-313. 10.3343/alm.2023.0356.
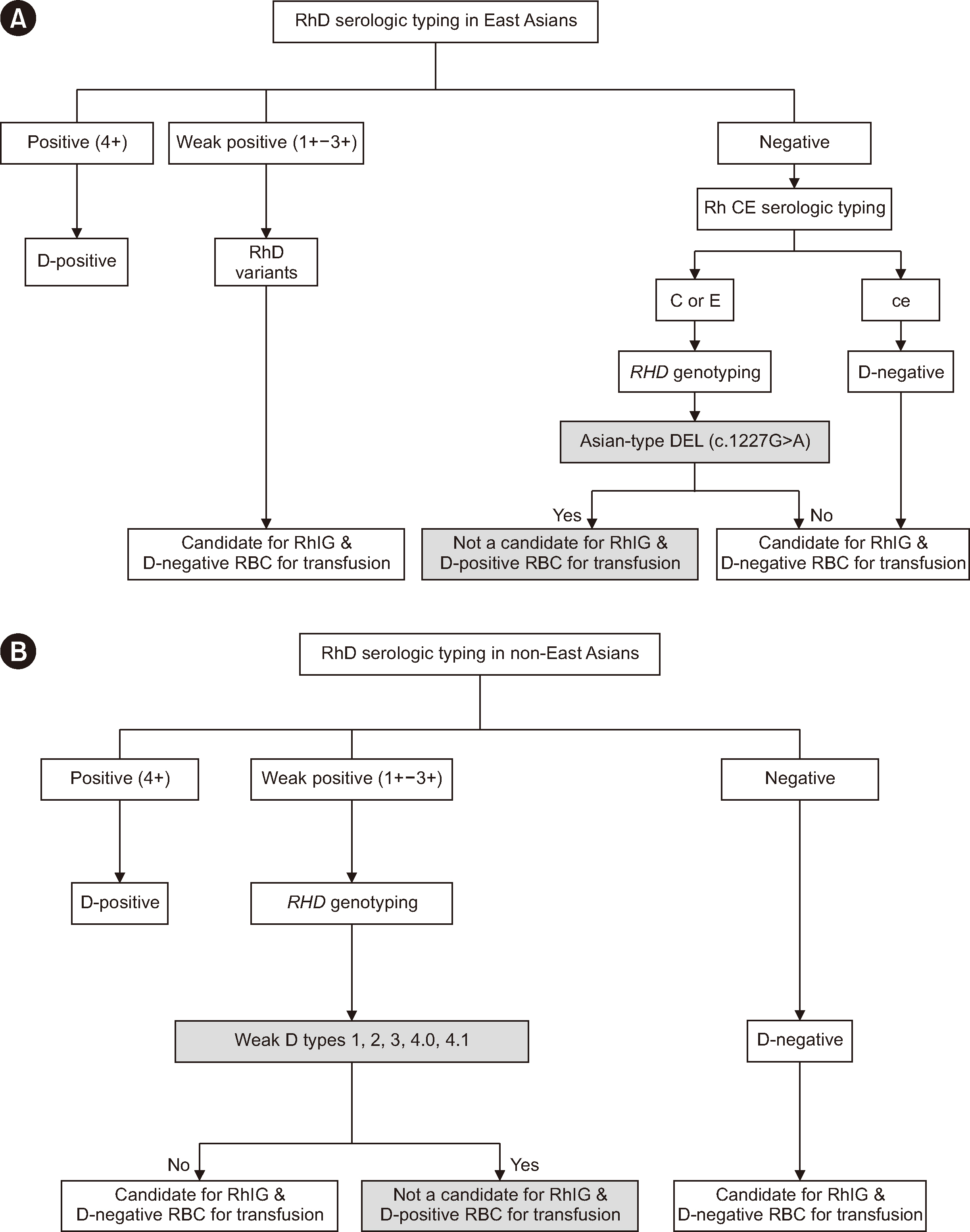
Guide to Rho(D) Immune Globulin in Women With Molecularly Defined Asian-type DEL (c.1227G>A)
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dong-A University Medical Center, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Health Sciences and Technology, Samsung Advanced Institute for Health Sciences and Technology (SAIHST), Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2557929
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.0356
Abstract
- Rh hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn is a potential risk for D-negative mothers who produce anti-D during pregnancy, which can lead to morbidity and mortality in subsequent pregnancies. To prevent this hemolytic disease, Rho(D) immune globulin (RhIG) is generally administered to D-negative mothers without anti-D at 28 weeks of gestation and shortly after delivery. However, current guidelines suggest that pregnant mothers with molecularly defined weak D types 1, 2, 3, 4.0, and 4.1 do not need RhIG as they are unlikely to produce alloanti-D when exposed to fetuses with D-positive red cells. This issue and the necessity of RHD genotyping have been extensively discussed in Western countries, where these variants are relatively common. Recent evidence indicates that women with Asiantype DEL (c.1227G > A) also do not form alloanti-D when exposed to D-positive red cells. We report that mothers with molecularly defined Asian-type DEL, similar to those with weak D types 1, 2, 3, 4.0, and 4.1, do not require RhIG before and after delivery. Collectively, this review could pave the way for the revision of international guidelines to include the selective use of RhIG based on specific genotypes, particularly in women with the Asian-type DEL.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Qureshi H, Massey E, Kirwan D, Davies T, Robson S, White J, et al. 2014; BCSH guideline for the use of anti-D immunoglobulin for the prevention of haemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. Transfus Med. 24:8–20. DOI: 10.1111/tme.12091. PMID: 25121158.
Article2. Sandler SG, Chen LN, Flegel WA. 2017; Serological weak D phenotypes: a review and guidance for interpreting the RhD blood type using the RHD genotype. Br J Haematol. 179:10–9. DOI: 10.1111/bjh.14757. PMID: 28508413. PMCID: PMC5612847.
Article3. Kwon DH, Sandler SG, Flegel WA. 2017; DEL phenotype. Immunohematology. 33:125–32. DOI: 10.21307/immunohematology-2019-019. PMID: 29043831. PMCID: PMC5676463.
Article4. Sandler SG, Flegel WA, Westhoff CM, Denomme GA, Delaney M, Keller MA, et al. 2015; It's time to phase in RHD genotyping for patients with a serologic weak D phenotype. College of American Pathologists Transfusion Medicine Resource Committee Work Group. Transfusion. 55:680–9. DOI: 10.1111/trf.12941. PMID: 25438646. PMCID: PMC4357540.
Article5. Flegel WA, Denomme GA, Queenan JT, Johnson ST, Keller MA, Westhoff CM, et al. 2020; It's time to phase out "serologic weak D phenotype" and resolve D types with RHD genotyping including weak D type 4. Transfusion. 60:855–9. DOI: 10.1111/trf.15741. PMID: 32163599. PMCID: PMC9121350.
Article6. Ji Y, Luo Y, Wen J, Sun Y, Jia S, Ou C, et al. 2023; Patients with Asian-type DEL can safely be transfused with RhD-positive blood. Blood. 141:2141–50. DOI: 10.1182/blood.2022018152. PMID: 36638337. PMCID: PMC10273079.7. Choi S, Chun S, Seo JY, Yang JH, Cho D. 2019; Planned transfusion of D-positive blood components in an Asia type DEL patient: proposed modification of the Korean national guidelines for blood transfusion. Ann Lab Med. 39:102–4. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2019.39.1.102. PMID: 30215239. PMCID: PMC6143459.
Article8. Hess JR. 2023; Safe transfusion in Asian-type DEL. Blood. 141:2044–6. DOI: 10.1182/blood.2023019646. PMID: 37103952.
Article9. Thongbut J, Raud L, Férec C, Promwong C, Nuchnoi P, Fichou Y. 2020; Comprehensive molecular analysis of serologically D-negative and weak/partial D phenotype in Thai Blood donors. Transfus Med Hemother. 47:54–60. DOI: 10.1159/000499087. PMID: 32110194. PMCID: PMC7036540.
Article10. Körmöczi GF, Gassner C, Shao CP, Uchikawa M, Legler TJ. 2005; A comprehensive analysis of DEL types: partial DEL individuals are prone to anti-D alloimmunization. Transfusion. 45:1561–7. DOI: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2005.00584.x. PMID: 16181205.
Article11. Wagner T, Körmöczi GF, Buchta C, Vadon M, Lanzer G, Mayr WR, et al. 2005; Anti-D immunization by DEL red blood cells. Transfusion. 45:520–6. DOI: 10.1111/j.0041-1132.2005.04256.x. PMID: 15819672.
Article12. Yasuda H, Ohto H, Sakuma S, Ishikawa Y. 2005; Secondary anti-D immunization by Del red blood cells. Transfusion. 45:1581–4. DOI: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2005.00579.x. PMID: 16181208.
Article13. Kim KH, Kim KE, Woo KS, Han JY, Kim JM, Park KU. 2009; Primary anti-D immunization by DEL red blood cells. Korean J Lab Med. 29:361–5. DOI: 10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.4.361. PMID: 19726900.
Article14. Yang HS, Lee MY, Park TS, Cho SY, Lee HJ, Lim G, et al. 2015; Primary anti-D alloimmunization induced by "Asian type" RHD (c.1227G>A) DEL red cell transfusion. Ann Lab Med. 35:554–6. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2015.35.5.554. PMID: 26206698. PMCID: PMC4510514.
Article15. Shao CP, Wang BY, Ye SH, Zhang WL, Xu H, Zhuang NB, et al. 2012; DEL RBC transfusion should be avoided in particular blood recipient in East Asia due to allosensitization and ineffectiveness. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 13:913–8. DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1100348. PMID: 23125084. PMCID: PMC3494030.
Article16. Thongbut J, Bénech C, Phiri N, Suwanwootichai P, Thongpao C, Bejrachandra S, et al. 2023; Anti-D alloimmunization by Asia type DEL red blood cell units in a D-negative Thai patient. Transfus Apher Sci. 62:103837. DOI: 10.1016/j.transci.2023.103837. PMID: 37872073.
Article17. Ohto H, Ito S, Srivastava K, Ogiyama Y, Uchikawa M, Nollet KE, et al. 2023; Asian-type DEL (RHD*DEL1) with an allo-anti-D: a paradoxical observation in a healthy multiparous woman. Transfusion. 63:1601–11. DOI: 10.1111/trf.17465. PMID: 37465939.
Article18. KCDC. 2022. National transfusion guideline. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;Seoul, Republic of Korea: DOI: 10.17945/kjbt.2016.27.2.155.19. Chown B. 1954; Anaemia from bleeding of the fetus into the mother's circulation. Lancet. 266:1213–5. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(54)92446-0. PMID: 13164357.20. 2017; Practice Bulletin No. 181: Prevention of Rh D alloimmunization. Obstet Gynecol. 130:e57–70. DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000002232. PMID: 28742673.21. Ware RE, Zimmerman SA. 1998; Anti-D: mechanisms of action. Semin Hematol. 35(S1):14–22.22. Avent ND, Reid ME. 2000; The Rh blood group system: a review. Blood. 95:375–87. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V95.2.375. PMID: 10627438.
Article23. Wagner FF, Frohmajer A, Ladewig B, Eicher NI, Lonicer CB, Müller TH, et al. 2000; Weak D alleles express distinct phenotypes. Blood. 95:2699–708. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V95.8.2699. PMID: 10753853.
Article24. Daniels G. 2013; Variants of RhD-current testing and clinical consequences. Br J Haematol. 161:461–70. DOI: 10.1111/bjh.12275. PMID: 23432139.
Article25. Westhoff CM. 2007; The structure and function of the Rh antigen complex. Semin Hematol. 44:42–50. DOI: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2006.09.010. PMID: 17198846. PMCID: PMC1831834.
Article26. Lee GH, Kim H, Hur M, So KA, Shin DW, Hong YJ, et al. 2023; RHD*DNT (RHD*38) showing D-positive reactivity on rhesus D typing and forming anti-D antibody. Ann Lab Med. 43:524–7. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.5.524. PMID: 37080757. PMCID: PMC10151267.
Article27. Tippett P, Lomas-Francis C, Wallace M. 1996; The Rh antigen D: partial D antigens and associated low incidence antigens. Vox Sang. 70:123–31. DOI: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1996.tb01309.x. PMID: 8740002.
Article28. Lubenko A, Contreras M, Habash J. 1989; Should anti-Rh immunoglobulin be given D variant women? Br J Haematol. 72:429–33. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb07727.x. PMID: 2504271.
Article29. Levitt J, editor. 2014. Standards for blood banks and transfusion services. 29th ed. AABB Press;Bethesda, MD:30. Westhoff CM, Nance S, Lomas-Francis C, Keller M, Chou ST. 2019; Experience with RHD*weak D type 4.0 in the USA. Blood Transfus. 17:91–3.31. Flegel WA, Peyrard T, Chiaroni J, Tournamille C, Jamet D, Pirenne F. 2019; A proposal for a rational transfusion strategy in patients of European and North African descent with weak D type 4.0 and 4.1 phenotypes. Blood Transfus. 17:89–90.32. Flegel WA, Bodnar M, Clarke G, Hannon J, Lieberman L. 2021; What constitutes the most cautious approach for a pregnant person with weak D type 4.0? CMAJ. 193:E916. DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.78986. PMID: 34860699. PMCID: PMC8248459.
Article33. Chung YN, Kim TY, Yu H, Bae JC, Cho D. 2021; Molecular basis of serological weak D phenotypes and RhD typing discrepancies identified in the Korean population. Blood Transfus. 19:327–34.34. Takeuchi-Baba C, Ito S, Kinjo R, Miyagi H, Yasuda H, Ogasawara K, et al. 2019; Production of RBC autoantibody mimicking anti-D specificity following transfusion in a patient with weak D Type 15. Transfusion. 59:1190–5. DOI: 10.1111/trf.15207. PMID: 30784074.
Article35. Wen J, Jia S, Wang Z, Chen J, Liang Q, Wei L, et al. 2023; Molecular and serological analysis of the D variant in the Chinese population and identification of seven novel RHD alleles. Transfusion. 63:402–14. DOI: 10.1111/trf.17186. PMID: 36382965.
Article36. Flegel WA. 2021; Proceed with care: the "uncommon" serologic weak D phenotypes. Blood Transfus. 19:272–6.37. Wagner FF, Gassner C, Müller TH, Schönitzer D, Schunter F, Flegel WA. 1999; Molecular basis of weak D phenotypes. Blood. 93:385–93. DOI: 10.1182/blood.V93.1.385. PMID: 9864185.
Article38. Daniels G. 2013. Human blood groups. 3d ed. Wiley-Blackwell;West Sussex, UK: DOI: 10.1002/9781118493595.39. Flegel WA. 2011; Molecular genetics and clinical applications for RH. Transfus Apher Sci. 44:81–91. DOI: 10.1016/j.transci.2010.12.013. PMID: 21277262. PMCID: PMC3042511.
Article40. Thongbut J, Laengsri V, Raud L, Promwong C, I-Na-Ayudhya C, Férec C, et al. 2021; Nation-wide investigation of RHD variants in Thai blood donors: impact for molecular diagnostics. Transfusion. 61:931–8. DOI: 10.1111/trf.16242. PMID: 33377204.
Article41. Nuchnoi P, Thongbut J, Bénech C, Kupatawintu P, Chaiwanichsiri D, Férec C, et al. 2023; Serologically D-negative blood donors in Thailand: molecular variants and diagnostic strategy. Blood Transfus. 21:209–17. DOI: 10.2450/2022.0160-22. PMID: 36346882. PMCID: PMC10159805.42. Yin Q, Flegel WA. 2021; DEL in China: the D antigen among serologic RhD-negative individuals. J Transl Med. 19:439. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-021-03116-6. PMID: 34670559. PMCID: PMC8527646. PMID: c813824e35614bdb82995b849845a27c.
Article43. Shao CP, Maas JH, Su YQ, Kohler M, Legler TJ. 2002; Molecular background of Rh D-positive, D-negative, D(el) and weak D phenotypes in Chinese. Vox Sang. 83:156–61. DOI: 10.1046/j.1423-0410.2002.00192.x. PMID: 12201845.44. Kim JY, Kim SY, Kim CA, Yon GS, Park SS. 2005; Molecular characterization of D- Korean persons: development of a diagnostic strategy. Transfusion. 45:345–52. DOI: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2005.04311.x. PMID: 15752151.
Article45. Okubo Y, Seno T, Yamano H, Yamaguchi H, Lomas C, Tippett P. 1991; Partial D antigens disclosed by a monoclonal anti-D in Japanese blood donors. Transfusion. 31:782. DOI: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1991.31892023512.x. PMID: 1926326.
Article46. Luettringhaus TA, Cho D, Ryang DW, Flegel WA. 2006; An easy RHD genotyping strategy for D- East Asian persons applied to Korean blood donors. Transfusion. 46:2128–37. DOI: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2006.01042.x. PMID: 17176325.
Article47. Seo MH, Won EJ, Hong YJ, Chun S, Kwon JR, Choi YS, et al. 2016; An effective diagnostic strategy for accurate detection of RhD variants including Asian DEL type in apparently RhD-negative blood donors in Korea. Vox Sang. 111:425–30. DOI: 10.1111/vox.12450. PMID: 27864976.48. Okubo Y, Yamaguchi H, Tomita T, Nagao N. 1984; A D variant, Del? Transfusion. 24:542. DOI: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1984.24685066827.x. PMID: 6438843.49. Okuda H, Kawano M, Iwamoto S, Tanaka M, Seno T, Okubo Y, et al. 1997; The RHD gene is highly detectable in RhD-negative Japanese donors. J Clin Invest. 100:373–9. DOI: 10.1172/JCI119543. PMID: 9218514. PMCID: PMC508200.50. Wagner FF, Flegel WA. 2014; The rhesus site. Transfus Med Hemother. 41:357–63. DOI: 10.1159/000366176. PMID: 25538538. PMCID: PMC4264492.
Article51. Shao CP. 2010; Transfusion of RhD-positive blood in "Asia type" DEL recipients. N Engl J Med. 362:472–3. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMc0909552. PMID: 20130261.
Article52. Beveridge HE. 1997; Dwindling supplies of anti-D. Med J Aust. 167:509–10. DOI: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1997.tb126698.x. PMID: 9397073.
Article53. Robson SC, Lee D, Urbaniak S. 1998; Anti-D immunoglobulin in RhD prophylaxis. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 105:129–34. DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1998.tb10039.x. PMID: 9501773.
Article54. Mark A, Foster AM, Grossman D, Prager SW, Reeves M, Velásquez CV, et al. 2019; Foregoing Rh testing and anti-D immunoglobulin for women presenting for early abortion: a recommendation from the National Abortion Federation's Clinical Policies Committee. Contraception. 99:265–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.contraception.2019.02.008. PMID: 30867121.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of successful Rh(D) immune prophylaxis with Rho(D) immune globulin after accidental Rh incompatible transfusion
- Detection of RHD 1227G>A and 1222T>C Using PCR-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism
- A Case of Primary Anti-D Alloimmunization by RHD (c.1227G>A) DEL Red Blood Cell Transfusion
- Application of Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification Assay for Genotyping Major Blood Group Systems Including DEL Variants in the D-Negative Korean Population
- The Experience of RHD Genotyping in D-negative Blood Donors