Korean J Pain.
2024 Jul;37(3):256-263. 10.3344/kjp.24087.
Current practices of cervical epidural block for cervical radicular pain: a multicenter survey conducted by the Korean Pain Society
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea
- KMID: 2557729
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.24087
Abstract
- Background
Cervical epidural block (CEB) is an effective intervention for managing cervical radicular pain. This study aimed to investigate the current status of performing CEB in South Korea.
Methods
Pain physicians affiliated with the Korean Pain Society were asked to complete anonymous questionnaires regarding CEB between September and October 2022. The questionnaire consisted of 24 questions assessing the current status and methods of CEB in detail.
Results
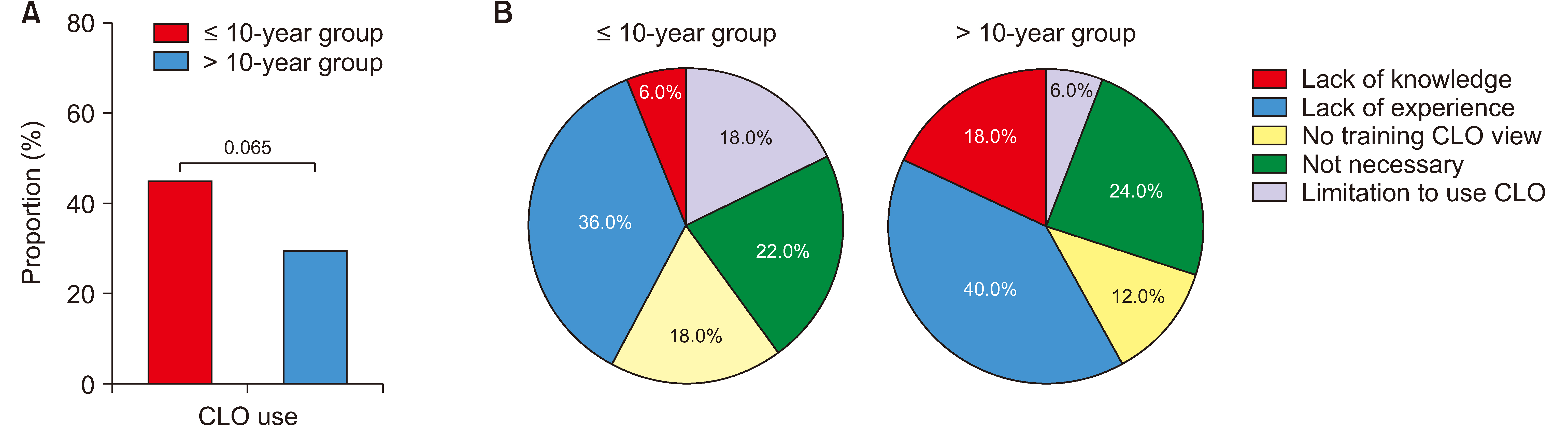
Of the 198 surveys collected, 171 physicians (86.4%) reported performing CEB. Among those, the majority (94.7%) used fluoroscopy during the procedure. The paramedian interlaminar (IL) approach was the most preferred method (50.3%). Respondents performing fluoroscopic-guided IL CEB were categorized into two groups based on clinical experience: those with ≤10 years of experience (≤10-year group, n = 91) and those with >10 years of experience (>10-year group, n = 71). The proportion of physicians obtaining informed consent in the ≤10-year group and >10-year group was 50.5% and 56.3%, respectively. When entering the epidural space during IL CEB, the contralateral oblique view was the second most frequently used in both groups (≤10-year group, 42.9%; >10-year group, 29.6%). In targeting the upper cervical lesions (C3–4), the proportion of respondents who used an IL space higher than C6–7 was 17.6% in the ≤10-year group and 29.5% in the >10-year experience group.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated variability in the CEB technique used by pain physicians in South Korea. The findings highlight the need for education on informed consent and techniques to enhance safety.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Peene L, Cohen SP, Brouwer B, James R, Wolff A, Van Boxem K, et al. 2023; 2. Cervical radicular pain. Pain Pract. 23:800–17. DOI: 10.1111/papr.13252. PMID: 37272250.
Article2. Manchikanti L, Knezevic NN, Navani A, Christo PJ, Limerick G, Calodney AK, et al. 2021; epidural interventions in the management of chronic spinal pain: American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians (ASIPP) comprehensive evidence-based guidelines. Pain Physician. 24(S1):S27–208. DOI: 10.36076/ppj.2021.24.S27-S208.3. Zhang X, Shi H, Zhou J, Xu Y, Pu S, Lv Y, et al. 2018; The effectiveness of ultrasound-guided cervical transforaminal epidural steroid injections in cervical radiculopathy: a prospective pilot study. J Pain Res. 12:171–7. DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S181915. PMID: 30643449. PMCID: PMC6318715.4. Manchikanti L, Nampiaparampil DE, Candido KD, Bakshi S, Grider JS, Falco FJ, et al. 2015; Do cervical epidural injections provide long-term relief in neck and upper extremity pain? A systematic review. Pain Physician. 18:39–60. DOI: 10.36076/ppj/2015.18.39. PMID: 25675059.
Article5. Kim YD, Moon HS. 2015; Review of medical dispute cases in the pain management in Korea: a medical malpractice liability insurance database study. Korean J Pain. 28:254–64. Erratum in: Korean J Pain 2016; 29: 62. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2015.28.4.254. PMID: 26495080. PMCID: PMC4610939.
Article6. Gill JS, Aner M, Nagda JV, Keel JC, Simopoulos TT. 2015; Contralateral oblique view is superior to lateral view for interlaminar cervical and cervicothoracic epidural access. Pain Med. 16:68–80. Erratum in: Pain Med 2015; 16: 2218. DOI: 10.1111/pme.12880. PMID: 26744890.
Article7. Sim JH, Kwon HJ, Kim CS, Kim EH, Kim DH, Choi SS, et al. 2022; Comparison of contralateral oblique view with the lateral view for fluoroscopic-guided cervical epidural steroid injection: a randomized clinical trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 47:171–6. DOI: 10.1136/rapm-2021-103177. PMID: 34853162.8. Kwon HJ, Kim CS, Kim J, Kim S, Shin JY, Choi SS, et al. 2023; Contralateral oblique view can prevent dural puncture in fluoroscopy-guided cervical epidural access: a prospective observational study. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 48:588–93. DOI: 10.1136/rapm-2022-104297. PMID: 37024268.9. Rathmell JP, Benzon HT, Dreyfuss P, Huntoon M, Wallace M, Baker R, et al. 2015; Safeguards to prevent neurologic complications after epidural steroid injections: consensus opinions from a multidisciplinary working group and national organizations. Anesthesiology. 122:974–84. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000614. PMID: 25668411.10. Schenker Y, Fernandez A, Sudore R, Schillinger D. 2011; Interventions to improve patient comprehension in informed consent for medical and surgical procedures: a systematic review. Med Decis Making. 31:151–73. DOI: 10.1177/0272989X10364247. PMID: 20357225. PMCID: PMC5419590.
Article11. Goodman B, Petalcorin JS, Mallempati S. 2010; Optimizing patient positioning and fluoroscopic imaging for the performance of cervical interlaminar epidural steroid injections. PM R. 2:783–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2010.05.017. PMID: 20709308.
Article12. Benzon HT, Huntoon MA, Rathmell JP. 2015; Improving the safety of epidural steroid injections. JAMA. 313:1713–4. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2015.2912. PMID: 25822848.13. Schultz DM, Hagedorn JM, Abd-Elsayed A, Stayner S. 2022; Safety of interlaminar cervical epidural injections: experience with 12,168 procedures in a single pain clinic. Pain Physician. 25:49–58.14. Manchikanti L, Malla Y, Cash KA, Pampati V. 2015; Do the gaps in the ligamentum flavum in the cervical spine translate into dural punctures? An analysis of 4,396 fluoroscopic interlaminar epidural injections. Pain Physician. 18:259–66. DOI: 10.36076/ppj.2015/18/259. PMID: 26000669.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Respiratory Arrest during Cervical Epidural Block: A case report
- Chronic Pain Control of SCI Patients after Cervical Epidural Block: Case report on 2 cases
- Acute Cervical Subdural Hematoma with Quadriparesis after Cervical Transforaminal Epidural Block
- Convulsion , Loss of Consciousness and Respiratory Arrest during Nerve Block at Neck
- Quadriplegia due to Epidural Abscess following Continuous Cervical Epidural Block: A case report