Acute Crit Care.
2024 May;39(2):234-242. 10.4266/acc.2023.00983.
Comparative evaluation of tocilizumab and itolizumab for treatment of severe COVID-19 in India: a retrospective cohort study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anaesthesiology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Patna, Patna, India
- 2Department of Anaesthesiology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Bhubaneswar, Bhubaneswar, India
- 3Department of Anaesthesiology, Acharya Harihar Post Graduate Institute of Cancer, Cuttack, India
- KMID: 2557239
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2023.00983
Abstract
- Background
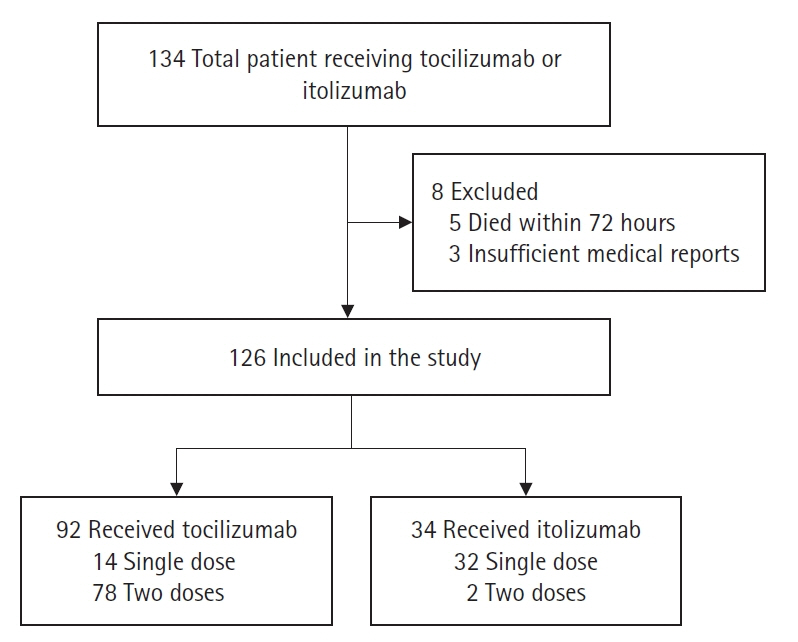
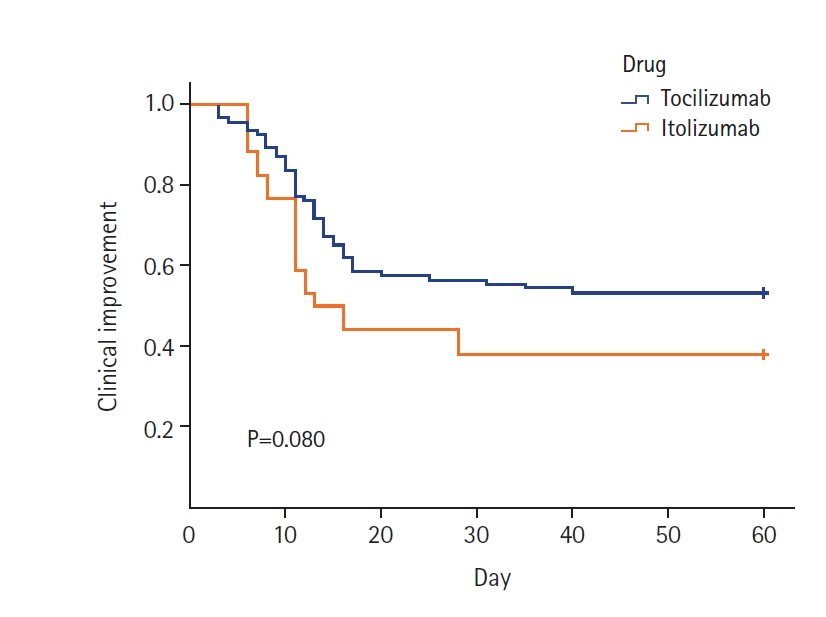
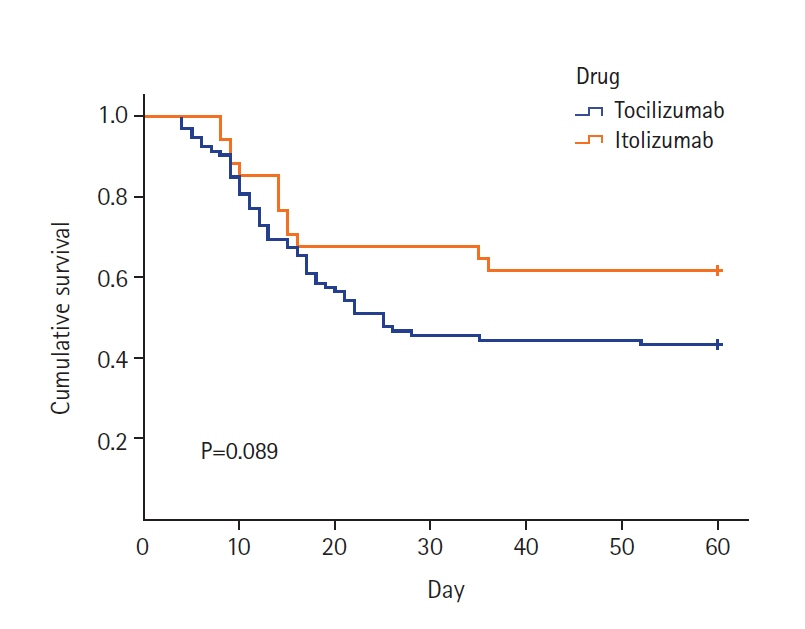
Itolizumab downregulates the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules by inhibiting CD6 leading to lower levels of interferon-γ, interleukin-6, and tumor necrotic factor-α and reduced T-cell infiltration at inflammatory sites. This study aims to compare the effects of tocilizumab and itolizumab in the management of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Methods: The study population was adults (>18 years) with severe COVID-19 pneumonia admitted to the intensive care unit receiving either tocilizumab or itolizumab during their stay. The primary outcome was clinical improvement (CI), defined as a two-point reduction on a seven-point ordinal scale in the status of the patient from initiating the drug or live discharge. The secondary outcomes were time until CI, improvement in PO2 /FiO2 ratio, best PO2 /FiO2 ratio, need for mechanical ventilation after administration of study drugs, time to discharge, and survival days. Results: Of the 126 patients included in the study, 92 received tocilizumab and 34 received itolizumab. CI was seen in 46.7% and 61.7% of the patients in the tocilizumab and itolizumab groups, respectively and was not statistically significant (P=0.134). The PO2 /FiO2 ratio was significantly better with itolizumab compared to tocilizumab (median [interquartile range]: 315 [200–380] vs. 250 [150–350], P=0.043). The incidence of serious adverse events due to the study drugs was significantly higher with itolizumab compared to tocilizumab (14.7% vs. 3.3%, P=0.032). Conclusions: The CI with itolizumab is similar to tocilizumab. Better oxygenation can be achieved with itolizumab and it can be a substitute for tocilizumab in managing severe COVID-19.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E, Tattersall RS, Manson JJ, et al. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet. 2020; 395:1033–4.
Article2. Heimfarth L, Serafini MR, Martins-Filho PR, Quintans JS, Quintans-Júnior LJ. Drug repurposing and cytokine management in response to COVID-19: a review. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020; 88:106947.
Article3. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Coronavirus (COVID-19) update: FDA authorizes drug for treatment of COVID-19 [Internet]. U.S. Food and Drug Administration;2021. [cited 2024 Jan 20] Available from: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-authorizes-drug-treatment-covid-19.4. REMAP-CAP Investigators, Gordon AC, Mouncey PR, Al-Beidh F, Rowan KM, Nichol AD, et al. Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384:1491–502.
Article5. RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet. 2021; 397:1637–45.6. Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. DCGI gives nod for restricted emergency use to itolizumab for moderate to severe COVID-19 patients [Internet]. Ministry of Health and Family Welfare;2020. [cited 2024 Jan 20] Available from: https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1637926.7. Loganathan S, Athalye SN, Joshi SR. Itolizumab, an anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody, as a potential treatment for COVID-19 complications. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2020; 20:1025–31.
Article8. Díaz Y, Ramos-Suzarte M, Martín Y, Calderón NA, Santiago W, Viñet O, et al. Use of a humanized anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody (itolizumab) in elderly patients with moderate COVID-19. medRxiv. [Preprint]. 2020 Jul 24 [cited 2024 Jan 20]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.24.20153833.
Article9. Kumari P, Kumar A, Sinha C, Kumar A, Singh PK, Arun SK. Off-label use of itolizumab in patients with COVID-19 ARDS: our clinical experience in a dedicated COVID center. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2021; 25:467–9.
Article10. Directorate General of Health Services; Ministry of Health and Family Welfare; Government of India. Clinical management protocol: COVID-19 [Internet]. Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India;2020. [cited 2024 Jan 20]. Available from: https://www.mohfw.gov.in/pdf/ClinicalManagementProtocolforCOVID19.pdf.11. Lee DW, Gardner R, Porter DL, Louis CU, Ahmed N, Jensen M, et al. Current concepts in the diagnosis and management of cytokine release syndrome. Blood. 2014; 124:188–95.
Article12. Fanelli V, Vlachou A, Ghannadian S, Simonetti U, Slutsky AS, Zhang H. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: new definition, current and future therapeutic options. J Thorac Dis. 2013; 5:326–34.13. Stone JH, Frigault MJ, Serling-Boyd NJ, Fernandes AD, Harvey L, Foulkes AS, et al. Efficacy of tocilizumab in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383:2333–44.
Article14. Hermine O, Mariette X, Tharaux PL, Resche-Rigon M, Porcher R, Ravaud P, et al. Effect of tocilizumab vs usual care in adults hospitalized with COVID-19 and moderate or severe pneumonia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2021; 181:32–40.15. Salvarani C, Dolci G, Massari M, Merlo DF, Cavuto S, Savoldi L, et al. Effect of tocilizumab vs standard care on clinical worsening in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. 2021; 181:24–31.
Article16. World Health Organisation. WHO prequalifies first monoclonal antibody - tocilizumab - to treat COVID-19 [Internet]. World Health Organisation;2022. [cited 2024 Jan 20]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news/item/11-02-2022-who-prequalifies-first-monoclonal-antibody---tocilizumab-to-treat-covid-19.17. Biocon.com. Biocon presented insights into clinical study that enabled DCGI approval of itolizumab for COVID19 [Internet]. Biocon.com;2022. [cited 2024 Jan 20]. Available from: https://www.biocon.com/biocon-presented-insights-into-clinical-study-that-enabled-dcgi-approval-of-itolizumab-for-covid19.18. Saavedra D, Añé-Kourí AL, Sánchez N, Filgueira LM, Betancourt J, Herrera C, et al. An anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody (Itolizumab) reduces circulating IL-6 in severe COVID-19 elderly patients. Research Square [Preprint]. 2020 [cited 2024 Jan 20]. Available from: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-32335/v1.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Corrigendum to: Comparative evaluation of tocilizumab and itolizumab for treatment of severe COVID-19 in India: a retrospective cohort study
- Severity-Adjusted Dexamethasone Dosing and Tocilizumab Combination for Severe COVID-19
- COVID-19 infection and severe clinical outcomes in patients with kidney disease by vaccination status: a nationwide cohort study in Korea
- How We Have Treated Severe to Critically Ill Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Korea
- Prediction of COVID-19 Outbreaks Using Google Trends in India: A Retrospective Analysis