Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2024 Jul;28(4):313-322. 10.4196/kjpp.2024.28.4.313.
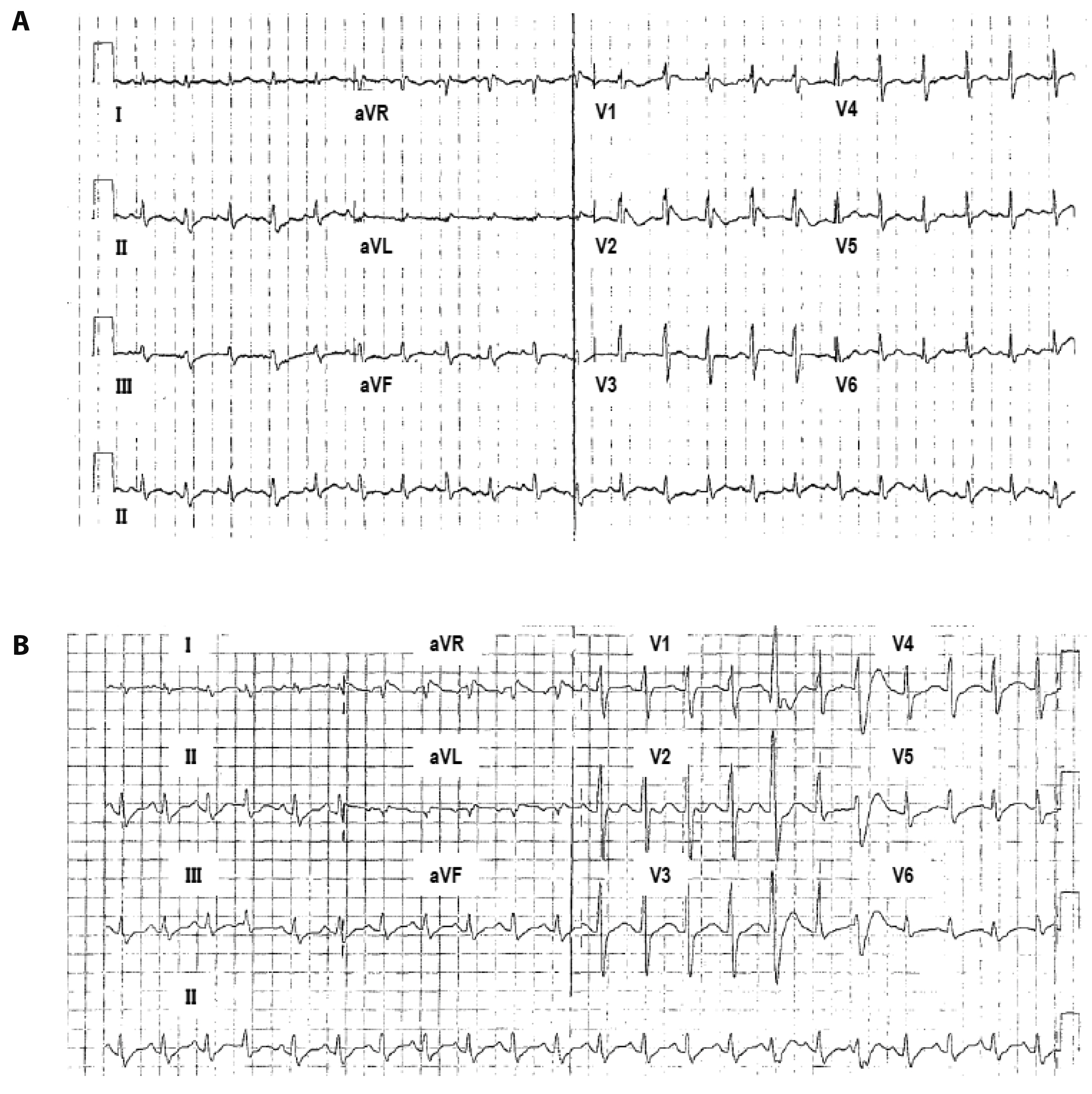
Requirement of βsubunit for the reduced voltage-gated Na+ current of a Brugada syndrome patient having novel double missense mutation (p.A385T/R504T) of SCN5A
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Korea
- 2Department of Physiology, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju 38066, Korea
- 3Channelopathy Research Center (CRC), Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang 10326, Korea
- 4R&D Center, Biosolvix Co. Ltd, Seoul 08502, Korea
- 5Department of Internal Medicine Graduate School of Medicine, Dongguk University, Goyang 10326, Korea
- 6Department of Animal Science and Technology, Chung- Ang University, Anseong 17546, Korea
- 7Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Uijeonbu St.Mary’s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 11765, Korea
- 8Department of Physiology & Ischemic/Hypoxic Disease Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 03080, Korea
- KMID: 2557202
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2024.28.4.313
Abstract
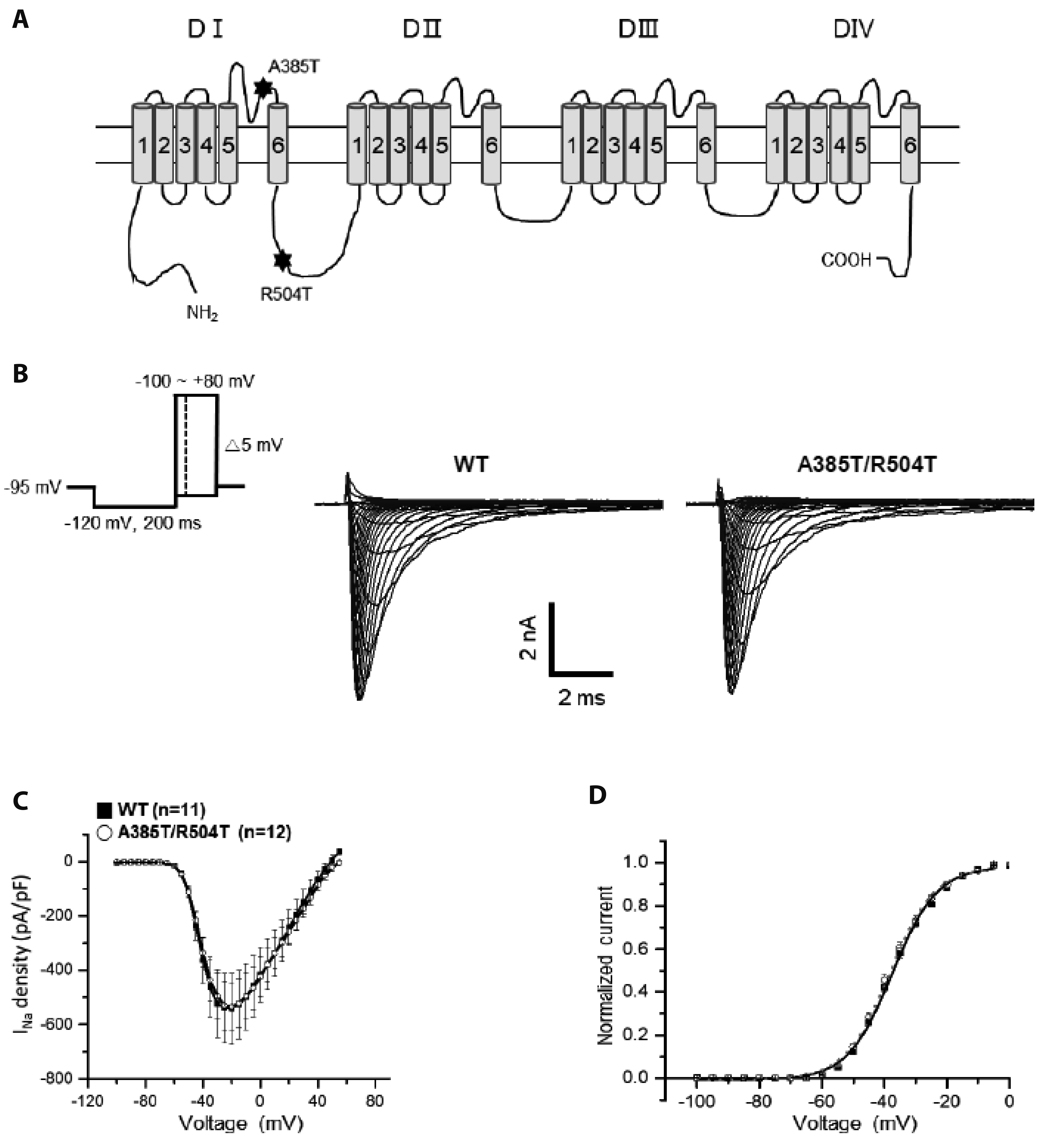
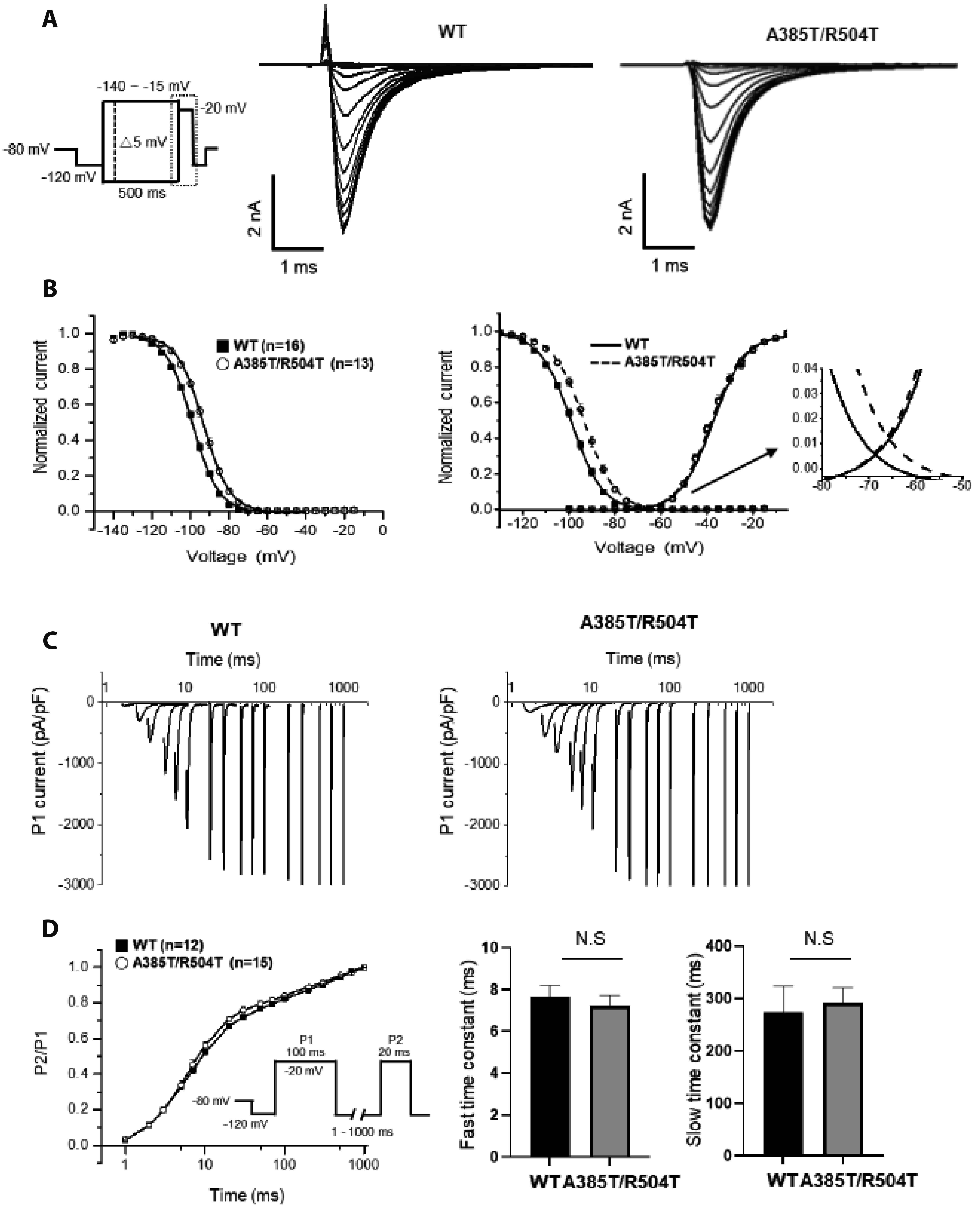
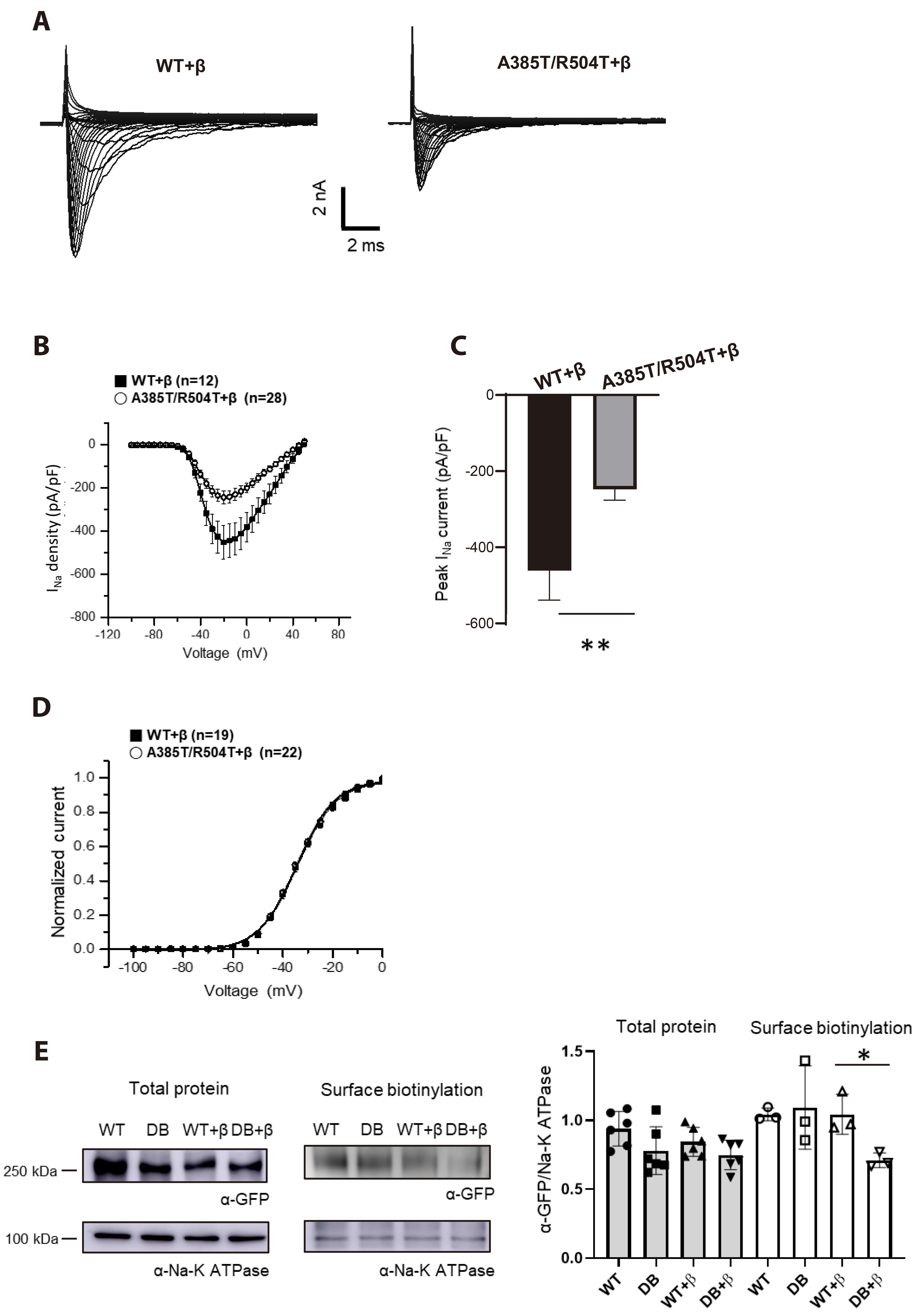
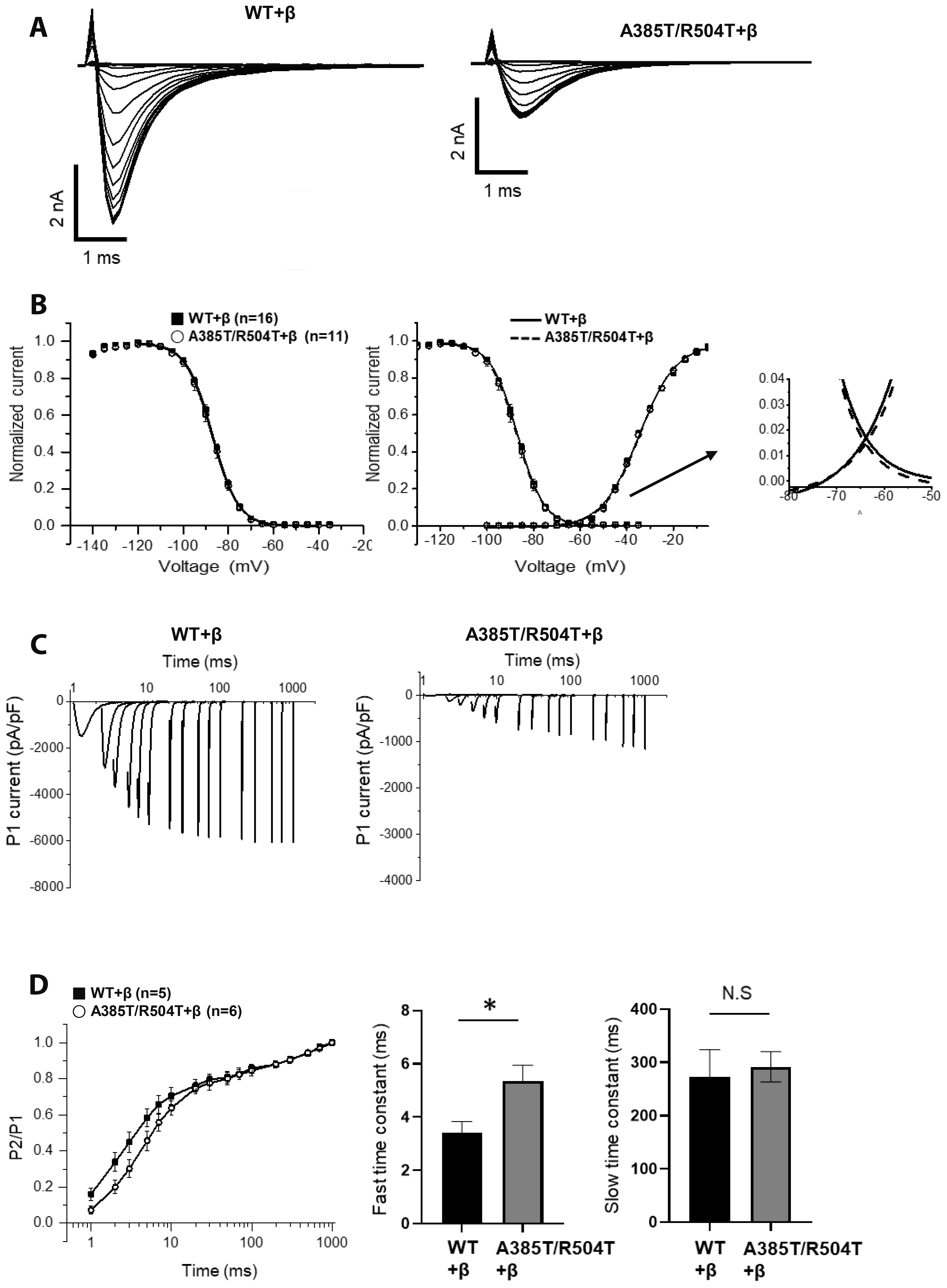
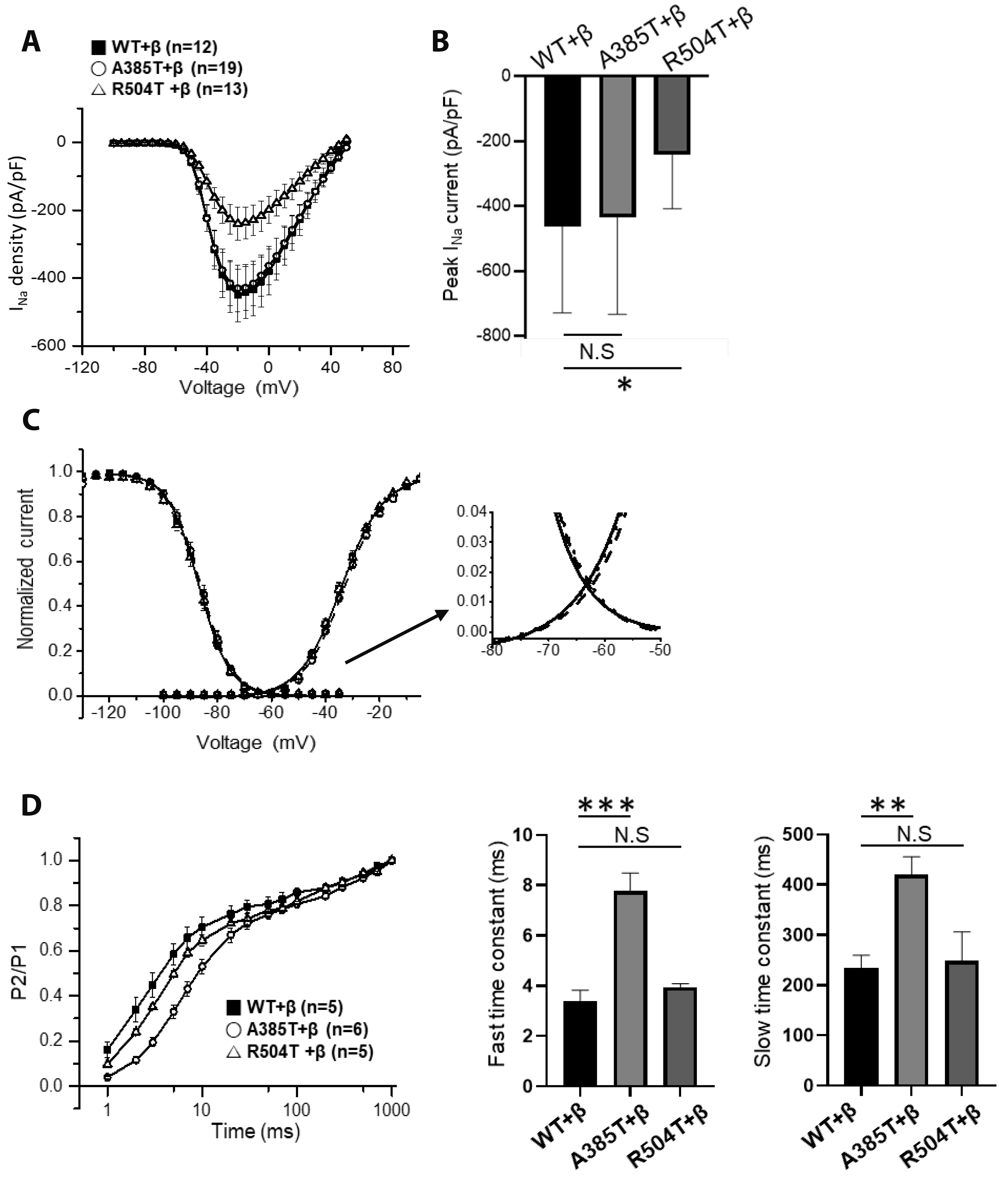
- Mutations within the SCN5A gene, which encodes the α-subunit 5 (NaV1.5) of the voltage-gated Na+ channel, have been linked to three distinct cardiac arrhythmia disorders: long QT syndrome type 3, Brugada syndrome (BrS), and cardiac conduction disorder. In this study, we have identified novel missense mutations (p.A385T/R504T) within SCN5A in a patient exhibiting overlap arrhythmia phenotypes. This study aims to elucidate the functional consequences of SCN5A mutants (p.A385T/R504T) to understand the clinical phenotypes. Whole-cell patch-clamp technique was used to analyze the NaV1.5 current (INa) in HEK293 cells transfected with the wild-type and mutant SCN5A with or without SCN1B co-expression. The amplitude of INa was not altered in mutant SCN5A (p.A385T/R504T) alone. Furthermore, a rightward shift of the voltage-dependent inactivation and faster recovery from inactivation was observed, suggesting a gain-of-function state. Intriguingly, the coexpression of SCN1B with p.A385T/R504T revealed significant reduction of INa and slower recovery from inactivation, consistent with the loss-of-function in Na+ channels. The SCN1B dependent reduction of INa was also observed in a single mutation p.R504T, but p.A385T co-expressed with SCN1B showed no reduction. In contrast, the slower recovery from inactivation with SCN1B was observed in A385T while not in R504T. The expression of SCN1B is indispensable for the electrophysiological phenotype of BrS with the novel double mutations; p.A385T and p.R504T contributed to the slower recovery from inactivation and reduced current density of NaV1.5, respectively.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Quetiapine competitively inhibits 5-HT3 receptor-mediated currents in NCB20 neuroblastoma cells
Yong Soo Park, Gyu Min Kim, Ho Jun Sung, Ju Yeong Yu, Ki-Wug Sung
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2025;29(3):373-384. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.24.363.
Reference
-
1. Napolitano C, Bloise R, Monteforte N, Priori SG. 2012; Sudden cardiac death and genetic ion channelopathies: long QT, Brugada, short QT, catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, and idiopathic ventricular fibrillation. Circulation. 125:2027–2034. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.055947. PMID: 22529064.2. Rook MB, Evers MM, Vos MA, Bierhuizen MF. 2012; Biology of cardiac sodium channel Nav1.5 expression. Cardiovasc Res. 93:12–23. DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvr252. PMID: 21937582.3. Wilde AAM, Amin AS. 2018; Clinical spectrum of SCN5A mutations: long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome, and cardiomyopathy. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 4:569–579. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacep.2018.03.006. PMID: 29798782.4. Carmeliet E. 2002; Congenital LQT syndrome from gene to torsade de pointes. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 6:1–8.5. Grant AO, Carboni MP, Neplioueva V, Starmer CF, Memmi M, Napolitano C, Priori S. 2002; Long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome, and conduction system disease are linked to a single sodium channel mutation. J Clin Invest. 110:1201–1209. DOI: 10.1172/JCI0215570. PMID: 12393856. PMCID: PMC150793.6. Remme CA, Wilde AA. 2008; SCN5A overlap syndromes: no end to disease complexity? Europace. 10:1253–1255. DOI: 10.1093/europace/eun267. PMID: 18820249.7. Porretta AP, Probst V, Bhuiyan ZA, Davoine E, Delinière A, Pascale P, Schlaepfer J, Superti-Furga A, Pruvot E. 2022; SCN5A overlap syndromes: an open-minded approach. Heart Rhythm. 19:1363–1368. DOI: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2022.03.1223. PMID: 35351625.8. Bezzina C, Veldkamp MW, van Den Berg MP, Postma AV, Rook MB, Viersma JW, van Langen IM, Tan-Sindhunata G, Bink-Boelkens MT, van Der Hout AH, Mannens MM, Wilde AA. 1999; A single Na(+) channel mutation causing both long-QT and Brugada syndromes. Circ Res. 85:1206–1213. DOI: 10.1161/01.RES.85.12.1206. PMID: 10590249.9. Remme CA, Wilde AA, Bezzina CR. 2008; Cardiac sodium channel overlap syndromes: different faces of SCN5A mutations. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 18:78–87. DOI: 10.1016/j.tcm.2008.01.002. PMID: 18436145.10. Nakaya H. 2014; SCN5A mutations associated with overlap phenotype of long QT syndrome type 3 and Brugada syndrome. Circ J. 78:1061–1062. DOI: 10.1253/circj.CJ-14-0319. PMID: 24694743.11. Chae H, Kim J, Lee GD, Jang W, Park J, Jekarl DW, Oh YS, Kim M, Kim Y. 2017; Considerations when using next-generation sequencing for genetic diagnosis of long-QT syndrome in the clinical testing laboratory. Clin Chim Acta. 464:128–135. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2016.11.013. PMID: 27871843.12. O'Malley HA, Isom LL. 2015; Sodium channel β subunits: emerging targets in channelopathies. Annu Rev Physiol. 77:481–504. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021014-071846. PMID: 25668026. PMCID: PMC4817109.13. Gaborit N, Le Bouter S, Szuts V, Varro A, Escande D, Nattel S, Demolombe S. 2007; Regional and tissue specific transcript signatures of ion channel genes in the non-diseased human heart. J Physiol. 582:675–693. DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.126714. PMID: 17478540. PMCID: PMC2075332.14. Makita N, Bennett PB Jr, George AL Jr. 1994; Voltage-gated Na+ channel beta 1 subunit mRNA expressed in adult human skeletal muscle, heart, and brain is encoded by a single gene. J Biol Chem. 269:7571–7578. DOI: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)37325-8. PMID: 8125980.15. Calhoun JD, Isom LL. 2014; The role of non-pore-forming β subunits in physiology and pathophysiology of voltage-gated sodium channels. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 221:51–89. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-41588-3_4. PMID: 24737232.16. Daimi H, Lozano-Velasco E, Aranega A, Franco D. 2022; Genomic and non-genomic regulatory mechanisms of the cardiac sodium channel in cardiac arrhythmias. Int J Mol Sci. 23:1381. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031381. PMID: 35163304. PMCID: PMC8835759.17. Abriel H, Rougier JS, Jalife J. 2015; Ion channel macromolecular complexes in cardiomyocytes: roles in sudden cardiac death. Circ Res. 116:1971–1988. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.305017. PMID: 26044251. PMCID: PMC4471480.18. Clatot J, Neyroud N, Cox R, Souil C, Huang J, Guicheney P, Antzelevitch C. 2020; Inter-regulation of Kv4.3 and voltage-gated sodium channels underlies predisposition to cardiac and neuronal channelopathies. Int J Mol Sci. 21:5057. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21145057. PMID: 32709127. PMCID: PMC7404392.19. Wan X, Wang Q, Kirsch GE. 2000; Functional suppression of sodium channels by beta(1)-subunits as a molecular mechanism of idiopathic ventricular fibrillation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 32:1873–1884. DOI: 10.1006/jmcc.2000.1223. PMID: 11013131.20. Zimmer T, Surber R. 2008; SCN5A channelopathies--an update on mutations and mechanisms. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 98:120–136. DOI: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2008.10.005. PMID: 19027780.21. Han D, Tan H, Sun C, Li G. 2018; Dysfunctional Nav1.5 channels due to SCN5A mutations. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 243:852–863. DOI: 10.1177/1535370218777972. PMID: 29806494. PMCID: PMC6022915.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Family with A Missense Mutation in the SCN5A Gene
- The Relationship Between Gastric Myoelectric Activity and SCN5A Mutation Suggesting Sodium Channelopathy in Patients With Brugada Syndrome and Functional Dyspepsia: A Pilot Study
- Childhood Brugada Syndrome in Two Korean Families
- SCN5A p.P1725L variant that showed ventricular fibrillation and recurrent pericarditis, and a family member with sick sinus syndrome
- A pediatric case of Brugada syndrome diagnosed by fever-provoked ventricular tachycardia