Prog Med Phys.
2024 Jun;35(2):36-44. 10.14316/pmp.2024.35.2.36.
Dosimetric Evaluations of HyperArc and RapidArc in Stereotactic Radiosurgery for a Single Brain Metastasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Veterans Health Service Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2557157
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2024.35.2.36
Abstract
- Purpose
This study assessed and compared the dosimetric performance of HyperArc and RapidArc in stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for a single brain metastasis.
Methods
Twenty patients with intracranial brain metastases, each presenting a distinct target volume, were retrospectively selected. Subsequently, volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) plans were designed using RapidArc (VMATRA ) and HyperArc (VMATHA ) for each patient. For planning comparisons, dose-volumetric histogram (DVH) parameters for planning target volumes (PTVs) and normal brain regions were computed across all VMAT plans. Subsequently, their total monitor units (MUs), total beam-on times, and modulation complexity scores for the VMAT (MCSv ) were compared. A statistical test was used to evaluate the dosimetric disparities in the DVH parameters, total MUs, total beam-on times, and MCSv between the MATHA and VMAT sub>RA plans.
Results
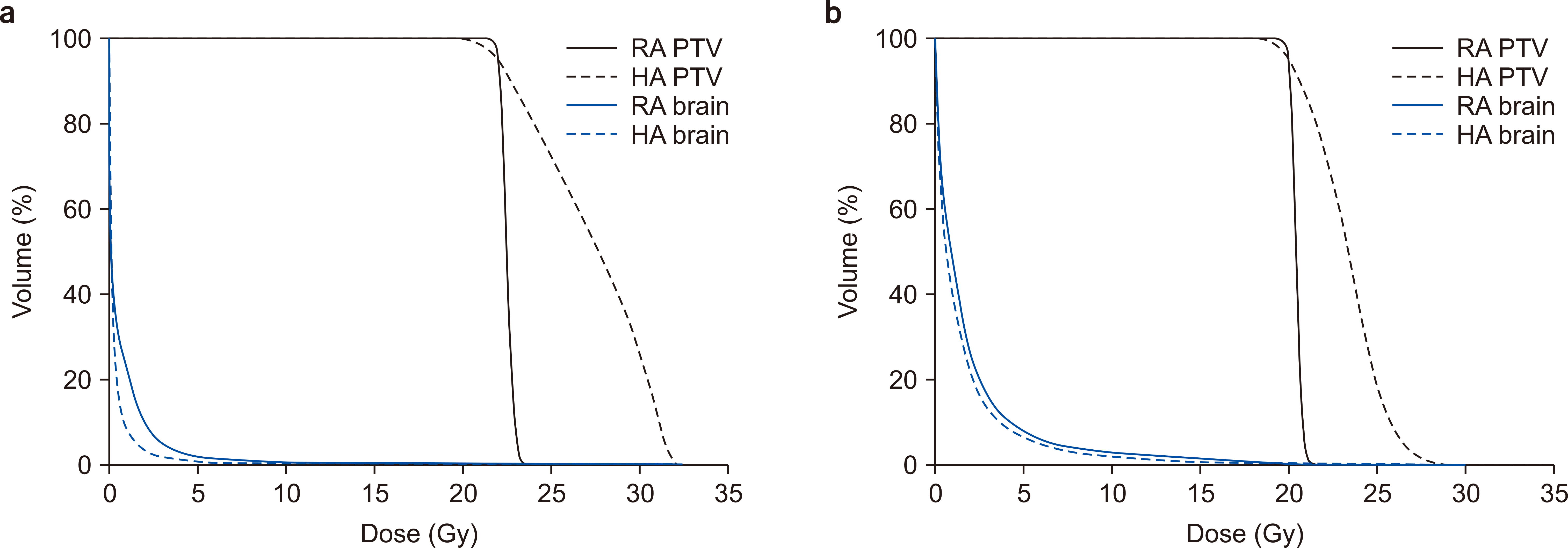
For the PTVs, VMATHA presented a higher homogeneity index (HI) than VMAT RA . Moreover, VMATHA presented significantly smaller gradient index (GI) values (P<0.001) than VMATRA . Thus, VMATHA demonstrated better performance in the DVH parameters for the PTV than VMATRA . For normal brain tissues, VMATHA presented lower volume receiving 50% of the prescription dose and V 2Gy to the normal brain tissues than VMATRA (P<0.0001). While the total MUs required for VMATHA was significantly higher than those for VMATRA , the total beam-on time for VMATHA was superior to that for VMATRA .
Conclusions
Thus, VMATHA exhibited superior performance in achieving rapid dose fall-offs (as indicated by the GI) and a higher HI at the PTV compared to VMATRA in brain SRS. This advancement positions HyperArc as a significant development in the field of radiation therapy, offering optimized treatment outcomes for brain SRS.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Sayan M, Mustafayev TZ, Balmuk A, Mamidanna S, Kefelioglu ESS, Gungor G, et al. 2020; Management of symptomatic radiation necrosis after stereotactic radiosurgery and clinical factors for treatment response. Radiat Oncol J. 38:176–180. DOI: 10.3857/roj.2020.00171. PMID: 33012145. PMCID: PMC7533401.
Article2. Leksell L. 1951; The stereotaxic method and radiosurgery of the brain. Acta Chir Scand. 102:316–319.3. Sayan M, Zoto Mustafayev T, Sahin B, Kefelioglu ESS, Wang SJ, Kurup V, et al. 2019; Evaluation of response to stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with radioresistant brain metastases. Radiat Oncol J. 37:265–270. DOI: 10.3857/roj.2019.00409. PMID: 31918464. PMCID: PMC6952719.
Article4. Kim IH. 2019; Appraisal of re-irradiation for the recurrent glioblastoma in the era of MGMT promotor methylation. Radiat Oncol J. 37:1–12. DOI: 10.3857/roj.2019.00171. PMID: 30947475. PMCID: PMC6453809.
Article5. Kondziolka D, Mathieu D, Lunsford LD, Martin JJ, Madhok R, Niranjan A, et al. 2008; Radiosurgery as definitive management of intracranial meningiomas. Neurosurgery. 62:53–58. discussion 58-60. DOI: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000311061.72626.0D. PMID: 18300891.
Article6. Minniti G, Esposito V, Amichetti M, Enrici RM. 2009; The role of fractionated radiotherapy and radiosurgery in the management of patients with craniopharyngioma. Neurosurg Rev. 32:125–132. discussion 132. DOI: 10.1007/s10143-009-0186-4. PMID: 19165514.
Article7. Murphy ES, Suh JH. 2011; Radiotherapy for vestibular schwannomas: a critical review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 79:985–997. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.10.010. PMID: 21353158.
Article8. Li X, Li Y, Cao Y, Li P, Liang B, Sun J, et al. 2017; Safety and efficacy of fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy and stereotactic radiosurgery for treatment of pituitary adenomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol Sci. 372:110–116. DOI: 10.1016/j.jns.2016.11.024. PMID: 28017195.
Article9. Yeung D, Palta J, Fontanesi J, Kun L. 1994; Systematic analysis of errors in target localization and treatment delivery in stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 28:493–498. DOI: 10.1016/0360-3016(94)90076-0. PMID: 8276666.
Article10. Van Buren JM, Houdek P, Ginsberg M. 1983; A multipurpose CT-guided stereotactic instrument of simple design. Appl Neurophysiol. 46:211–216. DOI: 10.1159/000101264. PMID: 6367649.
Article11. Lightstone AW, Benedict SH, Bova FJ, Solberg TD, Stern RL. 2005; Intracranial stereotactic positioning systems: report of the American Association of Physicists in Medicine Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group no. 68. Med Phys. 32:2380–2398. DOI: 10.1118/1.1945347.
Article12. Otto K. 2008; Volumetric modulated arc therapy: IMRT in a single gantry arc. Med Phys. 35:310–317. DOI: 10.1118/1.2818738. PMID: 18293586.
Article13. Roa DE, Schiffner DC, Zhang J, Dietrich SN, Kuo JV, Wong J, et al. 2012; The use of RapidArc volumetric-modulated arc therapy to deliver stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotactic body radiotherapy to intracranial and extracranial targets. Med Dosim. 37:257–264. DOI: 10.1016/j.meddos.2011.09.005. PMID: 22365418.
Article14. Clark GM, Popple RA, Prendergast BM, Spencer SA, Thomas EM, Stewart JG, et al. 2012; Plan quality and treatment planning technique for single isocenter cranial radiosurgery with volumetric modulated arc therapy. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2:306–313. DOI: 10.1016/j.prro.2011.12.003. PMID: 24674169.
Article15. Clark GM, Popple RA, Young PE, Fiveash JB. 2010; Feasibility of single-isocenter volumetric modulated arc radiosurgery for treatment of multiple brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 76:296–302. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.05.029. PMID: 19836151.
Article16. Vergalasova I, Liu H, Alonso-Basanta M, Dong L, Li J, Nie K, et al. 2019; Multi-institutional dosimetric evaluation of modern day stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) treatment options for multiple brain metastases. Front Oncol. 9:483. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00483. PMID: 31231614. PMCID: PMC6568036.
Article17. Smyth G, Evans PM, Bamber JC, Bedford JL. 2019; Recent developments in non-coplanar radiotherapy. Br J Radiol. 92:20180908. DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20180908. PMID: 30694086. PMCID: PMC6580906.
Article18. Ruggieri R, Naccarato S, Mazzola R, Ricchetti F, Corradini S, Fiorentino A, et al. 2018; Linac-based VMAT radiosurgery for multiple brain lesions: comparison between a conventional multi-isocenter approach and a new dedicated mono-isocenter technique. Radiat Oncol. 13:38. DOI: 10.1186/s13014-018-0985-2. PMID: 29506539. PMCID: PMC5836328.
Article19. Benedict SH, Yenice KM, Followill D, Galvin JM, Hinson W, Kavanagh B, et al. 2010; Stereotactic body radiation therapy: the report of AAPM Task Group 101. Med Phys. 37:4078–4101. Erratum in: Med Phys. 2023;50:3885. DOI: 10.1002/mp.16159. PMID: 36695548.
Article20. Ahn BS, Park SY, Park JM, Choi CH, Chun M, Kim JI. 2017; Dosimetric effects of sectional adjustments of collimator angles on volumetric modulated arc therapy for irregularly-shaped targets. PLoS One. 12:e0174924. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174924. PMID: 28384262. PMCID: PMC5383152.
Article21. Hodapp N. 2012; [The ICRU Report 83: prescribing, recording and reporting photon-beam intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT)]. Strahlenther Onkol. 188:97–99. German. DOI: 10.1007/s00066-011-0015-x. PMID: 22234506.22. Park JM, Park SY, Ye SJ, Kim JH, Carlson J, Wu HG. 2014; New conformity indices based on the calculation of distances between the target volume and the volume of reference isodose. Br J Radiol. 87:20140342. DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20140342. PMID: 25225915. PMCID: PMC4207167.
Article23. Masi L, Doro R, Favuzza V, Cipressi S, Livi L. 2013; Impact of plan parameters on the dosimetric accuracy of volumetric modulated arc therapy. Med Phys. 40(7):071718. DOI: 10.1118/1.4810969. PMID: 23822422.
Article24. Dong P, Lee P, Ruan D, Long T, Romeijn E, Low DA, et al. 2013; 4π noncoplanar stereotactic body radiation therapy for centrally located or larger lung tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 86:407–413. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.02.002. PMID: 23523322.
Article25. Rwigema JC, Nguyen D, Heron DE, Chen AM, Lee P, Wang PC, et al. 2015; 4π noncoplanar stereotactic body radiation therapy for head-and-neck cancer: potential to improve tumor control and late toxicity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 91:401–409. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2014.09.043. PMID: 25482301.
Article26. Nguyen D, Rwigema JC, Yu VY, Kaprealian T, Kupelian P, Selch M, et al. 2014; Feasibility of extreme dose escalation for glioblastoma multiforme using 4π radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol. 9:239. DOI: 10.1186/s13014-014-0239-x. PMID: 25377756. PMCID: PMC4230756.
Article27. Ohira S, Ueda Y, Isono M, Masaoka A, Hashimoto M, Miyazaki M, et al. 2017; Can clinically relevant dose errors in patient anatomy be detected by gamma passing rate or modulation complexity score in volumetric-modulated arc therapy for intracranial tumors? J Radiat Res. 58:685–692. DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrx006. PMID: 28339918. PMCID: PMC5737460.
Article28. Tanyi JA, Summers PA, McCracken CL, Chen Y, Ku LC, Fuss M. 2009; Implications of a high-definition multileaf collimator (HD-MLC) on treatment planning techniques for stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT): a planning study. Radiat Oncol. 4:22. DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-4-22. PMID: 19591687. PMCID: PMC2716348.
Article29. Asnaashari K, Chow JC, Heydarian M. 2013; Dosimetric comparison between two MLC systems commonly used for stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy: a Monte Carlo and experimental study. Phys Med. 29:350–356. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2012.05.001. PMID: 22658764.
Article30. Subramanian SV, Subramani V, Thirumalai Swamy S, Gandhi A, Chilukuri S, Kathirvel M. 2015; Is 5 mm MMLC suitable for VMAT-based lung SBRT? A dosimetric comparison with 2.5 mm HDMLC using RTOG-0813 treatment planning criteria for both conventional and high-dose flattening filter-free photon beams. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 16:112–124. DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v16i4.5415. PMID: 26219006. PMCID: PMC5690010.
Article31. Kang J, Ford EC, Smith K, Wong J, McNutt TR. 2010; A method for optimizing LINAC treatment geometry for volumetric modulated arc therapy of multiple brain metastases. Med Phys. 37:4146–4154. DOI: 10.1118/1.3455286. PMID: 20879575.
Article32. Wu Q, Snyder KC, Liu C, Huang Y, Zhao B, Chetty IJ, et al. 2016; Optimization of treatment geometry to reduce normal brain dose in radiosurgery of multiple brain metastases with single-isocenter volumetric modulated arc therapy. Sci Rep. 6:34511. DOI: 10.1038/srep34511. PMID: 27688047. PMCID: PMC5043272.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dosimetric comparison of volumetric modulated arc therapy with robotic stereotactic radiation therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases
- Characteristics and Treatments of Large Cystic Brain Metastasis: Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Aspiration
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Metastatic Brain Tumor
- Fractionated Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases Using the Novalis Tx® System