Anat Cell Biol.
2024 Jun;57(2):316-319. 10.5115/acb.23.302.
Bilateral unusual branching pattern of the external carotid artery in a human cadaver
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Histology, Cytology and Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Medical University – Pleven, Pleven, Bulgaria
- 2Department of Microbiology and Virology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Medical University – Pleven, Pleven, Bulgaria
- 3Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Medical University – Pleven, Pleven, Bulgaria
- KMID: 2556576
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.23.302
Abstract
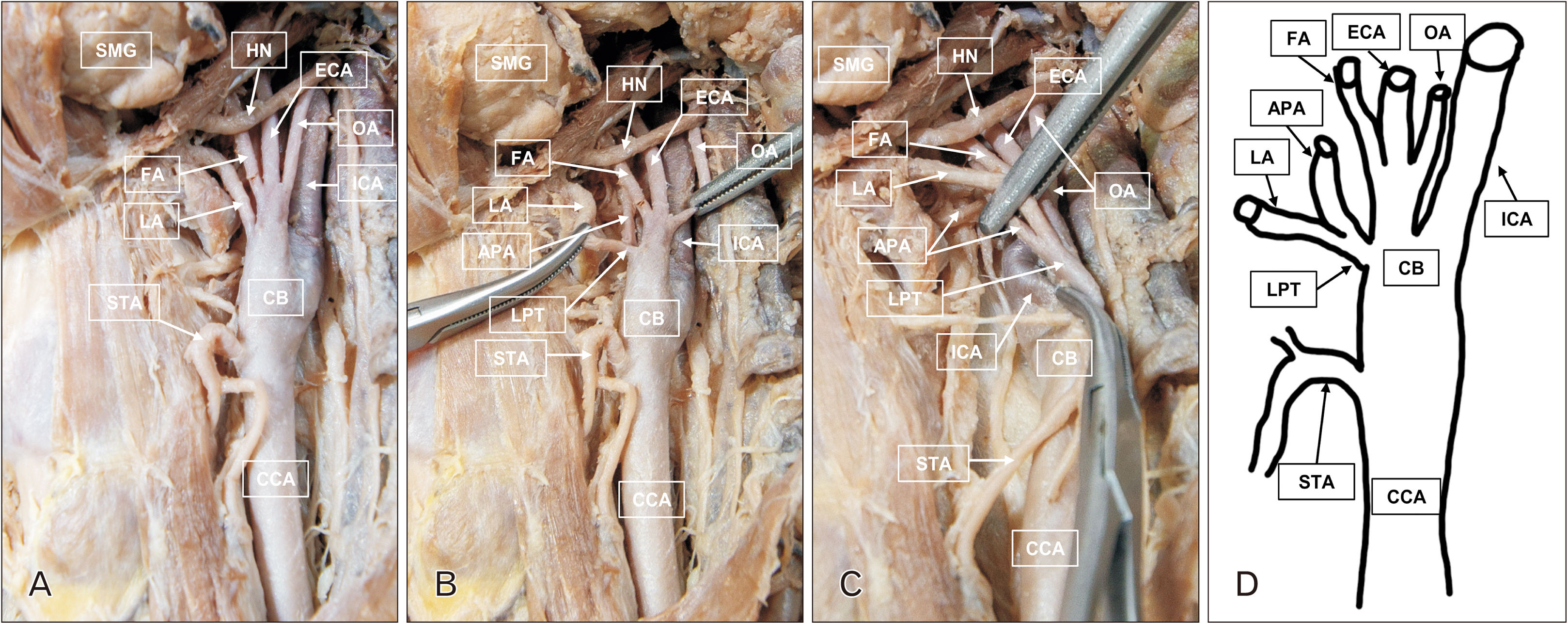
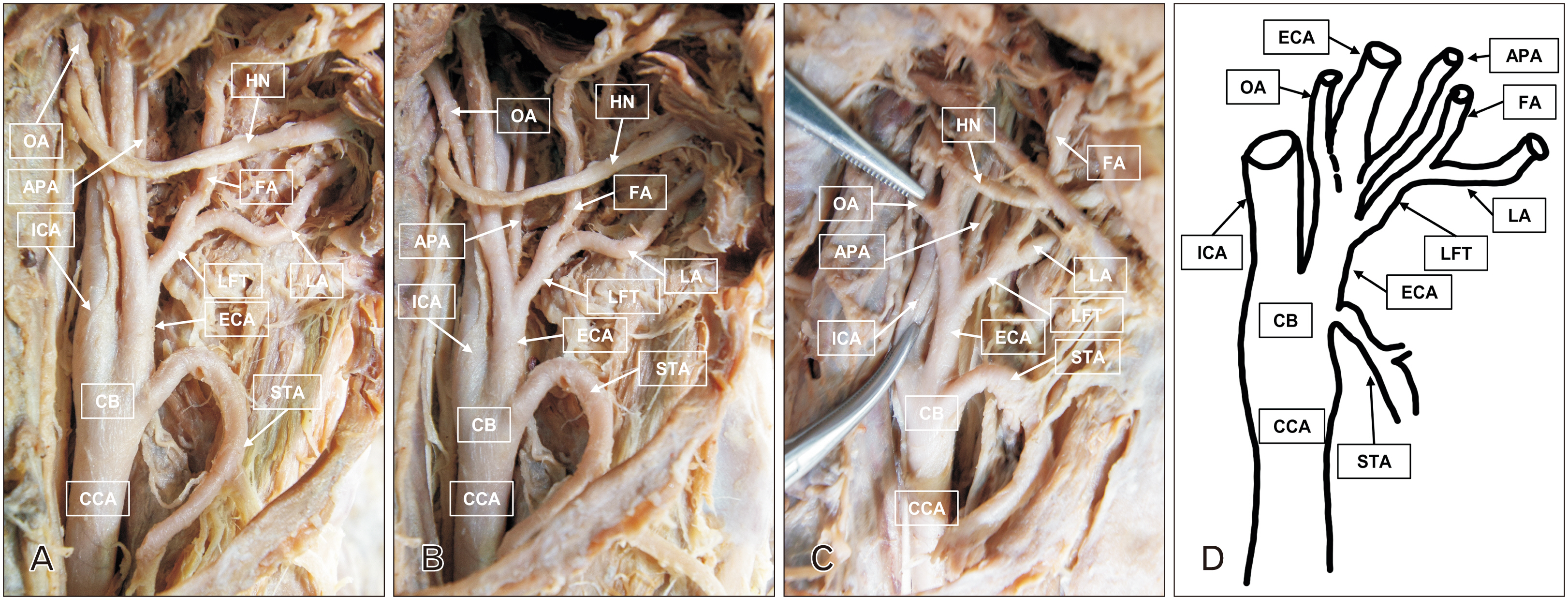
- Comprehensive understanding of the variations in the branching of the external carotid artery (ECA) is essential to minimizing vascular complications during cranio-facial and neck surgical procedures. We demonstrate a rare case of unusual branching of ECAs in both carotid triangles and anomalous origin of the left ascending pharyngeal artery (APA) during dissection of embalmed cadaver. The right and left common carotid arteries (CCA) bifurcated at the level of the upper border of the thyroid cartilage. The right superior thyroid artery (STA) originated anterior to the carotid bifurcation (CB), while the left STA originated from the anterior aspect of the left CCA. The right ECA trifurcated into linguofacial trunk, APA, and distal ECA, 15.7 mm from CB. On the left side, lingual artery and APA arose as a short common linguopharyngeal trunk, 1.9 mm from CB. The left facial and occipital arteries originated anteromedially and posteriorly at the same level.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Standring S. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 42nd ed. Elsevier;2020.2. Lucev N, Bobinac D, Maric I, Drescik I. 2000; Variations of the great arteries in the carotid triangle. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 122:590–1. DOI: 10.1067/mhn.2000.97982. PMID: 10740186.
Article3. Gluncic V, Petanjek Z, Marusic A, Gluncic I. 2001; High bifurcation of common carotid artery, anomalous origin of ascending pharyngeal artery and anomalous branching pattern of external carotid artery. Surg Radiol Anat. 23:123–5. DOI: 10.1007/s00276-001-0123-x. PMID: 11462860.
Article4. Thwin SS, Soe MM, Myint M, Than M, Lwin S. 2010; Variations of the origin and branches of the external carotid artery in a human cadaver. Singapore Med J. 51:e40–2. PMID: 20358142.5. Kishve PS, Kishve SP, Joshi M, Aarif SM, Kalakoti P. 2011; An unusual branching pattern of common and external carotid artery in a human cadaver: a case report. Australas Med J. 4:180–2. DOI: 10.4066/AMJ.2011.637. PMID: 23393509. PMCID: PMC3562896.
Article6. Rao TR. 2011; Unusual branching pattern of the external carotid artery in a cadaver. Chang Gung Med J. 34(6 Suppl):24–7. PMID: 22490454.7. Troupis T, Michalinos A, Dimovelis I, Demesticha T, Vlasis K, Skandalakis P. 2014; Bilateral abnormal origin of the anterior branches of the external carotid artery. Ann Vasc Surg. 28:494.e5–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.avsg.2013.04.020. PMID: 24295881.
Article8. Ogeng'o JA, Misiani MK, Loyal P, Ongeti KW, Gimongo J, Inyimili MI, Murunga AK. 2015; Variations in branching pattern of external carotid artery in a black Kenyan population. Anat J Afr. 4:584–90.9. Sanjeev IK, Anita H, Ashwini M, Mahesh U, Rairam GB. 2010; Branching pattern of external carotid artery in human cadavers. J Clin Diagn Res. 4:3128–33.10. Zümre O, Salbacak A, Ciçekcibaşi AE, Tuncer I, Seker M. 2005; Investigation of the bifurcation level of the common carotid artery and variations of the branches of the external carotid artery in human fetuses. Ann Anat. 187:361–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.aanat.2005.03.007. PMID: 16163849.
Article11. Devadas D, Pillay M, Sukumaran TT. 2018; A cadaveric study on variations in branching pattern of external carotid artery. Anat Cell Biol. 51:225–31. DOI: 10.5115/acb.2018.51.4.225. PMID: 30637155. PMCID: PMC6318462.
Article12. Yamamoto D, Koizumi H, Ishima D, Kuroda H, Shibahara I, Niki J, Miyasaka K, Watanabe T, Kondo R, Kumabe T. 2019; Angiographic characterization of the external carotid artery: special attention to variations in branching patterns. Tohoku J Exp Med. 249:185–92. DOI: 10.1620/tjem.249.185. PMID: 31761818.
Article13. Won SY. 2016; Anatomical considerations of the superior thyroid artery: its origins, variations, and position relative to the hyoid bone and thyroid cartilage. Anat Cell Biol. 49:138–42. DOI: 10.5115/acb.2016.49.2.138. PMID: 27382516. PMCID: PMC4927429.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bilateral thyrolinguofacial trunk: unusual and rare branching pattern of external carotid artery
- A cadaveric study on variations in branching pattern of external carotid artery
- Tri-ramification of left external carotid artery associated with anatomical variation of its branches and aneurysm formation
- Symptomatic Bilateral Carotid Artery Occlusion: An Uncommon Pattern of Carotid Pathology
- Morphology of the aortic arch branching pattern in raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides, Gray, 1834)