Anat Cell Biol.
2024 Jun;57(2):305-315. 10.5115/acb.23.251.
Vitronectin regulates osteoclastogenesis and bone remodeling in a mouse model of osteoporosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Graduate School of Humanities and Sciences, Ochanomizu University, Tokyo, Japan
- 2Institute for Human Life Science, Ochanomizu University, Tokyo, Japan
- KMID: 2556575
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.23.251
Abstract
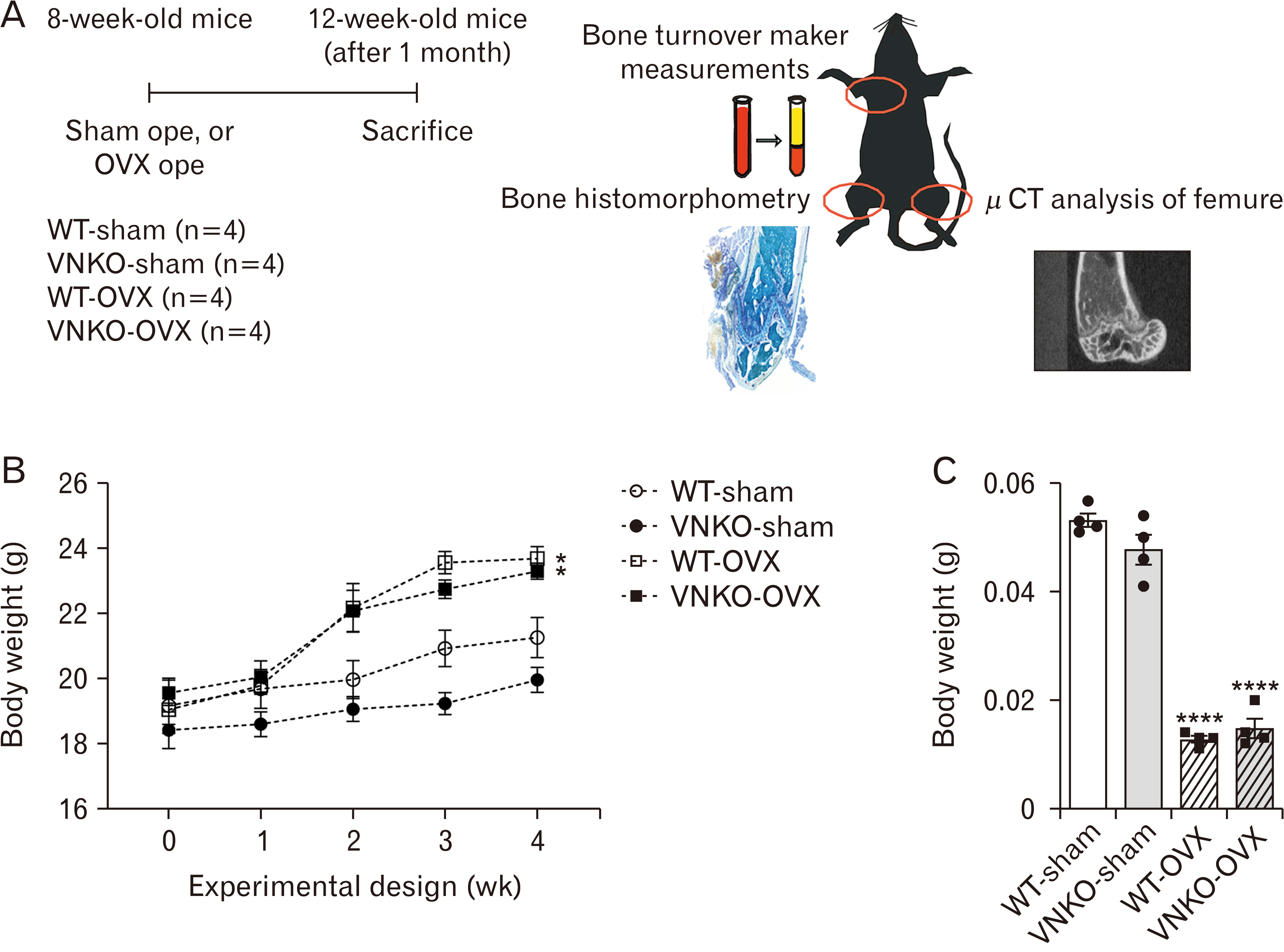
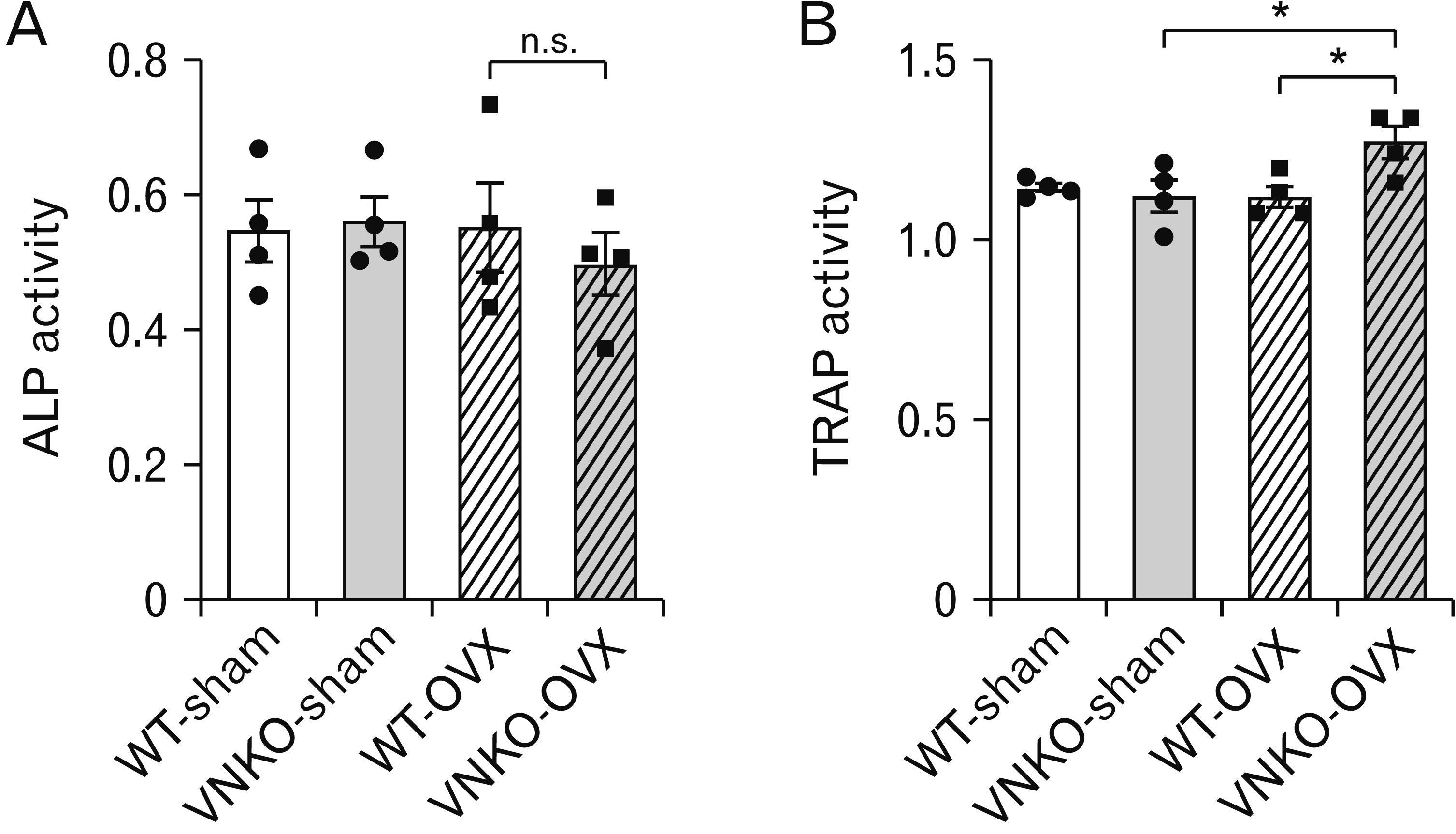
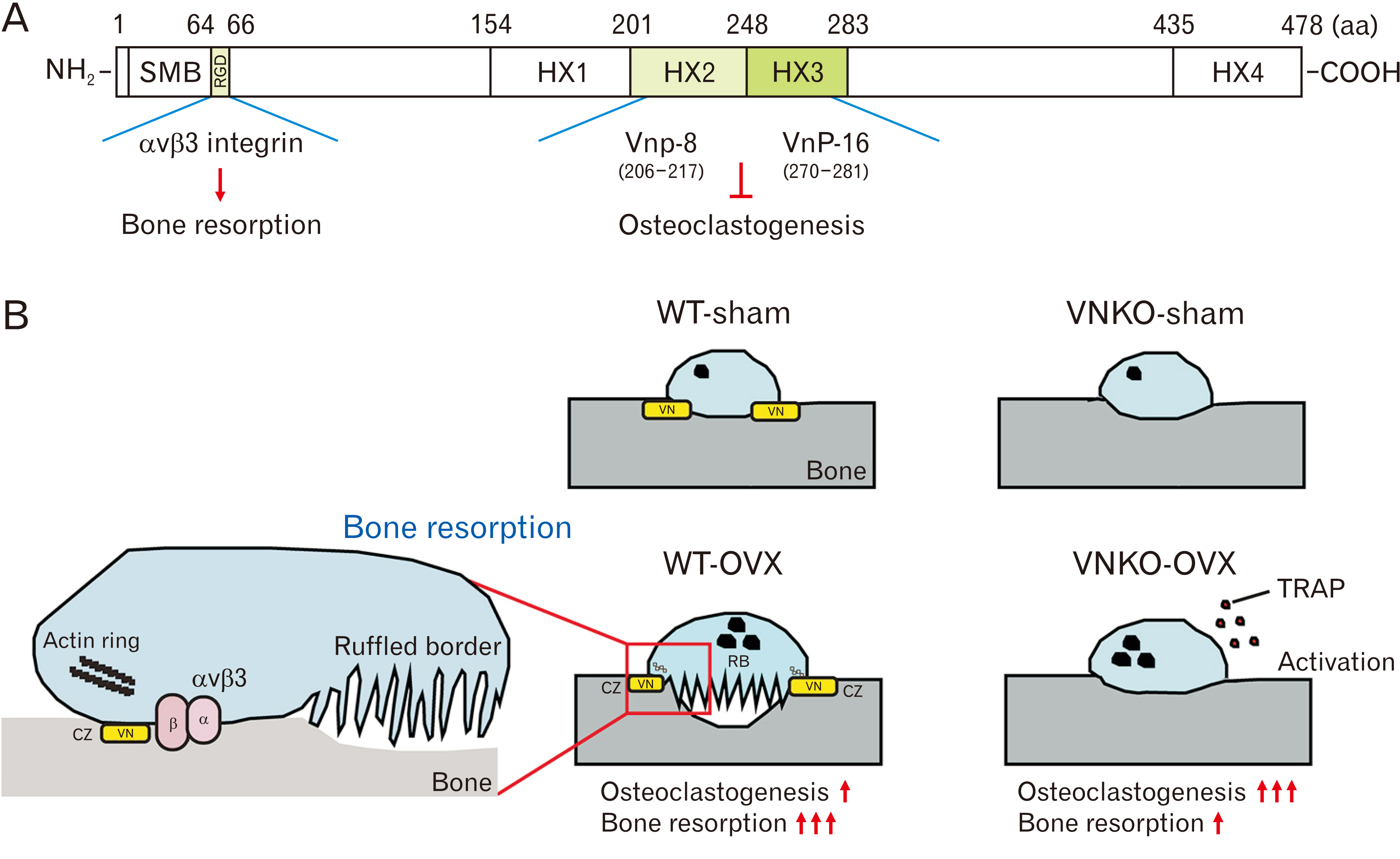
- Vitronectin (VN) is an extracellular matrix protein with a crucial role in regulating bone remodeling. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect of VN deficiency in a mouse model of osteoporosis induced by ovariectomy (OVX). The findings revealed that the absence of VN led to an increase in the activity of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), a marker for osteoclasts, in the plasma of OVX-operated mice. TRAP staining further demonstrated that VN deficiency resulted in a higher number of osteoclasts within the femurs of OVX-operated mice. X-ray micro-computed tomography analysis of the femurs in OVX-operated mice indicated that VN deficiency significantly suppressed the OVX-induced increase of marrow area and total volume of bone. Additionally, we assessed structural model index (SMI) and degree of anisotropy (DA) as indices of osteoporosis. The results showed that VN deficiency effectively attenuated the OVX-induced increase in SMI and DA among OVX-operated mice. In summary, our study demonstrates the vital role of VN in regulating osteoclastogenesis and bone remodeling in the mouse model of osteoporosis.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Wang L, You X, Zhang L, Zhang C, Zou W. 2022; Mechanical regulation of bone remodeling. Bone Res. 10:16. DOI: 10.1038/s41413-022-00190-4. PMID: 35181672. PMCID: PMC8857305.
Article2. Brun P, Scorzeto M, Vassanelli S, Castagliuolo I, Palù G, Ghezzo F, Messina GM, Iucci G, Battaglia V, Sivolella S, Bagno A, Polzonetti G, Marletta G, Dettin M. 2013; Mechanisms underlying the attachment and spreading of human osteoblasts: from transient interactions to focal adhesions on vitronectin-grafted bioactive surfaces. Acta Biomater. 9:6105–15. DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.12.018. PMID: 23261922.
Article3. Raisz LG. 2005; Pathogenesis of osteoporosis: concepts, conflicts, and prospects. J Clin Invest. 115:3318–25. DOI: 10.1172/JCI27071. PMID: 16322775. PMCID: PMC1297264.
Article4. Tella SH, Gallagher JC. 2014; Prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 142:155–70. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.09.008. PMID: 24176761. PMCID: PMC4187361.
Article5. Klein-Nulend J, van Oers RF, Bakker AD, Bacabac RG. 2015; Bone cell mechanosensitivity, estrogen deficiency, and osteoporosis. J Biomech. 48:855–65. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2014.12.007. PMID: 25582356.
Article6. Hayman EG, Pierschbacher MD, Ohgren Y, Ruoslahti E. 1983; Serum spreading factor (vitronectin) is present at the cell surface and in tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 80:4003–7. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4003. PMID: 6191326. PMCID: PMC394188.
Article7. Seiffert D. 1996; Detection of vitronectin in mineralized bone matrix. J Histochem Cytochem. 44:275–80. DOI: 10.1177/44.3.8648088. PMID: 8648088.
Article8. Min SK, Kang HK, Jung SY, Jang DH, Min BM. 2018; A vitronectin-derived peptide reverses ovariectomy-induced bone loss via regulation of osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. Cell Death Differ. 25:268–81. DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2017.153. PMID: 28937683. PMCID: PMC5762842.
Article9. Lee J, Min HK, Park CY, Kang HK, Jung SY, Min BM. 2022; A vitronectin-derived peptide prevents and restores alveolar bone loss by modulating bone re-modelling and expression of RANKL and IL-17A. J Clin Periodontol. 49:799–813. DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.13671. PMID: 35634689.
Article10. Date K, Sakagami H, Yura K. 2021; Regulatory properties of vitronectin and its glycosylation in collagen fibril formation and collagen-degrading enzyme cathepsin K activity. Sci Rep. 11:12023. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-91353-6. PMID: 34103584. PMCID: PMC8187593.
Article11. Fuller K, Ross JL, Szewczyk KA, Moss R, Chambers TJ. 2010; Bone is not essential for osteoclast activation. PLoS One. 5:e12837. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012837. PMID: 20862258. PMCID: PMC2941467.
Article12. Dutra SGV, Felix ACS, Gastaldi AC, De Paula Facioli T, Vieira S, De Souza HCD. 2017; Chronic treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor increases cardiac fibrosis in young rats submitted to early ovarian failure. Auton Neurosci. 206:28–34. DOI: 10.1016/j.autneu.2017.07.001. PMID: 28712539.
Article13. Ikegami H, Kawawa R, Ichi I, Ishikawa T, Koike T, Aoki Y, Fujiwara Y. 2017; Excessive vitamin E intake does not cause bone loss in male or ovariectomized female mice fed normal or high-fat diets. J Nutr. 147:1932–7. DOI: 10.3945/jn.117.248575. PMID: 28835390.
Article14. Li X, Udagawa N, Itoh K, Suda K, Murase Y, Nishihara T, Suda T, Takahashi N. 2002; p38 MAPK-mediated signals are required for inducing osteoclast differentiation but not for osteoclast function. Endocrinology. 143:3105–13. DOI: 10.1210/endo.143.8.8954. PMID: 12130576.
Article15. Feik SA, Thomas CD, Clement JG. 1997; Age-related changes in cortical porosity of the midshaft of the human femur. J Anat. 191(Pt 3):407–16. DOI: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.1997.19130407.x. PMID: 9418997. PMCID: PMC1467697.
Article16. Thomas CD, Feik SA, Clement JG. 2005; Regional variation of intracortical porosity in the midshaft of the human femur: age and sex differences. J Anat. 206:115–25. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00384.x. PMID: 15730477. PMCID: PMC1571459.
Article17. Lee SH, Kim JN, Shin KJ, Koh KS, Song WC. 2020; Three-dimensional microstructures of the intracortical canals in the animal model of osteoporosis. Anat Cell Biol. 53:162–8. DOI: 10.5115/acb.19.189. PMID: 32647084. PMCID: PMC7343558.
Article18. Wang B, Dong Y, Tian Z, Chen Y, Dong S. 2021; The role of dendritic cells derived osteoclasts in bone destruction diseases. Genes Dis. 8:401–11. DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2020.03.009. PMID: 34179305. PMCID: PMC8209356.
Article19. Väänänen HK, Zhao H, Mulari M, Halleen JM. 2000; The cell biology of osteoclast function. J Cell Sci. 113(Pt 3):377–81. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.113.3.377. PMID: 10639325.
Article20. Takeshita S, Kaji K, Kudo A. 2000; Identification and characterization of the new osteoclast progenitor with macrophage phenotypes being able to differentiate into mature osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res. 15:1477–88. DOI: 10.1359/jbmr.2000.15.8.1477. PMID: 10934646.
Article21. Tsurukai T, Udagawa N, Matsuzaki K, Takahashi N, Suda T. 2000; Roles of macrophage-colony stimulating factor and osteoclast differentiation factor in osteoclastogenesis. J Bone Miner Metab. 18:177–84. DOI: 10.1007/s007740070018. PMID: 10874596.
Article22. Jung SY, Min BM. 2022; A vitronectin-derived dimeric peptide suppresses osteoclastogenesis by binding to c-Fms and inhibiting M-CSF signaling. Exp Cell Res. 418:113252. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2022.113252. PMID: 35697077.
Article23. Kang HK, Park CY, Jung SY, Jo SB, Min BM. 2022; A vitronectin-derived peptide restores ovariectomy-induced bone loss by dual regulation of bone remodeling. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 19:1359–76. DOI: 10.1007/s13770-022-00486-w. PMID: 36207661. PMCID: PMC9679078.
Article24. Gramoun A, Azizi N, Sodek J, Heersche JN, Nakchbandi I, Manolson MF. 2010; Fibronectin inhibits osteoclastogenesis while enhancing osteoclast activity via nitric oxide and interleukin-1β-mediated signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem. 111:1020–34. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.22791. PMID: 20672308.
Article25. Geblinger D, Addadi L, Geiger B. 2010; Nano-topography sensing by osteoclasts. J Cell Sci. 123(Pt 9):1503–10. Erratum in: J Cell Sci 2010;123:1814. DOI: 10.1242/jcs.060954. PMID: 20375065. PMCID: PMC2858020.
Article26. Mc Donnell P, Harrison N, Liebschner MA, Mc Hugh PE. 2009; Simulation of vertebral trabecular bone loss using voxel finite element analysis. J Biomech. 42:2789–96. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.07.038. PMID: 19782987.
Article27. Ding M. 2000; Age variations in the properties of human tibial trabecular bone and cartilage. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 292:1–45. DOI: 10.1080/000164700753749791. PMID: 10951715.
Article28. Chambers TJ, Fuller K. 2011; How are osteoclasts induced to resorb bone? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1240:1–6. DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06249.x. PMID: 22172032.
Article29. Sanjay A, Houghton A, Neff L, DiDomenico E, Bardelay C, Antoine E, Levy J, Gailit J, Bowtell D, Horne WC, Baron R. 2001; Cbl associates with Pyk2 and Src to regulate Src kinase activity, alpha(v)beta(3) integrin-mediated signaling, cell adhesion, and osteoclast motility. J Cell Biol. 152:181–95. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.152.1.181. PMID: 11149930. PMCID: PMC2193648.30. Lakkakorpi PT, Horton MA, Helfrich MH, Karhukorpi EK, Väänänen HK. 1991; Vitronectin receptor has a role in bone resorption but does not mediate tight sealing zone attachment of osteoclasts to the bone surface. J Cell Biol. 115:1179–86. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.1179. PMID: 1720122. PMCID: PMC2289948.
Article31. Burgess TL, Qian Y, Kaufman S, Ring BD, Van G, Capparelli C, Kelley M, Hsu H, Boyle WJ, Dunstan CR, Hu S, Lacey DL. 1999; The ligand for osteoprotegerin (OPGL) directly activates mature osteoclasts. J Cell Biol. 145:527–38. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.145.3.527. PMID: 10225954. PMCID: PMC2185088.
Article32. Novack DV, Faccio R. 2011; Osteoclast motility: putting the brakes on bone resorption. Ageing Res Rev. 10:54–61. DOI: 10.1016/j.arr.2009.09.005. PMID: 19788940. PMCID: PMC2888603.
Article33. Stenbeck G. 2002; Formation and function of the ruffled border in osteoclasts. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 13:285–92. DOI: 10.1016/S1084952102000587. PMID: 12243728.
Article34. Davies J, Warwick J, Totty N, Philp R, Helfrich M, Horton M. 1989; The osteoclast functional antigen, implicated in the regulation of bone resorption, is biochemically related to the vitronectin receptor. J Cell Biol. 109(4 Pt 1):1817–26. DOI: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1817. PMID: 2477382. PMCID: PMC2115816.
Article35. Nesbitt S, Nesbit A, Helfrich M, Horton M. 1993; Biochemical characterization of human osteoclast integrins. Osteoclasts express alpha v beta 3, alpha 2 beta 1, and alpha v beta 1 integrins. J Biol Chem. 268:16737–45. DOI: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)85479-0. PMID: 8344953.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Vitronectin-Derived Peptide Restores Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss by Dual Regulation of Bone Remodeling
- Factors and Mechanisms Involved in the Coupling from Bone Resorption to Formation: How Osteoclasts Talk to Osteoblasts
- New Antiresorptive Therapies for Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
- Emerging Anabolic Therapies for Osteoporosis
- High extracellular Ca2+ alone stimulates osteoclast formation but inhibits in the presence of other osteoclastogenic factors