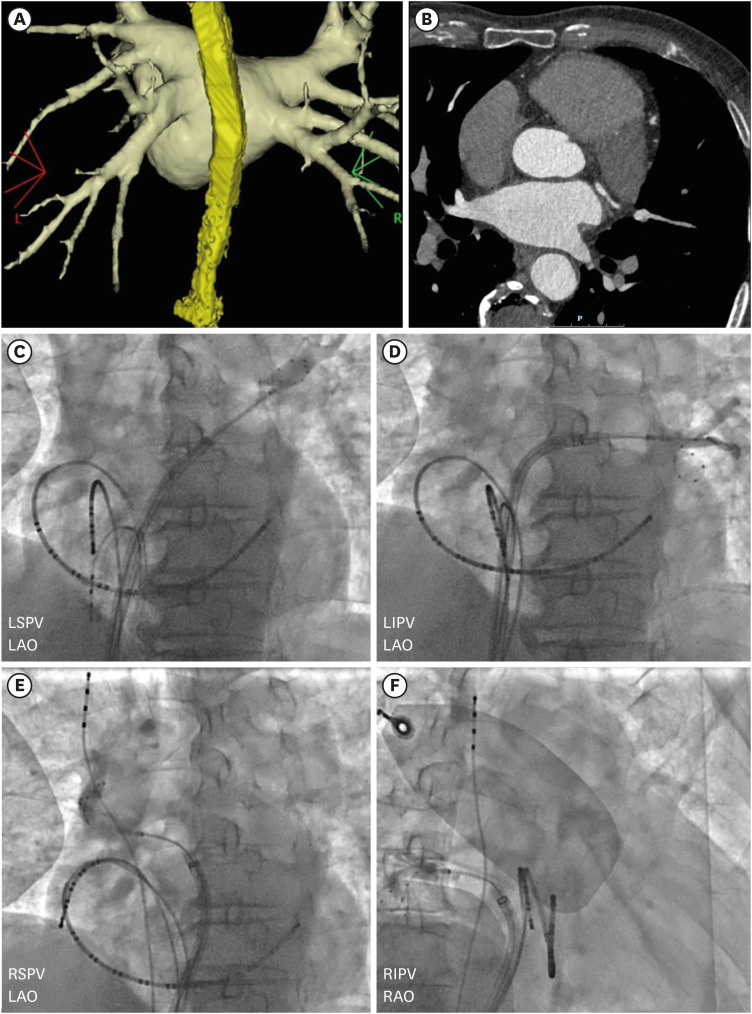
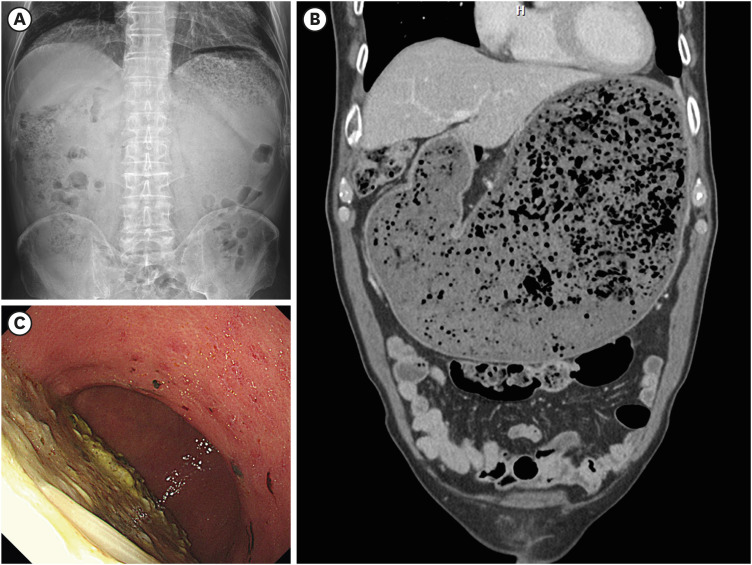
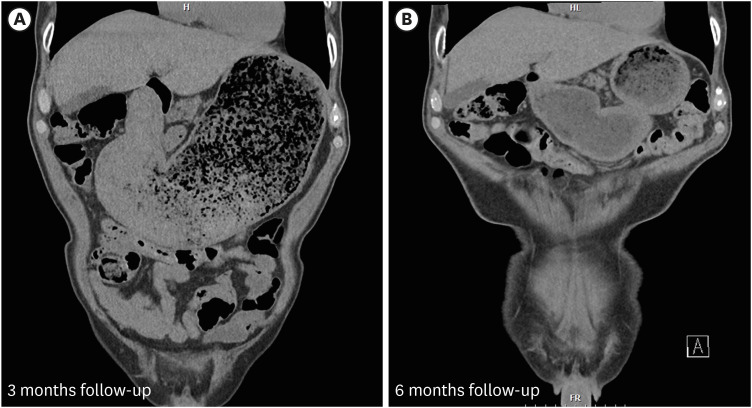
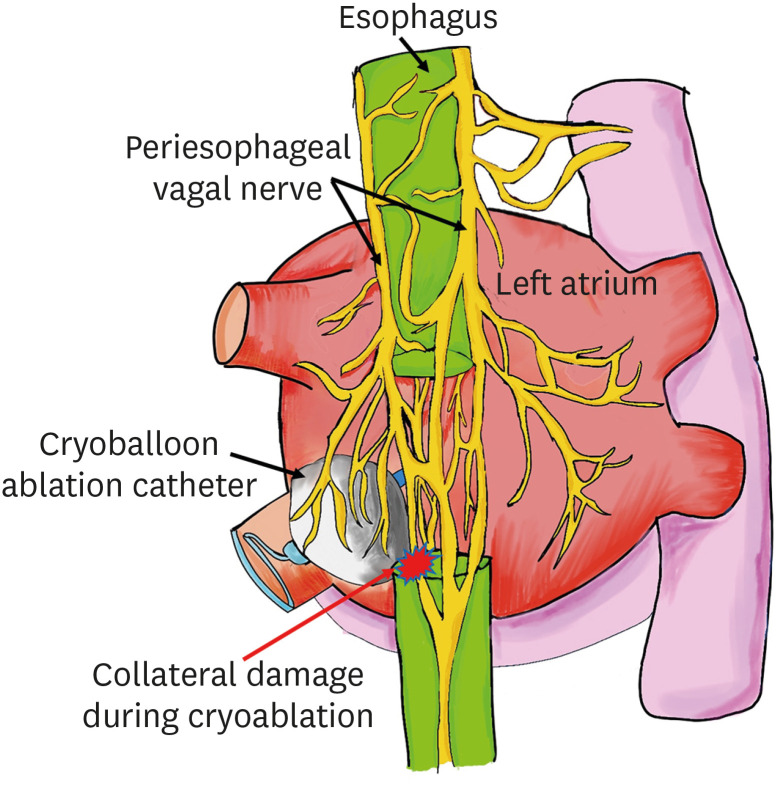
Korean Circ J.
2024 Jun;54(6):357-360. 10.4070/kcj.2024.0009.
Symptomatic Gastroparesis After Cryoballoon Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 2Department of Cardiology, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 3Department of Cardiology, Hanyang University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2556535
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2024.0009
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shah D, Dumonceau JM, Burri H, et al. Acute pyloric spasm and gastric hypomotility: an extracardiac adverse effect of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005; 46:327–330. PMID: 16022963.2. Akhtar T, Calkins H, Bulat R, Pollack MM, Spragg DD. Atrial fibrillation ablation-induced gastroparesis: a case report and literature review. HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2020; 6:249–252. PMID: 32461887.3. Yakabe D, Fukuyama Y, Araki M, Nakamura T. Anatomical evaluation of the esophagus using computed tomography to predict acute gastroparesis following atrial fibrillation ablation. J Arrhythm. 2021; 37:1330–1336. PMID: 34621432.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cryoballoon Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation: a Comprehensive Review and Practice Guide
- Cryoballoon or Radiofrequency Ablation for Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation
- Pulmonary veins isolation using cryoballoon and pulsed field ablation for atrial fibrillation: practical techniques in variable scenarios
- A Case of Successful Ablation of Right-Sided Accessory Pathway during Atrial Fibrillation
- Is ICE-Guided Cryoballoon Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation a New Advancement?