Ewha Med J.
2024 Apr;47(2):e22. 10.12771/emj.2024.e22.
What is the role of artificial intelligence in general surgery?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Critical Care Medicine, Department of Surgery, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Colorectal Surgery, Department of Surgery, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2556311
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2024.e22
Abstract
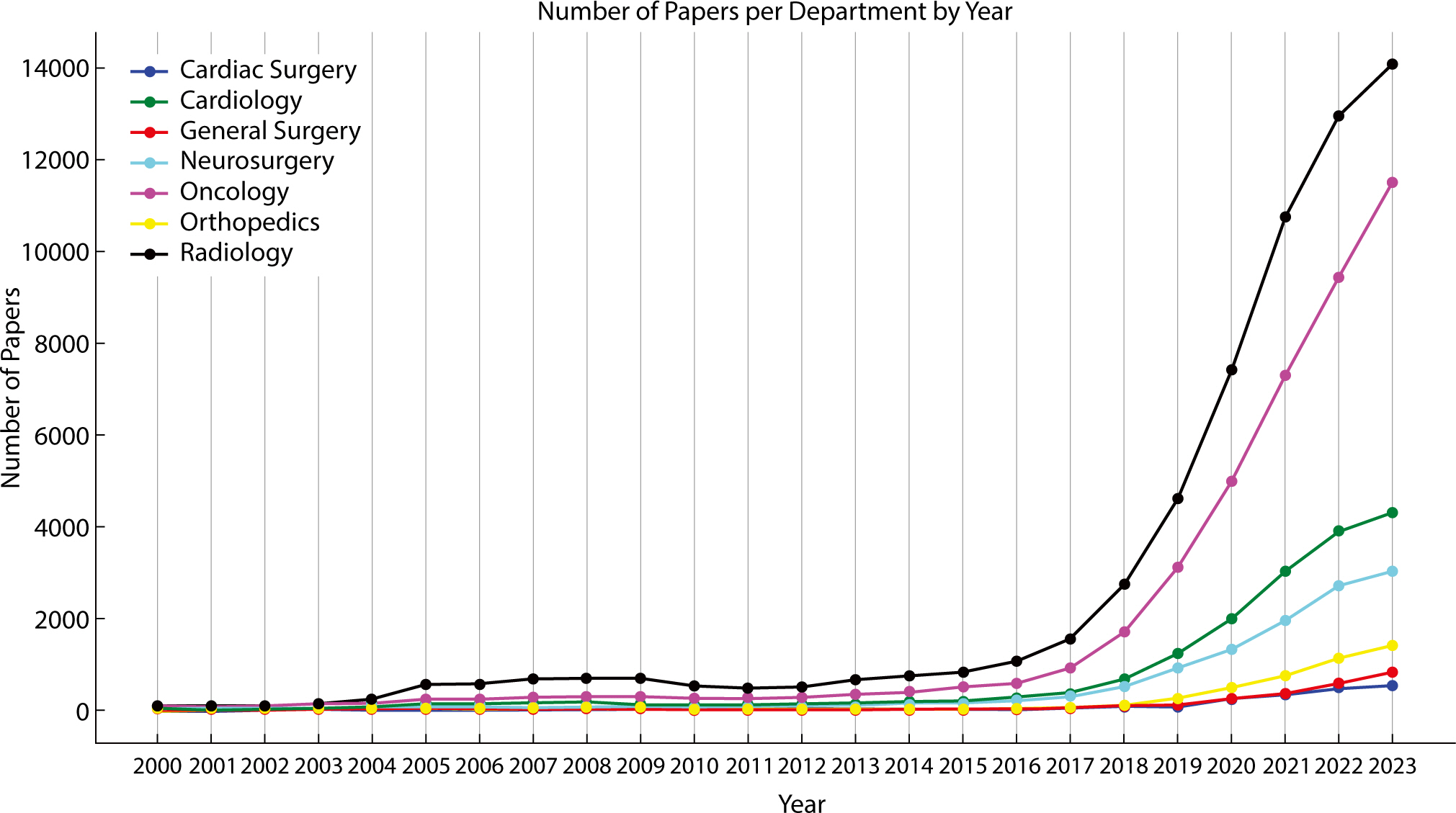
- The capabilities of artificial intelligence (AI) have recently surged, largely due to advancements in deep learning inspired by the structure and function of the neural networks of the human brain. In the medical field, the impact of AI spans from diagnostics and treatment recommendations to patient engagement and monitoring, considerably improving efficiency and outcomes. The clinical integration of AI has also been examined in specialties, including pathology, radiology, and oncology. General surgery primarily involves manual manipulation and includes preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care, all of which are critical for saving lives. Other fields have strived to utilize and adopt AI; nonetheless, general surgery appears to have retrogressed. In this review, we analyzed the published research, to understand how the application of AI in general surgery differs from that in other medical fields. Based on previous research in other fields, the application of AI in the preoperative stage is nearing feasibility. Ongoing research efforts aim to utilize AI to improve and predict operative outcomes, enhance performance, and improve patient care. However, the use of AI in the operating room remains significantly understudied. Moreover, ethical responsibilities are associated with such research, necessitating extensive work to gather evidence. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration and leveraging lessons from AI success stories in other fields, AI tools could be specifically tailored for general surgery. Surgeons should be prepared for the integration of AI into clinical practice to achieve better outcomes; therefore, the time has come to consider ethical and legal implications.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Mehta V. Artificial intelligence in medicine: revolutionizing healthcare for improved patient outcomes. J Med Res Innov. 2023; 7(2):e000292. DOI: 10.32892/jmri.292.2. Manfred D. Artificial intelligence (AI): what are the impacts for medicine? J Artif Intell Cloud Comput. 2019; 2(2):1–3. DOI: 10.47363/JAICC/2023(2)117.3. Paudyal R, Shah AD, Akin O, Do RKG, Konar AS, Hatzoglou V, et al. Artificial intelligence in CT and MR imaging for oncological applications. Cancers. 2023; 15(9):2573. DOI: 10.3390/cancers15092573. PMID: 37174039. PMCID: PMC10177423.4. Derevianko A, Pizzoli SFM, Pesapane F, Rotili A, Monzani D, Grasso R, et al. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in the radiology field: what is the state of doctor–patient communication in cancer diagnosis? Cancers. 2023; 15(2):470. DOI: 10.3390/cancers15020470. PMID: 36672417. PMCID: PMC9856827.5. Ram S, Bodduluri S. Implementation of artificial intelligence–assisted chest X-ray interpretation: it is about time. Am Thorac Soc. 2023; 20(5):641–642. DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202303-195ED. PMID: 37126001. PMCID: PMC10174129.6. Harry A. The future of medicine: harnessing the power of AI for revolutionizing healthcare. Int J Multidiscip Sci Arts. 2023; 2(1):36–47. DOI: 10.47709/ijmdsa.v2i1.2395.7. Demetriou DD, Hull R, Kgoebane-Maseko M, Lockhat Z, Dlamini Z. AI-enhanced digital pathology and radiogenomics in precision oncology. In. Dlamini Z, editor. editor. Artificial intelligence and precision oncology: bridging cancer research and clinical decision support. Cham:: 1Springer;2023. p. p. 93–113. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-21506-3_5.8. Zeineldin RA, Junger D, Mathis-Ullrich F, Burgert O. Development of an AI-driven system for neurosurgery with a usability study: a step towards minimal invasive robotics. at - Automatisierungstechnik. 2023; 71(7):537–546. DOI: 10.1515/auto-2023-0061.9. Vidal-Perez R, Vazquez-Rodriguez JM. Role of artificial intelligence in cardiology. World J Cardiol. 2023; 15(4):116–118. DOI: 10.4330/wjc.v15.i4.116. PMID: 37124979. PMCID: PMC10130891.10. Voskens FJ, Abbing JR, Ruys AT, Ruurda JP, Broeders IAMJ. A nationwide survey on the perceptions of general surgeons on artificial intelligence. Artif Intell Surg. 2022; 2(1):8–17. DOI: 10.20517/ais.2021.10.11. Lång K, Josefsson V, Larsson AM, Larsson S, Högberg C, Sartor H, et al. Artificial intelligence-supported screen reading versus standard double reading in the Mammography Screening with Artificial Intelligence trial (MASAI): a clinical safety analysis of a randomised, controlled, non-inferiority, single-blinded, screening accuracy study. Lancet Oncol. 2023; 24(8):936–944. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(23)00298-X. PMID: 37541274.12. Nam JG, Hwang EJ, Kim J, Park N, Lee EH, Kim HJ, et al. AI improves nodule detection on chest radiographs in a health screening population: a randomized controlled trial. Radiology. 2023; 307(2):e221894. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.221894. PMID: 36749213.13. Sachpekidis C, Enqvist O, Ulén J, Kopp-Schneider A, Pan L, Jauch A, et al. Application of an artificial intelligence-based tool in [18F]FDG PET/CT for the assessment of bone marrow involvement in multiple myeloma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023; 50(12):3697–3708. DOI: 10.1007/s00259-023-06339-5. PMID: 37493665. PMCID: PMC10547616.14. Clift AK, Dodwell D, Lord S, Petrou S, Brady M, Collins GS, et al. Development and internal-external validation of statistical and machine learning models for breast cancer prognostication: cohort study. BMJ. 2023; 381:e073800. DOI: 10.1136/bmj-2022-073800. PMID: 37164379. PMCID: PMC10170264.15. Alaimo L, Lima HA, Moazzam Z, Endo Y, Yang J, Ruzzenente A, et al. Development and validation of a machine-learning model to predict early recurrence of intrahepatic xholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2023; 30(9):5406–5415. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-023-13636-8. PMID: 37210452.16. Liu M, Wu J, Wang N, Zhang X, Bai Y, Guo J, et al. The value of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLOS ONE. 2023; 18(3):e0273445. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273445. PMID: 36952523. PMCID: PMC10035910.17. Subhan S, Malik J, Haq A, Qadeer MS, Zaidi SMJ, Orooj F, et al. Role of artificial intelligence and machine learning in interventional cardiology. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023; 48(7):101698. DOI: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.101698. PMID: 36921654.18. Hughes A, Shandhi MMH, Master H, Dunn J, Brittain E. Wearable devices in cardiovascular medicine. Circ Res. 2023; 132(5):652–670. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.322389. PMID: 36862812. PMCID: PMC9991078.19. Ishii M, Kaikita K, Yasuda S, Akao M, Ako J, Matoba T, et al. Risk prediction score for clinical outcome in atrial fibrillation and stable coronary artery disease. Open Heart. 2023; 10(1):e002292. DOI: 10.1136/openhrt-2023-002292. PMID: 37173099. PMCID: PMC10186465.20. Yankam Njiwa J, Gray KR, Costes N, Mauguiere F, Ryvlin P, Hammers A. Advanced [18F]FDG and [11C]flumazenil PET analysis for individual outcome prediction after temporal lobe epilepsy surgery for hippocampal sclerosis. Neuroimage Clin. 2015; 7:122–131. DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2014.11.013. PMID: 25610774. PMCID: PMC4299974.21. Ma C, Wang L, Song D, Gao C, Jing L, Lu Y, et al. Multimodal-based machine learning strategy for accurate and non-invasive prediction of intramedullary glioma grade and mutation status of molecular markers: a retrospective study. BMC Med. 2023; 21(1):198. DOI: 10.1186/s12916-023-02898-4. PMID: 37248527. PMCID: PMC10228074.22. Liu Z, Zhang C, Ge S. Efficacy and safety of robotic-assisted versus median sternotomy for cardiac surgery: results from a university affiliated hospital. J Thorac Dis. 2023; 15(4):1861–1871. DOI: 10.21037/jtd-23-197. PMID: 37197544. PMCID: PMC10183528.23. Fujita T, Kakuta T, Kawamoto N, Shimahara Y, Yajima S, Tadokoro N, et al. Benefits of robotically-assisted surgery for complex mitral valve repair. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2021; 32(3):417–425. DOI: 10.1093/icvts/ivaa271. PMID: 33221856. PMCID: PMC8906674.24. Palmieri V, Montisci A, Vietri MT, Colombo PC, Sala S, Maiello C, et al. Artificial intelligence, big data and heart transplantation: actualities. Int J Med Inform. 2023; 176:105110. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2023.105110. PMID: 37285695.25. Houserman DJ, Berend KR, Lombardi AV Jr, Fischetti CE, Duhaime EP, Jain A, et al. The viability of an artificial intelligence/machine learning prediction model to determine candidates for knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2023; 38(10):2075–2080. DOI: 10.1016/j.arth.2022.04.003. PMID: 35398523.26. Jang SJ, Kunze KN, Bornes TD, Anderson CG, Mayman DJ, Jerabek SA, et al. Leg-length discrepancy variability on standard anteroposterior pelvis radiographs: an analysis using deep learning measurements. J Arthroplasty. 2023; 38(10):2017–2023. E3. DOI: 10.1016/j.arth.2023.03.006. PMID: 36898486.27. Endo Y, Tokuyasu T, Mori Y, Asai K, Umezawa A, Kawamura M, et al. Impact of AI system on recognition for anatomical landmarks related to reducing bile duct injury during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surg Endosc. 2023; 37(7):5752–5759. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-023-10224-5. PMID: 37365396. PMCID: PMC10322759.28. Zhang R, Chen J, Wang Z, Yang Z, Ren Y, Shi P, et al. A step towards conditional autonomy - robotic appendectomy. IEEE Robot Autom Lett. 2023; 8(5):2429–2436. DOI: 10.1109/LRA.2023.3254859.29. Moheb M, Gebran A, Maurer LR, Naar L, El Hechi M, Breen K, et al. Artificial intelligence versus surgeon gestalt in predicting risk of emergency general surgery. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023; 95(4):565–572. DOI: 10.1097/TA.0000000000004030. PMID: 37314698.30. Tomé F, Michelin L, Lins RS, Bringmann DR, Corso LL. Using artificial neural networks for pattern recognition of post-surgical infections. Braz J Health Rev. 2023; 6(1):3329–3339. DOI: 10.34119/bjhrv6n1-260.31. Kokkinakis S, Kritsotakis EI, Lasithiotakis K. Artificial intelligence in surgical risk prediction. J Clin Med. 2023; 12(12):4016. DOI: 10.3390/jcm12124016. PMID: 37373709. PMCID: PMC10299093.32. Watanabe A, Wiseman SM. A new era in surgical research: the evolving role of artificial intelligence. Am J Surg. 2023; 226(6):923–925. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2023.06.040. PMID: 37419728.33. Rimmer L, Howard C, Picca L, Bashir M. The automaton as a surgeon: the future of artificial intelligence in emergency and general surgery. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2021; 47(3):757–762. DOI: 10.1007/s00068-020-01444-8. PMID: 32715331.34. Zhou XY, Guo Y, Shen M, Yang GZ. Application of artificial intelligence in surgery. Front Med. 2020; 14(4):417–430. DOI: 10.1007/s11684-020-0770-0. PMID: 32705406.35. Mangano A, Valle V, Dreifuss NH, Aguiluz G, Masrur MA. Role of artificial intelligence (AI) in surgery: introduction, general principles, and potential applications. Surg Technol Int. 2020; 38:17–21. DOI: 10.52198/21.STI.38.SO1369. PMID: 33370842.36. McCartney J. AI is poised to “revolutionize” surgery [Internet]. Chicago (IL): American College of Surgeons;c2023. [cited 2024 Jan 10]. Available from. https://www.facs.org/for-medical-professionals/news-publications/news-and-articles/bulletin/2023/june-2023-volume-108-issue-6/ai-is-poised-to-revolutionize-surgery/.37. Egert M, Steward JE, Sundaram CP. Machine learning and artificial intelligence in surgical fields. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2020; 11(4):573–577. DOI: 10.1007/s13193-020-01166-8. PMID: 33299275. PMCID: PMC7714893.38. Bar O, Neimark D, Zohar M, Hager GD, Girshick R, Fried GM, et al. Impact of data on generalization of AI for surgical intelligence applications. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):22208. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-79173-6. PMID: 33335191. PMCID: PMC7747564.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of artificial intelligence in diagnosing Barrett’s esophagus-related neoplasia
- The Role of medical doctor in the era of artificial intelligence
- Artificial Intelligence in Pathology
- New surgical robots on the horizon and the potential role of artificial intelligence
- Role of Artificial Intelligence in Achieving Universal Health Coverage: A Mongolian Perspective