J Korean Med Sci.
2024 May;39(20):e159. 10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e159.
A Brief Review of Anatomy Education in Korea, Encompassing Its Past, Present, and Future Direction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy and Catholic Institute for Applied Anatomy, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- 3Department of Anatomy, Jeonbuk National University Medical School and Institute for Medical Sciences, Jeonbuk National University, Jeonju, Korea
- 4Department of Anatomy, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2556282
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e159
Abstract
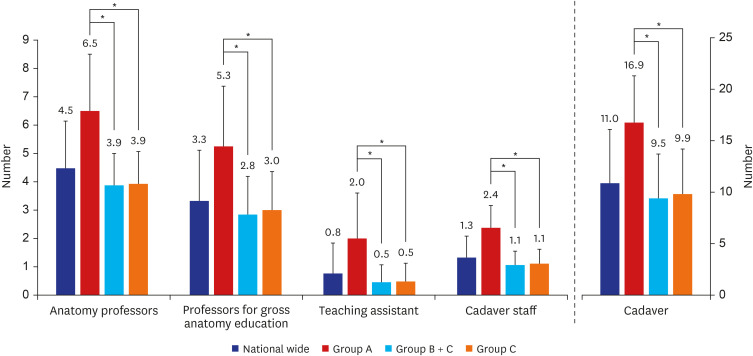
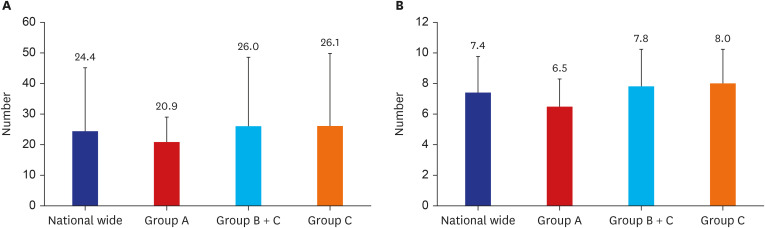
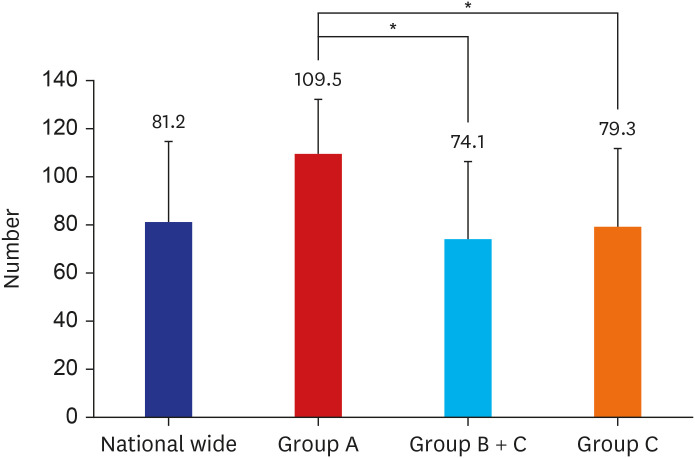
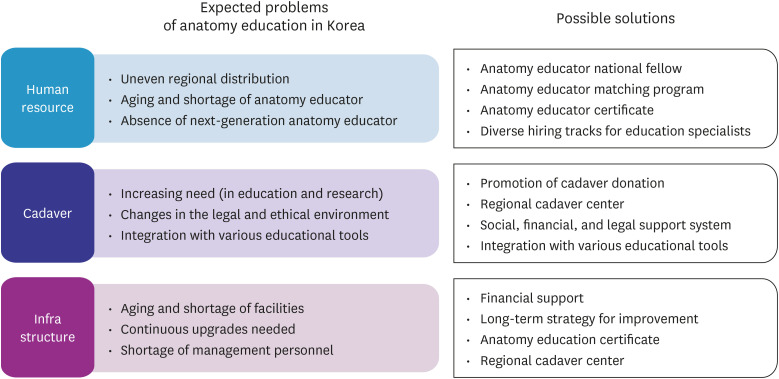
- Anatomy is a foundational subject in medicine and serves as its language. Hippocrates highlighted its importance, while Herophilus pioneered human dissection, earning him the title of the founder of anatomy. Vesalius later established modern anatomy, which has since evolved historically. In Korea, formal anatomy education for medical training began with the introduction of Western medicine during the late Joseon Dynasty. Before and after the Japanese occupation, anatomy education was conducted in the German style, and after liberation, it was maintained and developed by a small number of domestic anatomists. Medicine in Korea has grown alongside the country’s rapid economic and social development. Today, 40 medical colleges produce world-class doctors to provide the best medical care service in the country. However, the societal demand for more doctors is growing in order to proactively address to challenges such as public healthcare issues, essential healthcare provision, regional medical service disparities, and an aging population. This study examines the history, current state, and challenges of anatomy education in Korea, emphasizing the availability of medical educators, support staff, and cadavers for gross anatomy instruction. While variations exist between Seoul and provincial medical colleges, each manages to deliver adequate education under challenging conditions. However, the rapid increase in medical student enrollment threatens to strain existing anatomy education resources, potentially compromising educational quality. To address these concerns, we propose strategies for training qualified gross anatomy educators, ensuring a sustainable cadaver supply, and enhancing infrastructure.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Davis CR, Bates AS, Ellis H, Roberts AM. Human anatomy: let the students tell us how to teach. Anat Sci Educ. 2014; 7(4):262–272. PMID: 24249485.2. Sugand K, Abrahams P, Khurana A. The anatomy of anatomy: a review for its modernization. Anat Sci Educ. 2010; 3(2):83–93. PMID: 20205265.3. Persaud TV. Early History of Human Anatomy. Springfield, IL: Charles C Thomas;1984. p. 29–30.4. Debernardi A, Sala E, D’Aliberti G, Talamonti G, Franchini AF, Collice M. Alcmaeon of Croton. Neurosurgery. 2010; 66(2):247–252. PMID: 20087125.5. Kleisiaris CF, Sfakianakis C, Papathanasiou IV. Health care practices in ancient Greece: the Hippocratic ideal. J Med Ethics Hist Med. 2014; 7(6):6. PMID: 25512827.6. Reverón RR. Herophilus and Erasistratus, pioneers of human anatomical dissection. Vesalius. 2014; 20(1):55–58. PMID: 25181783.7. Dunn PM. Galen (AD 129-200) of Pergamun: anatomist and experimental physiologist. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2003; 88(5):F441–F443. PMID: 12937057.8. Wilson L. The performance of the body in the renaissance theater of anatomy. Representations (Berkeley). 1987; 17:62–95.9. Crivellato E, Ribatti D. Mondino de’ Liuzzi and his Anothomia: a milestone in the development of modern anatomy. Clin Anat. 2006; 19(7):581–587. PMID: 16583420.10. Persaud TV, Loukas M, Tubbs RS. A History of Human Anatomy. Springfield, IL, USA: Charles C Thomas;2014. p. 60–68. p. 72–75.11. Singer CJ. A Short History of Anatomy From the Greeks to Harvey. New York, NY, USA: Dover Publications;1957.12. Desmond A. The Politics of Evolution. Morphology, Medicine, and Reform in Radical London. Chicago, IL, USA: University of Chicago Press;1989.13. Cope Z. The private medical schools in London (1746-1914). Poynter FNL, editor. The Evolution of Medical Education in Britain. London, UK: Pitman Medical;1966.14. Richardson R. Death, Dissection and the Destitute. London, UK: Routledge & Kegan Paul Ltd;1987.15. Coakley D. Anatomy and art: Irish dimensions. Kennedy BP, Coakley D, editors. The Anatomy Lesson: Art and Medicine. Dublin, Ireland: The National Gallery of Ireland;1992. p. 57–58.16. Shultz SM. Body Snatching. Jefferson, NC, USA: McFarland;1992.17. Richardson R. “Trading assassins” and the licensing of anatomy. French R, Wear A, editors. British Medicine in an Age of Reform. London, UK: Routledge;1991. p. 74–91.18. Rothstein WG. American Medical Schools and the Practice of Medicine. New York, NY, USA: Oxford University Press;1987.19. McCuskey RS, Carmichael SW, Kirch DG. The importance of anatomy in health professions education and the shortage of qualified educators. Acad Med. 2005; 80(4):349–351. PMID: 15793018.20. Chang HJ, Kim HJ, Rhyu IJ, Lee YM, Uhm CS. Emotional experiences of medical students during cadaver dissection and the role of memorial ceremonies: a qualitative study. BMC Med Educ. 2018; 18(1):255. PMID: 30419880.21. Choi GY, Kim JM, Seo JH, Sohn HJ. Becoming a doctor through learning anatomy: narrative analysis of the educational experience. Korean J Phys Anthropol. 2009; 22(3):213–224.22. Franchi T. The impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on current anatomy education and future careers: a student’s perspective. Anat Sci Educ. 2020; 13(3):312–315. PMID: 32301588.23. Park B. Gov’t set to announce allocation of increased medical school seats. Yonhap News;Updated 2024. Accessed April 8, 2024. https://en.yna.co.kr/view/AEN20240320001600315 .24. Korean Association of Anatomists. History of Korean Anatomy. Seoul, Korea: Book publishing Jeong Seok;2017. p. 35p. 42p. 46p. 164–175. p. 186p. 18825. Korean Association of Basic Medical Scientists. History of Korean Basic Medical Science. Seoul, Korea: Korean Association of Basic Medical Scientists;2008. p. 63–67.26. Korean Association of Anatomists. 50th Anniversary of Korean Association of Anatomists. Seoul, Korea: Hamchun Hanhwa;1997. p. 35–37. p. 4027. Korean Association of Anatomists. Yesterday and Today of Korean Anatomy Education. Seoul, Korea: Gyechuk Munhwasa;1987. p. 50.28. Shin M, Prasad A, Sabo G, Macnow AS, Sheth NP, Cross MB, et al. Anatomy education in US medical schools: before, during, and beyond COVID-19. BMC Med Educ. 2022; 22(1):103. PMID: 35172819.29. Kim W, Kim MK, Yoo SM, Jung SH, Kim MJ, Kim SJ, et al. The Current Status and Future of Basic Medical Education in Korea. Seoul, Korea: Korea Association of Medical Colleges;2023.30. Smith CF, Freeman SK, Heylings D, Finn GM, Davies DC. Anatomy education for medical students in the United Kingdom and Republic of Ireland in 2019: A 20-year follow-up. Anat Sci Educ. 2022; 15(6):993–1006. PMID: 34314569.31. Ye Z, Dun A, Jiang H, Nie C, Zhao S, Wang T, et al. The role of 3D printed models in the teaching of human anatomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med Educ. 2020; 20(1):335. PMID: 32993608.32. da Cruz Torquato M, Menezes JM, Belchior G, Mazzotti FP, Bittar JS, Dos Santos GG, et al. Virtual reality as a complementary learning tool in anatomy education for medical students. Med Sci Educ. 2023; 33(2):507–516. PMID: 37261021.33. Memon I. Cadaver dissection is obsolete in medical training! A misinterpreted notion. Med Princ Pract. 2018; 27(3):201–210. PMID: 29529601.34. Tugtag Demir B, Altintas HM, Bilecenoglu B. Investigation of medical faculty students’ views on cadaver and cadaver teaching in anatomy. Morphologie. 2023; 107(356):47–54. PMID: 35659717.35. Tjalma WA, Degueldre M, Van Herendael B, D’Herde K, Weyers S. Postgraduate cadaver surgery: an educational course which aims at improving surgical skills. Facts Views Vis Obgyn. 2013; 5(1):61–65. PMID: 24753929.36. Attaluri P, Wirth P, Gander B, Siebert J, Upton J. Importance of cadaveric dissections and surgical simulation in plastic surgery residency. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022; 10(10):e4596. PMID: 36262687.37. Kim IB, Hwang SJ, Lee UY, Lee HJ, Cho SH, Choi JW. Study to Facilitate Cadaver Donation. Sejong, Korea: Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare;2023.38. Paik SJ. Proposal to honor and support cadaver donors to facilitate a culture of donation. In : Public Hearing Fact Sheet on the Study on How to Improve the Honor and Support System for Human Body Donation; November 24, 2023; Seoul, Korea. Seoul, Korea: Korea National Institute for Bioethics Policy;2023.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study of the Historical Development and Directions of Premedical Education
- A Proposal for the Future of Medical Education Accreditation
- Analysis of the current status of medical humanities education at domestic medical schools and proposal of educational system.
- The Future Direction of Admission Policy in Korean Medical Colleges: Quo Vadis?
- Medical Education: Past, Present, and Future