Korean J Gastroenterol.
2024 Mar;83(3):94-101. 10.4166/kjg.2024.016.
Current State of Pharmacotherapy in Obesity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung Asan Hospital, Gangneung, Korea
- KMID: 2554262
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2024.016
Abstract
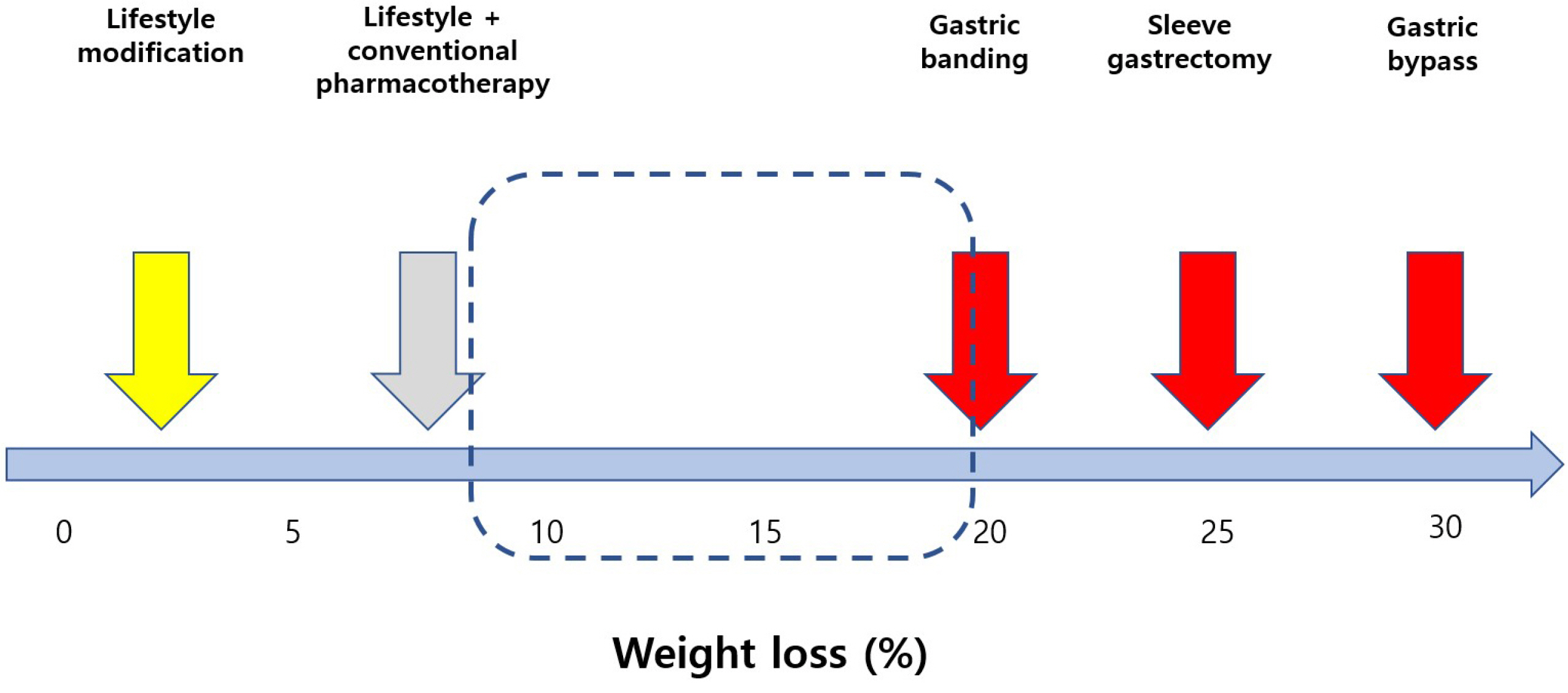
- The prevalence of obesity with various complications is increasing rapidly in Korea. Although lifestyle modification is fundamental in obesity treatment, more effective treatment tools are required. Many advances in obesity treatment have been reported recently, including lifestyle modifications and pharmacological, endoscopic, and surgical treatments. Drugs with proven long-term efficacy and safety are preferred because management for obesity treatment is a long-term process. Currently, four medications are available for long-term use in Korea: Orlistat, Naltrexone/bupuropion NR, Phentermine/topiramate capsule, and Liraglutide. Recently, semaglutide and tirzepatide have been attracting attention because of their effectiveness and convenience, but they are not yet available in Korea. In addition, there are limitations such as the yo-yo effect when discontinuing the drug, long-term safety, and cost. Patients and medical staff must be aware of the advantages and side effects of each medication to ensure the successful treatment of obesity.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park JH, Yoon SJ, Lee H, et al. 2006; Burden of disease attributable to obesity and overweight in Korea. Int J Obes (Lond). 30:1661–1669. DOI: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0803321. PMID: 16534516.
Article2. Haam JH, Kim BT, Kim EM, et al. 2023; Diagnosis of obesity: 2022 Update of clinical practice guidelines for obesity by the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. J Obes Metab Syndr. 32:121–129. DOI: 10.7570/jomes23031. PMID: 37386771. PMCID: PMC10327686.
Article3. Nam GE, Kim YH, Han K, et al. Obesity fact sheet in Korea, 2018: Data focusing on waist circumference and obesity-related comorbidities. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2019; 28:236–245. DOI: 10.7570/jomes.2019.28.4.236. PMID: 31909366. PMCID: PMC6939699.4. Yang YS, Han BD, Han K, et al. Obesity fact sheet in Korea, 2021: Trends in obesity prevalence and obesity-related comorbidity incidence stratified by age from 2009 to 2019. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2022; 31:169–177. DOI: 10.7570/jomes22024. PMID: 35770450. PMCID: PMC9284570.
Article5. Bassett J International Diabetes Institute; World Health Organization Regional Office for the Western Pacific; International Association for the Study of Obesity; International Obesity Task Force. 2000. The Asia-Pacific perspective: redefining obesity and its treatment. Health Communications Australia;Melbourne:6. Global BMI Mortality Collaboration. 2016; Body-mass index and all-cause mortality: individual-participant-data meta-analysis of 239 prospective studies in four continents. Lancet. 388:776–786. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30175-1. PMID: 27423262.7. Korean Endocrine Society. 2022. Endocrinology & Metabolism. 3rd ed. Paju: Koonja Publishing Inc;p. 1173–1182.8. Fu C, Jiang Y, Guo J, Su Z. 2016; Natural products with anti-obesity effects and different mechanisms of action. J Agric Food Chem. 64:9571–9585. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b04468. PMID: 27931098.
Article9. Kim WJ, Lee CB. 2016; New drugs for obesity treatment. Korean J Med. 90:121–126. DOI: 10.3904/kjm.2016.90.2.121.
Article10. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). c2020. FDA requests the withdrawal of the weight-loss drug Belviq, Belviq XR (lorcaserin) from the market [Internet]. FDA;Silver Spring (MD): Available from: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requests-withdrawal-weight-loss-drugbelviq-belviq-xr-lorcaserin-market. cited 2020 Mar 23.11. Sharma AM. 2023; The transformative impact of new anti-obesity medications: A paradigm shift in medical practice? J Obes Metab Syndr. 32:285–288. DOI: 10.7570/jomes23078. PMID: 38123356. PMCID: PMC10786208.
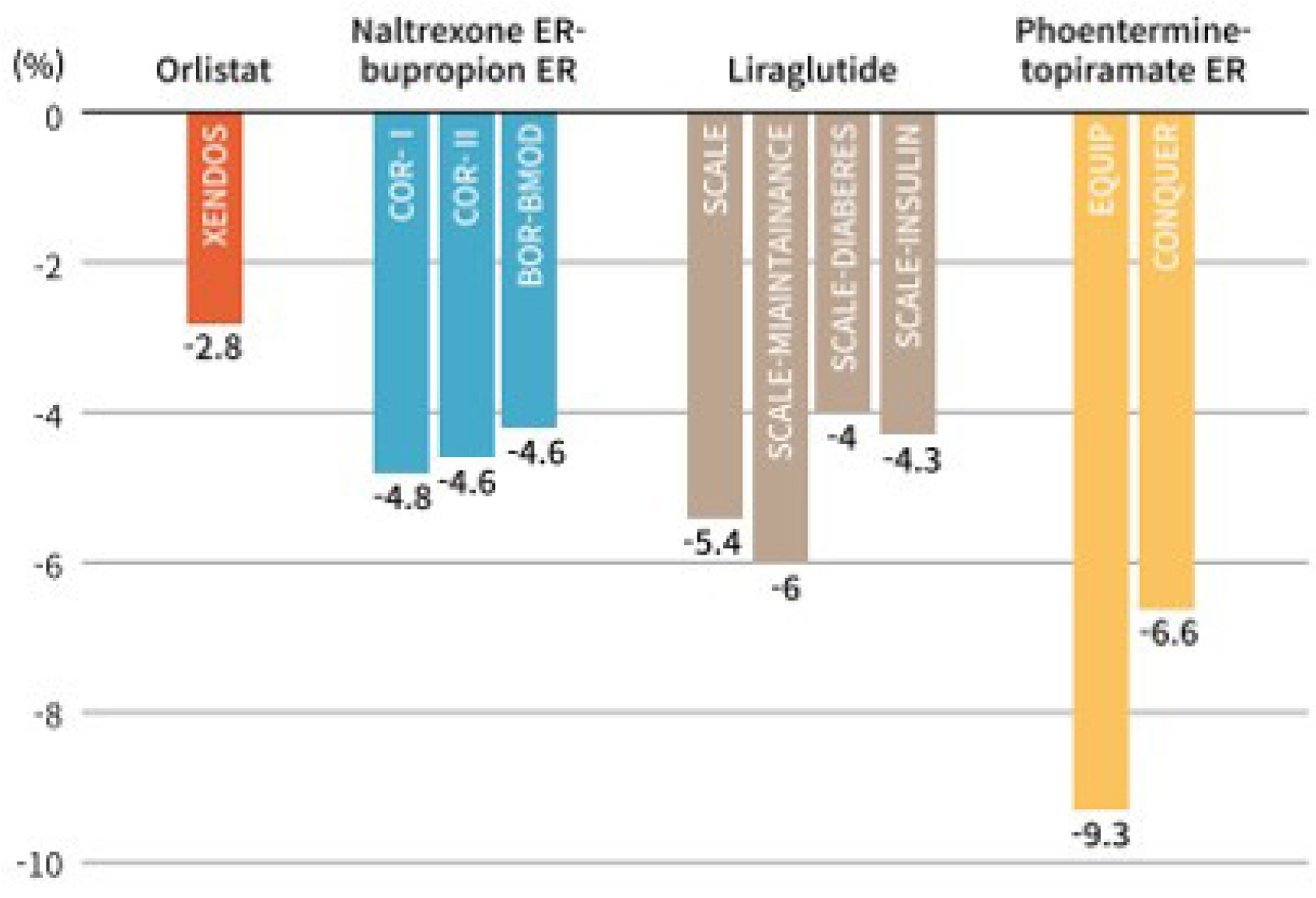
Article12. Torgerson JS, Hauptman J, Boldrin MN, Sjöström L. 2004; XENical in the prevention of diabetes in obese subjects (XENDOS) study: a randomized study of orlistat as an adjunct to lifestyle changes for the prevention of type 2 diabetes in obese patients. Diabetes Care. 27:155–161. DOI: 10.2337/diacare.27.1.155. PMID: 14693982.13. Greenway FL, Fujioka K, Plodkowski RA, et al. 2010; Effect of naltrexone plus bupropion on weight loss in overweight and obese adults (COR-I): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 376:595–605. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60888-4. PMID: 20673995.
Article14. Makowski CT, Gwinn KM, Hurren KM. 2011; Naltrexone/bupropion: an investigational combination for weight loss and maintenance. Obes Facts. 4:489–494. DOI: 10.1159/000335352. PMID: 22249001. PMCID: PMC6444555.
Article15. Wadden TA, Foreyt JP, Foster GD, et al. 2011; Weight loss with naltrexone SR/bupropion SR combination therapy as an adjunct to behavior modification: the COR-BMOD trial. Obesity (Silver Spring). 19:110–120. DOI: 10.1038/oby.2010.147. PMID: 20559296. PMCID: PMC4459776.
Article16. Apovian CM, Aronne L, Rubino D, et al. 2013; A randomized, phase 3 trial of naltrexone SR/bupropion SR on weight and obesity-related risk factors (COR-II). Obesity (Silver Spring). 21:935–943. DOI: 10.1002/oby.20309. PMID: 23408728. PMCID: PMC3739931.
Article17. Bray GA, Greenway FL. 2007; Pharmacological treatment of the overweight patient. Pharmacol Rev. 59:151–184. DOI: 10.1124/pr.59.2.2. PMID: 17540905.
Article18. Allison DB, Gadde KM, Garvey WT, et al. 2012; Controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in severely obese adults: a randomized controlled trial (EQUIP). Obesity (Silver Spring). 20:330–342. DOI: 10.1038/oby.2011.330. PMID: 22051941. PMCID: PMC3270297.
Article19. Verrotti A, Scaparrotta A, Agostinelli S, Di Pillo S, Chiarelli F, Grosso S. 2011; Topiramate-induced weight loss: a review. Epilepsy Res. 95:189–199. DOI: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2011.05.014. PMID: 21684121.
Article20. Gadde KM, Allison DB, Ryan DH, et al. 2011; Effects of low-dose, controlled-release, phentermine plus topiramate combination on weight and associated comorbidities in overweight and obese adults (CONQUER): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 377:1341–1352. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60205-5. PMID: 21481449.
Article21. Garvey WT, Ryan DH, Look M, et al. 2012; Two-year sustained weight loss and metabolic benefits with controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in obese and overweight adults (SEQUEL): a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 extension study. Am J Clin Nutr. 95:297–308. DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.111.024927. PMID: 22158731. PMCID: PMC3260065.22. Cho YJ, Kim KK. 2022; Pharmacotherapy in obesity: the current state and the near future. J Korean Med Assoc. 65:514–531. DOI: 10.5124/jkma.2022.65.8.514.
Article23. Oh SJ. 2011; New Therapeutics for diabetes using incretin hormone. Korean J Med. 80:625–634.24. Knudsen LB, Lau J. 2019; The discovery and development of liraglutide and semaglutide. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 10:155. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00155. PMID: 31031702. PMCID: PMC6474072.
Article25. Pi-Sunyer X, Astrup A, Fujioka K, et al. 2015; A randomized, controlled trial of 3.0 mg of liraglutide in weight management. N Engl J Med. 373:11–22. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1411892. PMID: 26132939.
Article26. Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, et al. 2021; Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 384:989–1002. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2032183. PMID: 33567185.
Article27. Wadden TA, Bailey TS, Billings LK, et al. 2021; Effect of subcutaneous semaglutide vs placebo as an adjunct to intensive behavioral therapy on body weight in adults with overweight or obesity: The STEP 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 325:1403–1413. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2021.1831. PMID: 33625476. PMCID: PMC7905697.
Article28. Kadowaki T, Isendahl J, Khalid U, et al. 2022; Semaglutide once a week in adults with overweight or obesity, with or without type 2 diabetes in an east Asian population (STEP 6): a randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 10:193–206. DOI: 10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00008-0. PMID: 35131037.
Article29. Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, et al. 2016; Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 375:1834–1844. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1607141. PMID: 27633186.
Article30. Husain M, Birkenfeld AL, Donsmark M, et al. 2019; Oral semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 381:841–851. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1901118. PMID: 31185157.
Article31. Kim KK. 2022; Peptides in obesity treatment. Arch Obes Metab. 1:4–13.32. Nauck MA, Heimesaat MM, Orskov C, et al. 1993; Preserved incretin activity of glucagon-like peptide 1 [7-36 amide] but not of synthetic human gastric inhibitory polypeptide in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 91:301–307. DOI: 10.1172/JCI116186. PMID: 8423228. PMCID: PMC330027.
Article33. Kaplan AM, Vigna SR. 1994; Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) binding sites in rat brain. Peptides. 15:297–302. DOI: 10.1016/0196-9781(94)90016-7. PMID: 8008635.
Article34. Kim SJ, Nian C, Karunakaran S, Clee SM, Isales CM, McIntosh CH. 2012; GIP-overexpressing mice demonstrate reduced diet-induced obesity and steatosis, and improved glucose homeostasis. PLoS One. 7:e40156. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040156. PMID: 22802954. PMCID: PMC3388996.
Article35. Samms RJ, Coghlan MP, Sloop KW. 2020; How may GIP enhance the therapeutic efficacy of GLP-1? Trends Endocrinol Metab. 31:410–421. DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2020.02.006. PMID: 32396843.
Article36. Jastreboff AM, Aronne LJ, Ahmad NN, et al. 2022; Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity. N Engl J Med. 387:205–216. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2206038. PMID: 35658024.
Article37. Del Prato S, Kahn SE, Pavo I, et al. 2021; Tirzepatide versus insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes and increased cardiovascular risk (SURPASS-4): a randomised, open-label, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 398:1811–1824. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02188-7. PMID: 34672967.38. Frías JP, Davies MJ, Rosenstock J, et al. 2021; Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 385:503–515. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2107519. PMID: 34170647.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effective and appropriate use of weight loss medication in pediatric obesity: a narrative review
- Current options in obesity pharmacotherapy for children and adolescents
- Pharmacotherapy in obesity: the current state and the near future
- Current status of obesity treatment in Korea:based on the 2020 Korean Society for the Study of Obesity guidelines for obesity management
- Pharmacotherapy for Obesity in Mood Disorders