J Korean Med Sci.
2024 Mar;39(8):e100. 10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e100.
Adverse Reactions After Intradermal Vaccination With JYNNEOS for Mpox in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 2Infectious Diseases Response Team, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2553323
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e100
Abstract
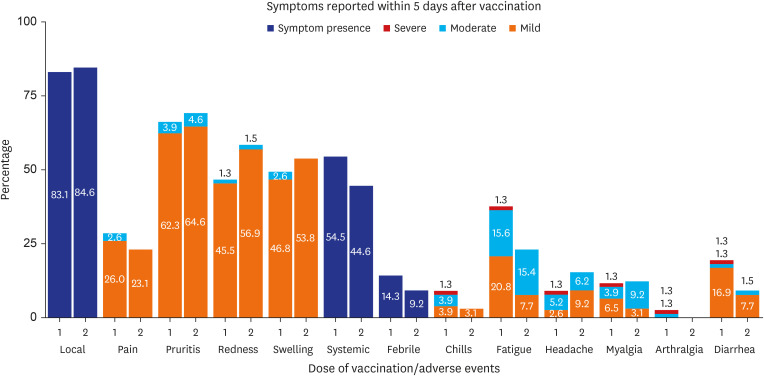
- In response to the Mpox domestic epidemic, South Korea initiated a nationwide vaccination program in May 2023, administering a 0.1 mL intradermal dose of JYNNEOS (Modified Vaccinia Ankara vaccine, Bavarian Nordic) to a high-risk group. To investigate the adverse reactions after intradermal JYNNEOS vaccination, an anonymous online survey was conducted at the National Medical Center from May 22 to July 31, 2023. Overall, 142 individuals responded. Over 80% of the respondents reported local reactions of predominantly mild severity. The predominant local reactions were pruritus, redness, and swelling; their incidence rates after the first dose were 66.2%, 48.1%, and 49.4%, respectively; the corresponding rates after the second dose were 69.2%, 60.6%, and 53.8%. Fewer respondents reported systemic symptoms. The most common systemic symptom was fatigue, the incidence rates of which after the first and second doses were 37.7% and 24.6%, respectively. Overall, the intradermally administered JYNNEOS vaccine appeared well tolerated.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kwon SL, Ban S, Shin J, Bae H, Park H, Kwon GY. Monkeypox vaccination in the Republic of Korea: Identifying the high-risk target group. J Korean Med Sci. 2022; 37(29):e239. PMID: 35880509.2. Frey SE, Wald A, Edupuganti S, Jackson LA, Stapleton JT, El Sahly H, et al. Comparison of lyophilized versus liquid modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA) formulations and subcutaneous versus intradermal routes of administration in healthy vaccinia-naïve subjects. Vaccine. 2015; 33(39):5225–5234. PMID: 26143613.3. Duffy J, Marquez P, Moro P, Weintraub E, Yu Y, Boersma P, et al. Safety Monitoring of JYNNEOS vaccine during the 2022 Mpox outbreak - United States, May 22-October 21, 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022; 71(49):1555–1559. PMID: 36480476.4. Deng L, Lopez LK, Glover C, Cashman P, Reynolds R, Macartney K, et al. Short-term adverse events following immunization with modified Vaccinia Ankara-Bavarian Nordic (MVA-BN) vaccine for Mpox. JAMA. 2023; 329(23):2091–2094. PMID: 37145654.5. Lee J, Kwon SL, Park J, Bae H, Lee H, Kwon GY. JYNNEOS vaccine safety monitoring in the Republic of Korea, 2022: a cross-sectional study. Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023; 14(5):433–438. PMID: 37920899.6. Food and Drug Administration. Toxicity Grading Scale for Healthy Adult and Adolescent Volunteers Enrolled in Preventive Vaccine Clinical Trials. Silver Spring, MD, USA: Food and Drug Administration, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services;2007.7. Montalti M, Di Valerio Z, Angelini R, Bovolenta E, Castellazzi F, Cleva M, et al. Safety of monkeypox vaccine using active surveillance, two-center observational study in Italy. Vaccines (Basel). 2023; 11(7):1163. PMID: 37514979.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- JYNNEOS vaccine safety monitoring in the Republic of Korea, 2022: a cross-sectional study
- Two Cases of Eczematoid Reactions following BCG Vaccinations
- Cutaneous Adverse Reaction After COVID-19 Vaccination
- Measles, Mumps, and Rubella Immunization in Children with Egg Allergies
- The Adverse Reactions of Influenza Vaccination in the Healthcare Workers in a University Hospital