Lab Med Online.
2023 Oct;13(4):332-340. 10.47429/lmo.2023.13.4.332.
Comparison Between Two Different Second-Generation Parathyroid Hormone Assays
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea
- KMID: 2552760
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.47429/lmo.2023.13.4.332
Abstract
- Background
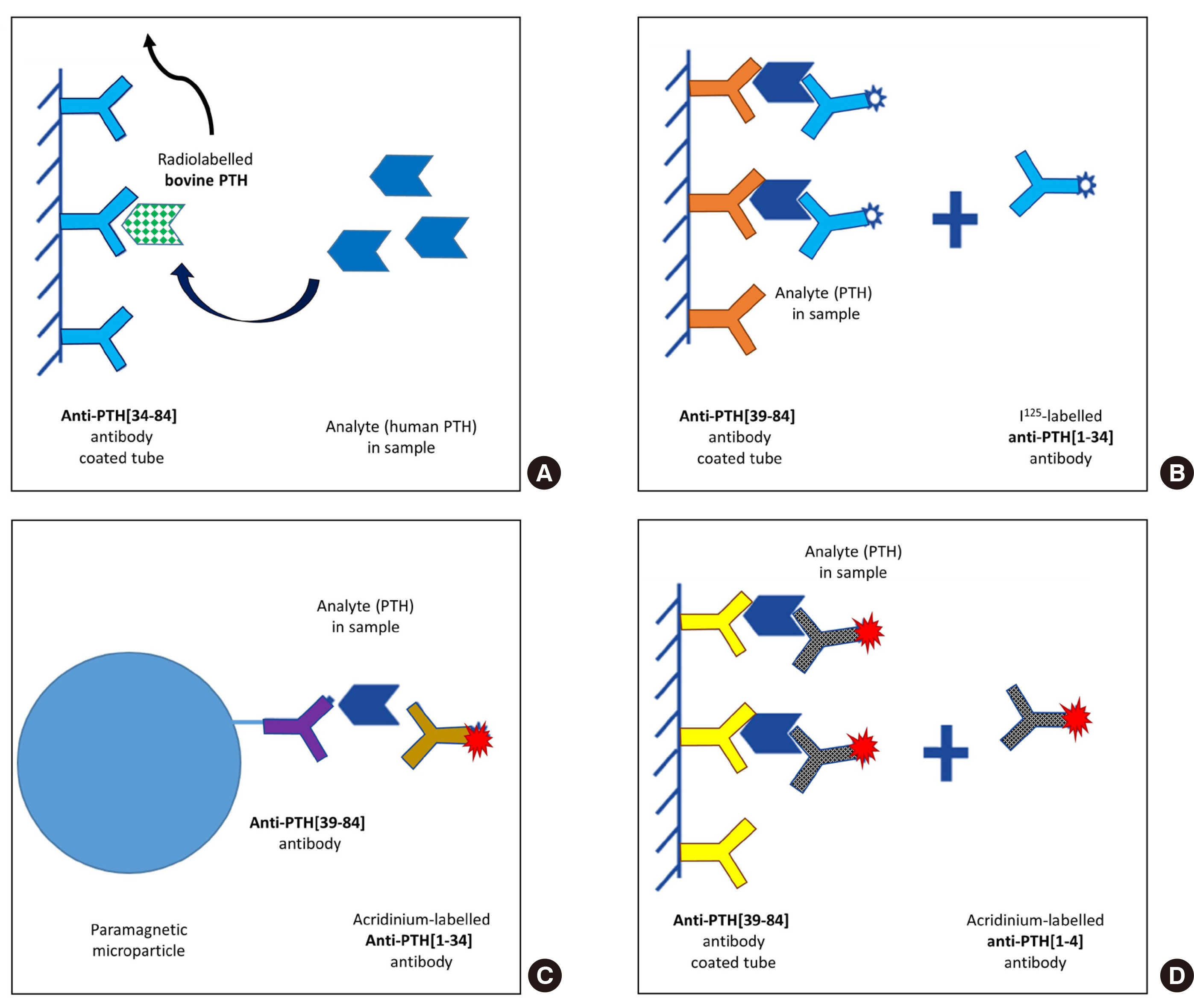
Accurate measurement of parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels is crucial for the diagnosis and treatment of hyperparathyroidism and hypoparathyroidism. Given the existence of various PTH forms in the bloodstream, it is well-known that there are variations in PTH levels depending on the measurement method. This study aimed to evaluate two different second-generation PTH assays.
Methods
A total of 56 residual samples originally requested for PTH testing were utilized for comparing the two methods. Each sample was subjected to analysis using an immunoradiometric assay (ELSA-PTH; Cisbio Bioassays, France) and a chemiluminescence microparticle immunoassay (Alinity i Intact PTH; Abbott, USA). Precision and linearity were analyzed, and reference interval and limit of quantitation (LoQ) were verified to investigate the performance of the Alinity i Intact PTH assay.
Results
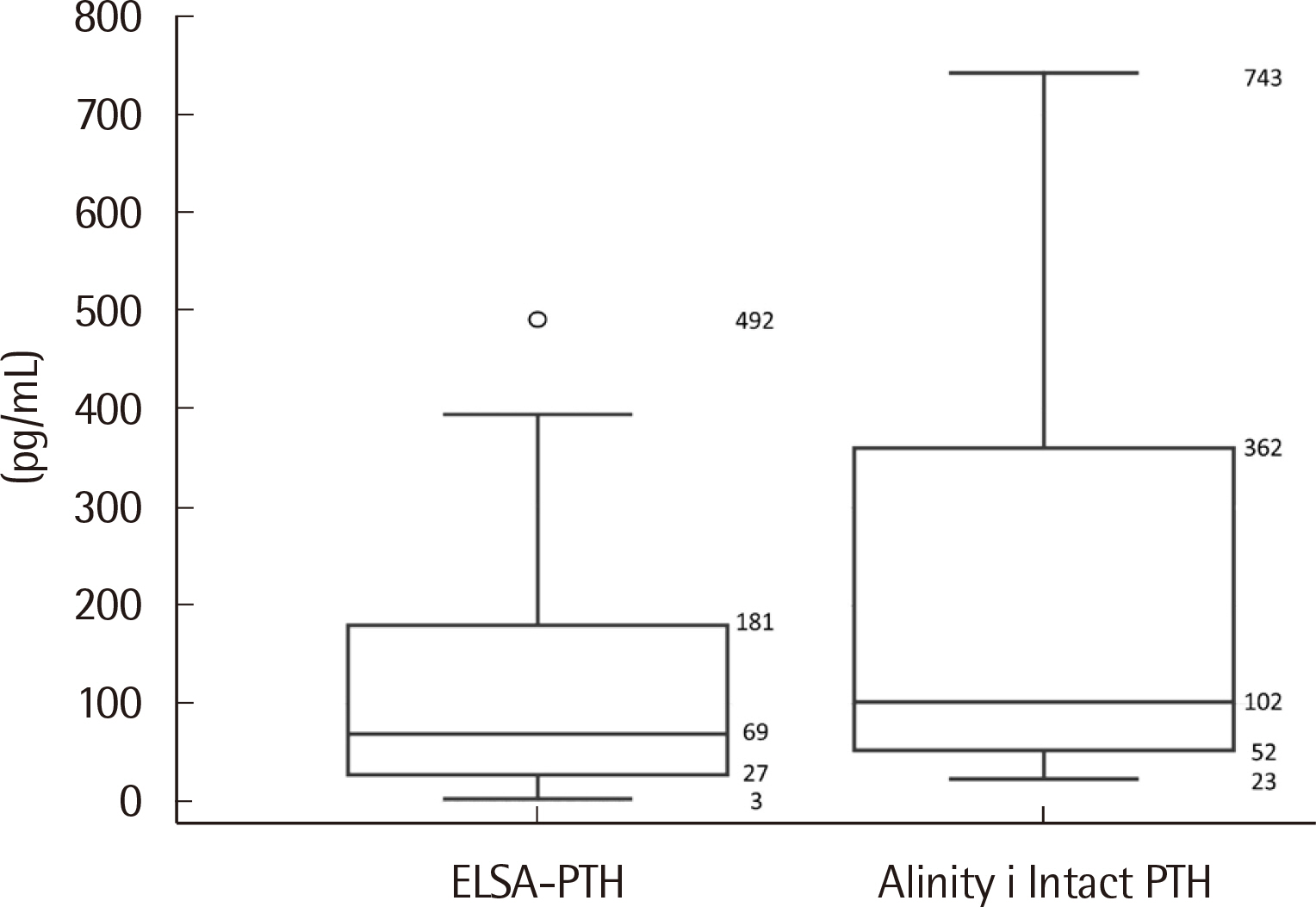
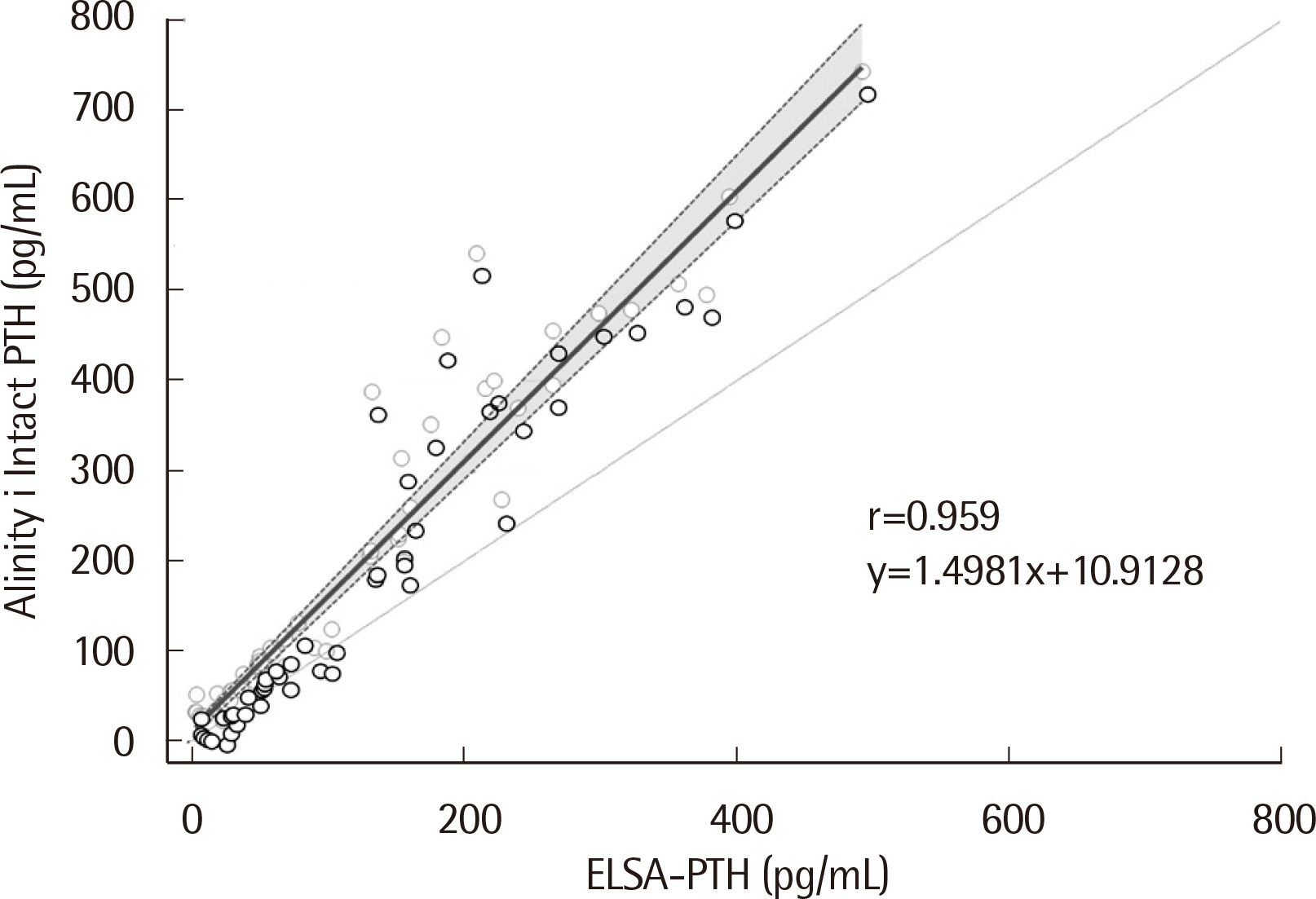
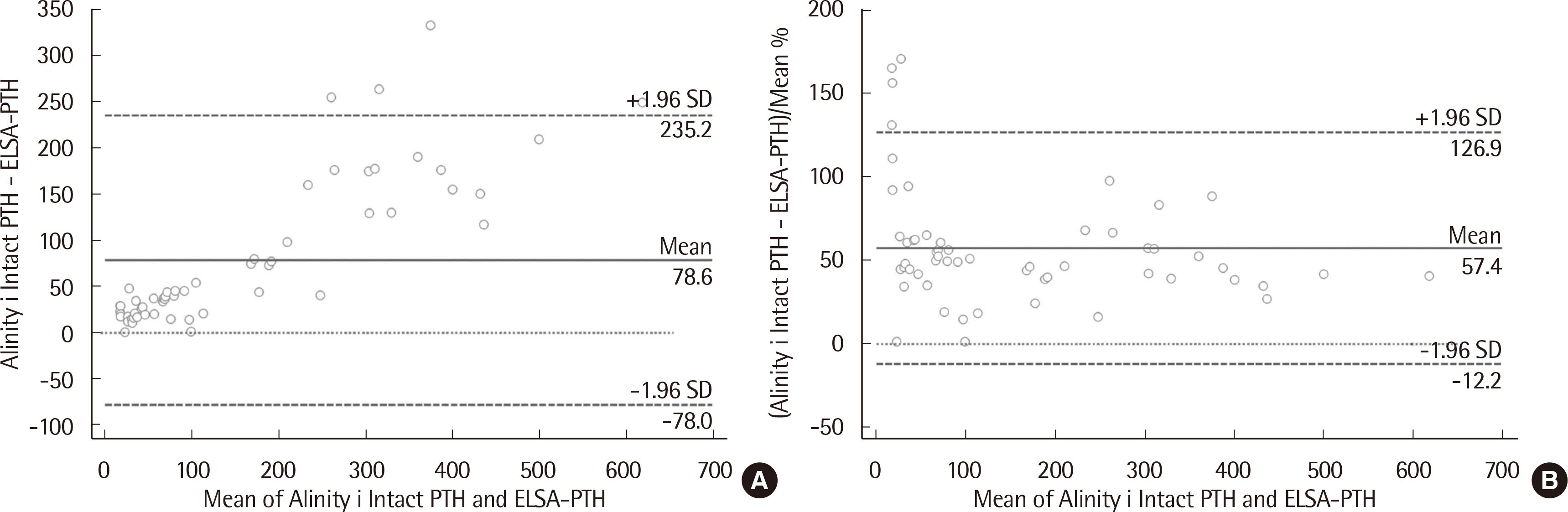
The median PTH values of ELSA-PTH and Alinity i Intact PTH were 69.0 pg/mL and 101.9 pg/mL, respectively, with significantly higher PTH values for Alinity i Intact PTH (P < 0.0001). The Pearson correlation coefficient was 0.959, and the average difference between the two tests was 78.57 pg/mL. For Alinity i Intact PTH, the coefficient of variation obtained at three concentrations was 1.9%, 2.4%, 1.8% for repeatability, and 2.0%, 2.7%, 2.7% for within-laboratory precision. Linearity was observed in the range of 3–3,000 pg/mL. The reference interval and LoQ reported by the manufacturer were verified.
Conclusions
The PTH results of the ELSA-PTH and Alinity i Intact PTH assays showed a strong correlation, and the Alinity i Intact PTH assay demonstrated acceptable analytical performance.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Naveh-Many T, Silver J, et al. Bilezikian JP, Martin TG, editors. 2019. Parathyroid hormone molecular biology. Principles of bone biology. 4th ed. San Diego, CA: Elsevier;p. 575–94.2. Gardella TJ, Axelrod D, Rubin D, Keutmann HT, Potts JT Jr, Kronenberg HM, et al. 1991; Mutational analysis of the receptor-activating region of human parathyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 266:13141–6. DOI: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)98816-2. PMID: 1649179.3. D'Amour P, Brossard JH, Rousseau L, Nguyen-Yamamoto L, Nassif E, Lazure C, et al. 2005; Structure of non-(1-84) PTH fragments secreted by parathyroid glands in primary and secondary hyperparathyroidism. Kidney Int. 68:998–1007. DOI: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00493.x. PMID: 16105030.4. D'Amour P, Brossard JH, Rousseau L, Roy L, Gao P, Cantor T. 2003; Amino-terminal form of parathyroid hormone (PTH) with immunologic similarities to hPTH(1-84) is overproduced in primary and secondary hyperparathyroidism. Clin Chem. 49:2037–44. DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2003.021592. PMID: 14633875.5. Fraser WD. 2009; Hyperparathyroidism. Lancet. 374:145–58. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60507-9. PMID: 19595349.6. Bilezikian JP, Khan A, Potts JT Jr, Brandi ML, Clarke BL, Shoback D, et al. 2011; Hypoparathyroidism in the adult: epidemiology, diagnosis, pathophysiology, target-organ involvement, treatment, and challenges for future research. J Bone Miner Res. 26:2317–37. DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.483. PMID: 21812031. PMCID: PMC3405491.7. Nussbaum SR, Thompson AR, Hutcheson KA, Gaz RD, Wang CA. 1988; Intraoperative measurement of parathyroid hormone in the surgical management of hyperparathyroidism. Surgery. 104:1121–7.8. Bhangu JS, Riss P. 2019; The role of intraoperative parathyroid hormone (IOPTH) determination for identification and surgical strategy of sporadic multiglandular disease in primary hyperparathyroidism (pHPT). Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 33:101310. DOI: 10.1016/j.beem.2019.101310. PMID: 31409538.9. Cavalier E, Vasikaran S, Bhattoa HP, Heijboer AC, Makris K, Ulmer CZ. 2021; The path to the standardization of PTH: is this a realistic possibility? A position paper of the IFCC C-BM. Clin Chim Acta. 515:44–51. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.12.022. PMID: 33412144. PMCID: PMC7920929.10. Cavalier E. 2019; Parathyroid hormone results interpretation in the background of variable analytical performance. J Lab Precis Med. 4:1–10. DOI: 10.21037/jlpm.2018.12.03.11. Nawrot I, Woźniewicz B, Szmidt J, Śladowski D, Zając K, Chudziński W. 2014; Xenotransplantation of human cultured parathyroid progenitor cells into mouse peritoneum does not induce rejection reaction. Cent Eur J Immunol. 39:279–84. DOI: 10.5114/ceji.2014.45937. PMID: 26155136. PMCID: PMC4440013.12. González-Casaus ML, Fernández-Calle P, Buño Soto AB. 2021; Should clinical laboratories adapt to the reality of chronic kidney disease in the determination of parathyroid hormone? Adv Lab Med. 2:342–51. DOI: 10.1515/almed-2021-0046. PMID: 37362408. PMCID: PMC10197458.13. Censi S, Iacobone M, Simmini S, Manso J, Franceschet G, Plebani M, et al. 2020; PTH: redefining reference ranges in a healthy population-The role of interfering factors and the type of laboratory assay. Int J Endocrinol. 2020:1053719. DOI: 10.1155/2020/1053719. PMID: 32148482. PMCID: PMC7054804.14. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2014. User verification of precision and estimation of bias; Approved guideline-Third edition. CLSI document EP15-A3. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:15. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2020. Evaluation of linearity of quantitative measurement procedures, 2nd edition. CLSI guideline EP06. Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute;Wayne, PA:16. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2008. Defining, establishing, and verifying reference intervals in the clinical laboratory; Approved guideline-Third edition. CLSI document C28-A3c. Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute;Wayne, PA:17. Berson SA, Yalow RS, Aurbach GD, Potts JT. 1963; Immunoassay of bovine and human parathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 49:613–7. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.613. PMID: 16591075. PMCID: PMC299933.18. Nussbaum SR, Zahradnik RJ, Lavigne JR, Brennan GL, Nozawa-Ung K, Kim LY, et al. 1987; Highly sensitive two-site immunoradiometric assay of parathyrin, and its clinical utility in evaluating patients with hypercalcemia. Clin Chem. 33:1364–7. DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/33.8.1364. PMID: 3608153.19. Quarles LD, Lobaugh B, Murphy G. 1992; Intact parathyroid hormone overestimates the presence and severity of parathyroid-mediated osseous abnormalities in uremia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 75:145–50. DOI: 10.1210/jcem.75.1.1619003. PMID: 1619003.20. Wang M, Hercz G, Sherrard DJ, Maloney NA, Segre GV, Pei Y. 1995; Relationship between intact 1-84 parathyroid hormone and bone histomorphometric parameters in dialysis patients without aluminum toxicity. Am J Kidney Dis. 26:836–44. DOI: 10.1016/0272-6386(95)90453-0. PMID: 7485142.21. John MR, Goodman WG, Gao P, Cantor TL, Salusky IB, Jüppner H. 1999; A novel immunoradiometric assay detects full-length human PTH but not amino-terminally truncated fragments: implications for PTH measurements in renal failure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 84:4287–90. DOI: 10.1210/jcem.84.11.6236. PMID: 10566687.22. D'Amour P, Brossard JH, Rousseau L, Roy L, Gao P, Cantor T. 2003; Amino-terminal form of parathyroid hormone (PTH) with immunologic similarities to hPTH(1-84) is overproduced in primary and secondary hyperparathyroidism. Clin Chem. 49:2037–44. DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2003.021592. PMID: 14633875.23. Einbinder Y, Benchetrit S, Golan E, Zitman-Gal T. 2017; Comparison of intact PTH and bio-intact PTH assays among non-dialysis dependent chronic kidney disease patients. Ann Lab Med. 37:381–7. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2017.37.5.381. PMID: 28643486. PMCID: PMC5500736.24. Hecking M, Kainz A, Bielesz B, Plischke M, Beilhack G, Hörl WH, et al. 2012; Clinical evaluation of two novel biointact PTH(1-84) assays in hemodialysis patients. Clin Biochem. 45:1645–51. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.08.006. PMID: 23217247.25. Au DH, Kim JY, Seok JD. 2010; The usefulness according to the incubation time of PTH as prediction index of hypocalcemia. J Nucl Med Technol. 14:138–42.26. D'Amour P. 2006; Circulating PTH molecular forms: what we know and what we don't. Kidney Int Suppl. 70:S29–33. DOI: 10.1038/sj.ki.5001599. PMID: 16810307.27. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD-MBD Update Work Group. 2017; KDIGO 2017 Clinical practice guideline update for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD). Kidney Int Suppl. 7:1–59. DOI: 10.1016/j.kisu.2017.04.001. PMID: 30675420. PMCID: PMC6340919.28. Youngwirth L, Benavidez J, Sippel R, Chen H. 2010; Parathyroid hormone deficiency after total thyroidectomy: incidence and time. J Surg Res. 163:69–71. DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2010.03.059. PMID: 20605611.29. Souberbielle JC, Roth H, Fouque DP. 2010; Parathyroid hormone measurement in CKD. Kidney Int. 77:93–100. DOI: 10.1038/ki.2009.374. PMID: 19812537.30. Korean Association of External Quality Assessment Service. 2022. 2022년도 01차 신빙도조사 호르몬검사 2 공통 보고서. Korean Association of External Quality Assessment Service (KEQAS);Seoul:
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Aging and Hormone: Estrogen, Parathyroid hormone and Bone Metabolism
- Comparison of Intact PTH and Bio-Intact PTH Assays Among Non-Dialysis Dependent Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
- Sequential and Combination Therapy using Parathyroid Hormone for Osteoporosis
- The effects of long-term lithium treatment on the parathyroid hormone and calcium level
- Parathyroid Adenoma without Hyperparathyroidism Presenting as a Large Neck Mass