Lab Med Online.
2023 Apr;13(2):91-96. 10.47429/lmo.2023.13.2.91.
Coffin-Siris Syndrome: Genotype-Phenotype Clustering and Novel Variants
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine , Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul
- 2Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2552731
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.47429/lmo.2023.13.2.91
Abstract
- Background
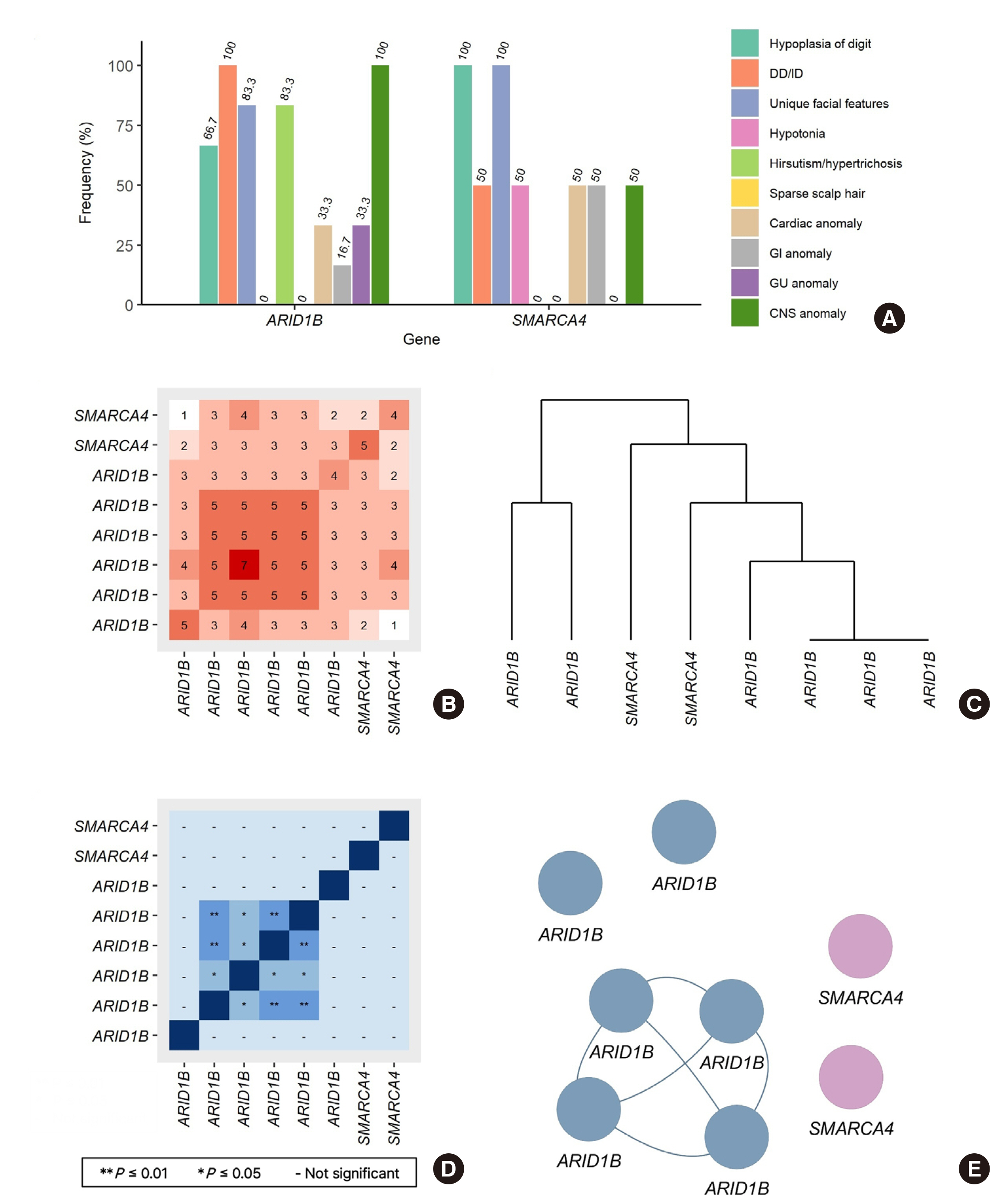
Coffin-Siris syndrome (CSS) is a rare disease characterized by features such as developmental delay, intellectual disability, unique facial feature, hypoplasia of the fifth finger or toe, hypertrichosis, and sparse scalp hair. CSS is currently diagnosed through a molecular genetic test that detects heterozygous pathogenic variants and deletion/duplication in the causative genes.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 23 suspected patients with CSS enrolled in the rare disease diagnostic program of the Korean Disease Control and Prevention Agency from January 2017 to December 2020, including whole-exome sequencing (WES) reports. Statistical analysis was performed using cluster analysis through Jaccard/Tanimoto similarity test using the R version 4.2.0.
Results
Eight cases were genetically diagnosed with the CSS. Five cases were identified to have a novel variant: ARID1B (NM_020732.3) Gln958*, Asn1320*, Gly1696*, Gly806Trpfs*, and SMARCA4 (NM_001128849.1) Asn916Ser. Central nervous system symptoms were observed in all ARID1Bcases, and the fifth digit hypoplasia was observed in all SMARCA4 cases. SMARCA4 Asn916Ser was identified as de novo. A similarity network was identified using cluster analysis, a relatively fresh approach to genotype-phenotype analysis.
Conclusions
We reported eight patients diagnosed with CSS, five of whom have novel genetic variants of ARID1B or SMARCA4. A novel case of SMARCA4 was de novo. This study contributes to describing the CSS phenotype. Future studies may facilitate easier diagnosis of CSS in patients who present with atypical traits as more in-depth genetic testing, such as WES, is applied to rare disorders.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vasko A, Drivas TG, Schrier Vergano SA. 2021; Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in 208 Individuals with Coffin-Siris Syndrome. Genes. 12:937. DOI: 10.3390/genes12060937. PMID: 34205270. PMCID: PMC8233770.2. Liu M, Wan L, Wang C, Yuan H, Peng Y, Wan N, et al. 2022; Coffin-Siris syndrome in two chinese patients with novel pathogenic variants of ARID1A and SMARCA4. Genes Genomics. 44:1061–70. DOI: 10.1007/s13258-022-01231-2. PMID: 35353340.3. Kosho T, Miyake N, Carey JC. 2014; Coffin-Siris syndrome and related disorders involving components of the BAF (mSWI/SNF) complex: Historical review and recent advances using next generation sequencing. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 166C:241–51. DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31415. PMID: 25169878.4. Alfert A, Moreno N, Kerl K. 2019; The BAF complex in development and disease. Epigenetics Chromatin. 12:19. DOI: 10.1186/s13072-019-0264-y. PMID: 30898143. PMCID: PMC6427853.5. Sim JC, White SM, Lockhart PJ. 2015; ARID1B-mediated disorders: Mutations and possible mechanisms. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 4:17–23. DOI: 10.5582/irdr.2014.01021. PMID: 25674384. PMCID: PMC4322591.6. OMIM®, # 135900 COFFIN-SIRIS SYNDROME 1; CSS1. https://www.omim.org/entry/135900. Update on Feb 2020.7. Guo X, Song Y, Liu S, Gao M, Qi Y, Shang X. 2021; Linking genotype to phenotype in multi-omics data of small sample. BMC Genomics. 22:537. DOI: 10.1186/s12864-021-07867-w. PMID: 34256701. PMCID: PMC8278664.8. Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, et al. 2015; Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 17:405–24. DOI: 10.1038/gim.2015.30. PMID: 25741868. PMCID: PMC4544753.9. Chung NC, Miasojedow B, Startek M, Gambin A. 2019; Jaccard/Tanimoto similarity test and estimation methods for biological presence-absence data. BMC Bioinformatics. 20(Suppl 15):644. DOI: 10.1186/s12859-019-3118-5. PMID: 31874610. PMCID: PMC6929325.10. Fokkema IFAC, Kroon M, López Hernández JA, Asscheman D, Lugtenburg I, Hoogenboom J, et al. 2021; The LOVD3 platform: efficient genome-wide sharing of genetic variants. Eur J Hum Genet. 29:1796–803. DOI: 10.1038/s41431-021-00959-x. PMID: 34521998. PMCID: PMC8632977.11. Schrier Vergano S, Santen G, Wieczorek D, Wollnik B, Matsumoto N, Deardorff MA. Coffin-Siris Syndrome. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK131811/. Update on Aug 2021.12. Moffat JJ, Smith AL, Jung EM, Ka M, Kim WY. 2022; Neurobiology of ARID1B haploinsufficiency related to neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 27:476–89. DOI: 10.1038/s41380-021-01060-x. PMID: 33686214. PMCID: PMC8423853.13. Santen GW, Aten E, Vulto-van Silfhout AT, Pottinger C, van Bon BW, van Minderhout IJ, et al. 2013; Coffin-Siris syndrome and the BAF complex: genotype-phenotype study in 63 patients. Hum Mutat. 34:1519–28. DOI: 10.1002/humu.22394. PMID: 23929686.14. Hoyer J, Ekici AB, Endele S, Popp B, Zweier C, Wiesener A, et al. 2012; Haploinsufficiency of ARID1B, a member of the SWI/SNF-a chromatin-remodeling complex, is a frequent cause of intellectual disability. Am J Hum Genet. 90:565–72. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.02.007. PMID: 22405089. PMCID: PMC3309205.15. Vergano SA, van der Sluijs PJ, Santen G. ARID1B-Related Disorder. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK541502/. Updated on May 2019.16. Lisi EC, Cohn RD. 2011; Genetic evaluation of the pediatric patient with hypotonia: perspective from a hypotonia specialty clinic and review of the literature. Dev Med Child Neurol. 53:586–99. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2011.03918.x. PMID: 21418198.17. Harris SR. 2008; Congenital hypotonia: clinical and developmental assessment. Dev Med Child Neurol. 50:889–92. DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.2008.03097.x. PMID: 19046184.18. Hodges HC, Stanton BZ, Cermakova K, Chang CY, Miller EL, Kirkland JG, et al. 2018; Dominant-negative SMARCA4 mutants alter the accessibility landscape of tissue-unrestricted enhancers. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 25:61–72. DOI: 10.1038/s41594-017-0007-3. PMID: 29323272. PMCID: PMC5909405.19. Veltman JA, Brunner HG. 2012; De novo mutations in human genetic disease. Nat Rev Genet. 13:565–75. DOI: 10.1038/nrg3241. PMID: 22805709.20. Tsurusaki Y, Okamoto N, Ohashi H, Kosho T, Imai Y, Hibi-Ko Y, et al. 2012; Mutations affecting components of the SWI/SNF complex cause Coffin-Siris syndrome. Nat Genet. 44:376–8. DOI: 10.1038/ng.2219. PMID: 22426308.21. Fernando TM, Piskol R, Bainer R, Sokol ES, Trabucco SE, Zhang Q, et al. 2020; Functional characterization of SMARCA4 variants identified by targeted exome-sequencing of 131,668 cancer patients. Nat Commun. 11:5551. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19402-8. PMID: 33144586. PMCID: PMC7609548.22. Stanton BZ, Hodges C, Calarco JP, Braun SM, Ku WL, Kadoch C, et al. 2017; Smarca4 ATPase mutations disrupt direct eviction of PRC1 from chromatin. Nat Genet. 49:282–8. DOI: 10.1038/ng.3735. PMID: 27941795. PMCID: PMC5373480.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Novel De Novo Heterozygous ARID1A Missense Variant Cluster in cis c.[5954C>G;6314C>T;6334C>T; 6843G>C] causes a Coffin–Siris Syndrome
- A case of Coffin-Lowry syndrome
- Prediction and visualization of CYP2D6 genotype-based phenotype using clustering algorithms
- Spectrum of MNX1 Pathogenic Variants and Associated Clinical Features in Korean Patients with Currarino Syndrome
- Genotypic and Phenotypic Characteristics of Hereditary Leiomyomatosis and Renal Cell Cancer Syndrome in Korean Patients