Ann Lab Med.
2023 Nov;43(6):539-553. 10.3343/alm.2023.43.6.539.
Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Cutoff Value Selection and Acute Kidney Injury Classification System Determine Phenotype Allocation and Associated Outcomes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nephrology and Endocrinology, Ernst von Bergmann Hospital, Potsdam, Germany
- 2University Clinic for Cardiology and Angiology, Otto-von-Guericke University Magdeburg, Germany
- 3Department of Intensive Care, The Austin Hospital, Melbourne, Australia
- 4Centre for Integrated Critical Care, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia
- 5Medical Faculty, Otto-von-Guericke University Magdeburg, Germany
- 6Diamedikum, Potsdam, Germany
- 7Department of Nephrology and Hypertension, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany
- 8Department of Nephrology, Central Clinic Bad Berka, Bad Berka, Germany
- KMID: 2552024
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.6.539
Abstract
- Background
We explored the extent to which neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) cutoff value selection and the acute kidney injury (AKI) classification system determine clinical AKI-phenotype allocation and associated outcomes.
Methods
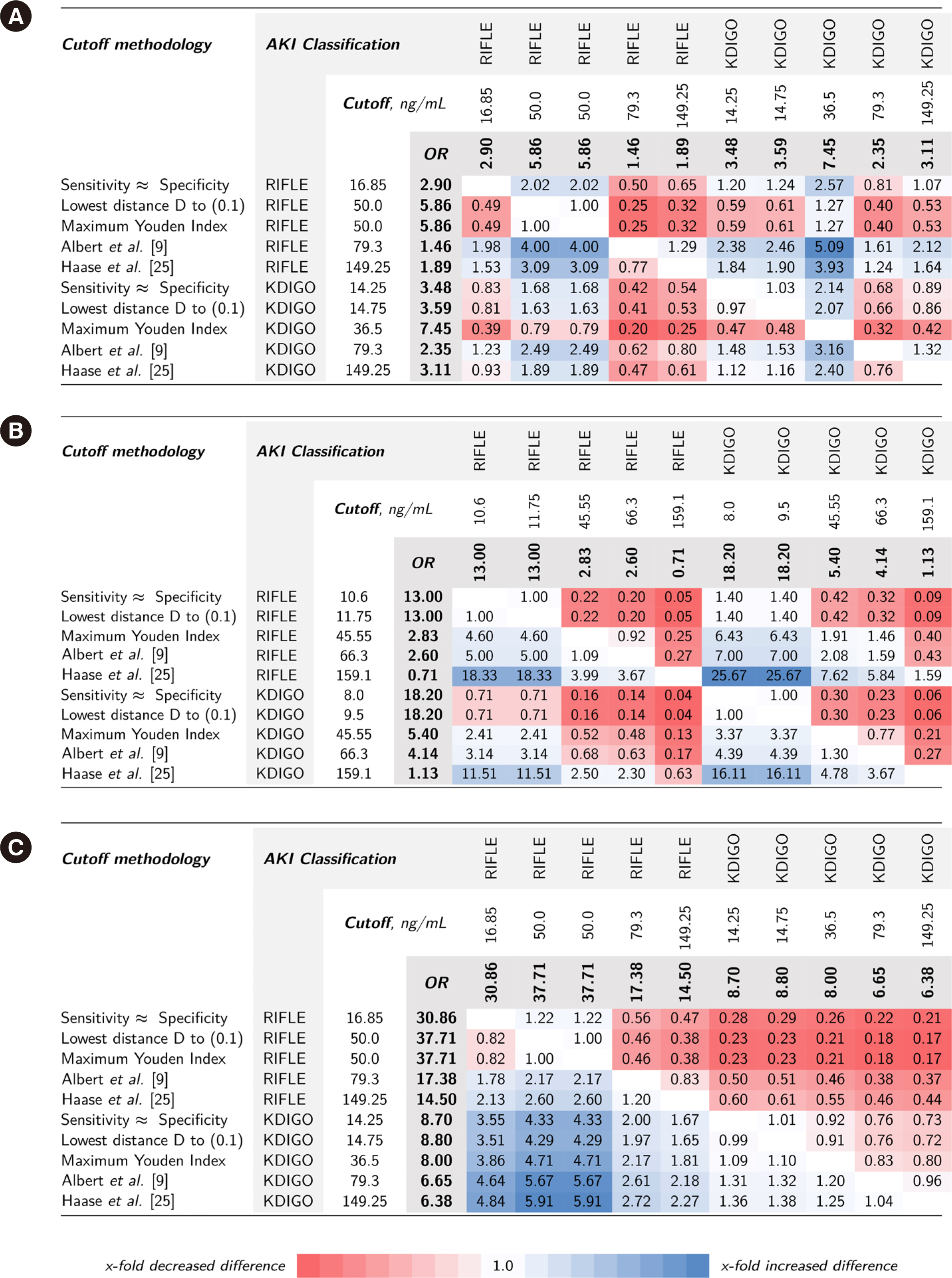
Cutoff values from ROC curves of data from two independent prospective cardiac surgery study cohorts (Magdeburg and Berlin, Germany) were used to predict Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcome (KDIGO)- or Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss of kidney function, End-stage (RIFLE)-defined AKI. Statistical methodologies (maximum Youden index, lowest distance to [0, 1] in ROC space, sensitivity≈specificity) and cutoff values from two NGAL meta-analyses were evaluated. Associated risks of adverse outcomes (acute dialysis initiation and in-hospital mortality) were compared.
Results
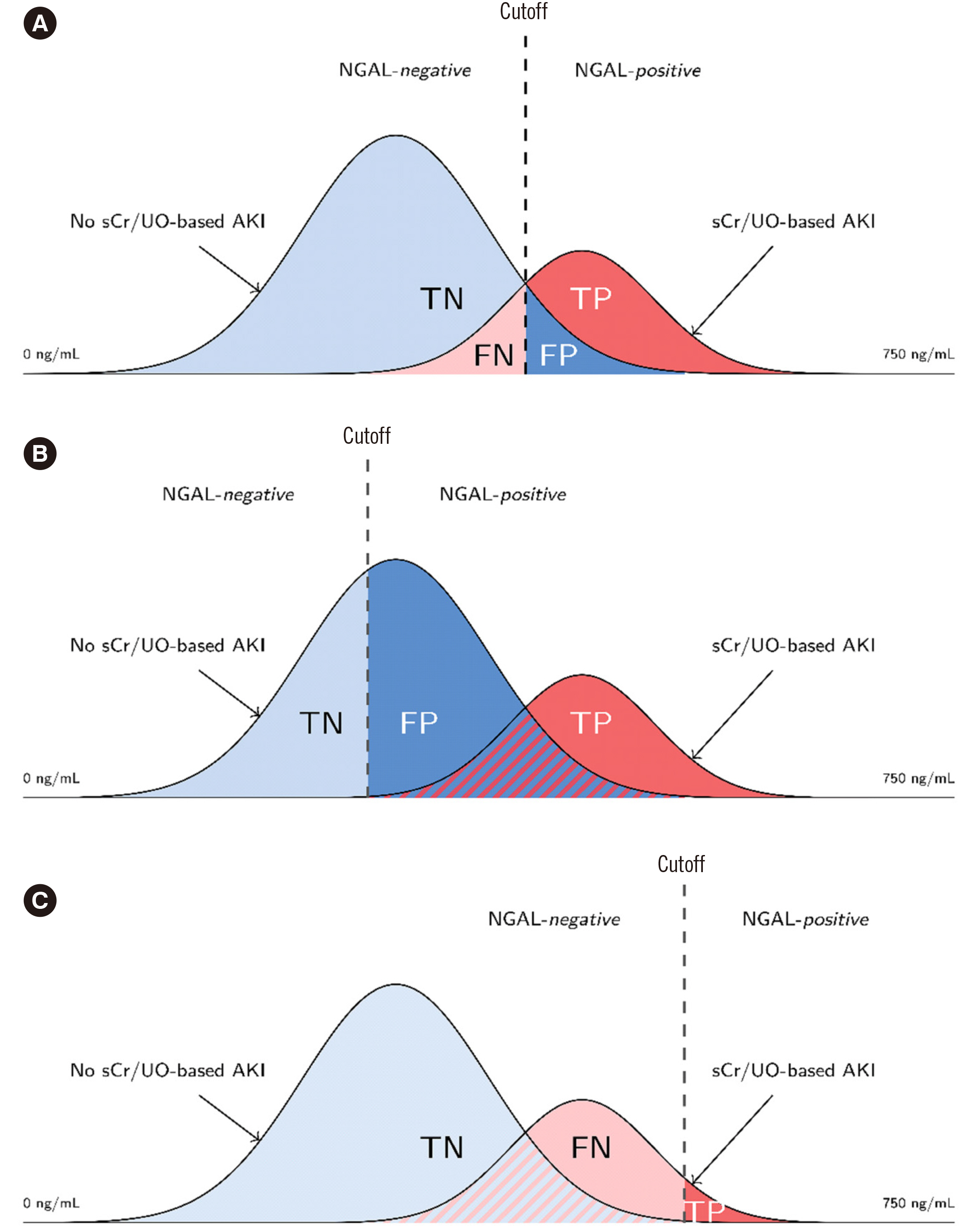
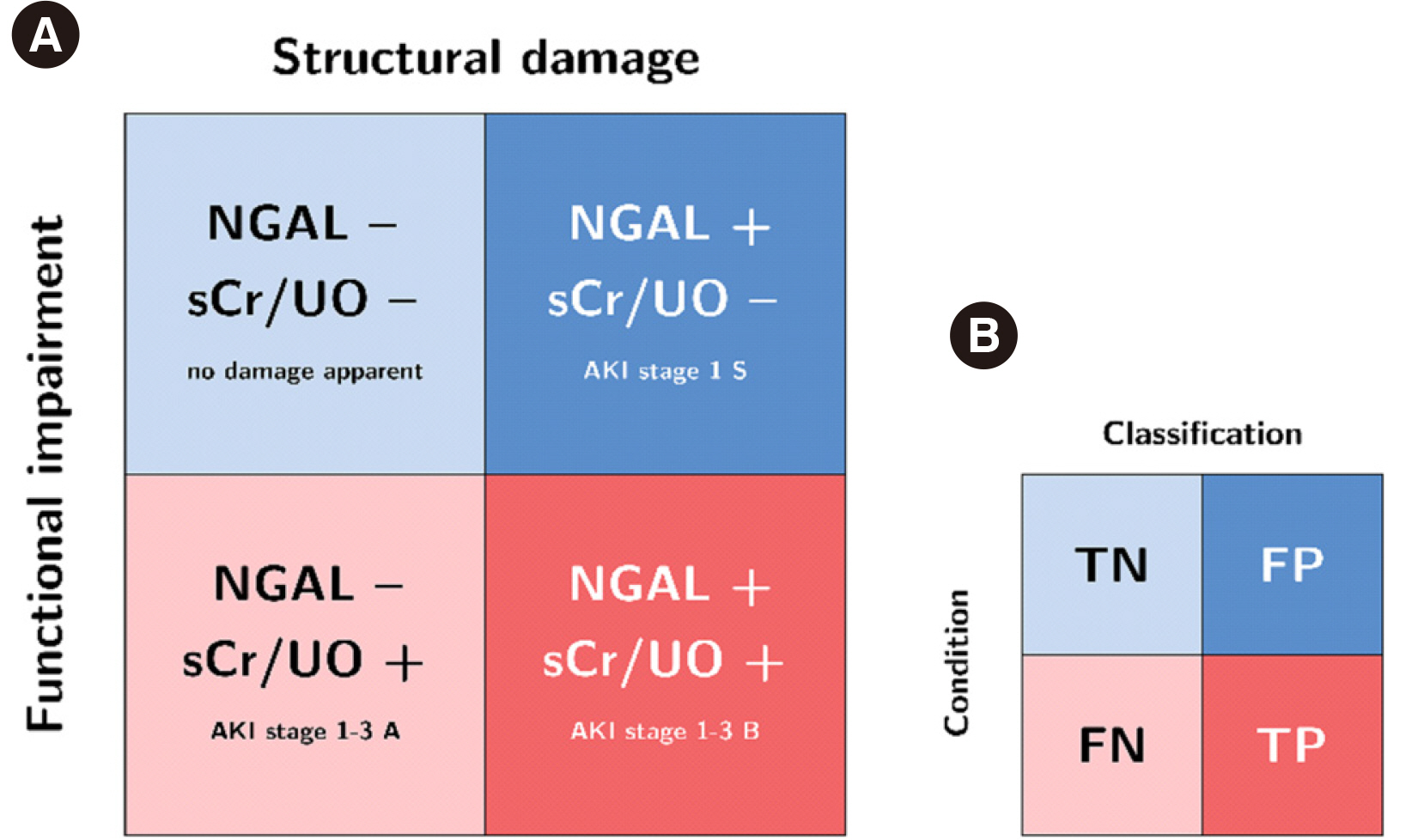
NGAL cutoff concentrations calculated from ROC curves to predict AKI varied according to the statistical methodology and AKI classification system (10.6–159.1 and 16.85–149.3 ng/mL in the Magdeburg and Berlin cohorts, respectively). Proportions of attributed subclinical AKI ranged 2%–33.0% and 10.1%–33.1% in the Magdeburg and Berlin cohorts, respectively. The difference in calculated risk for adverse outcomes (fraction of odds ratios for AKI-phenotype group differences) varied considerably when changing the cutoff concentration within the RIFLE or KDIGO classification (up to 18.33- and 16.11-times risk difference, respectively) and was even greater when comparing cutoff methodologies between RIFLE and KDIGO classifications (up to 25.7-times risk difference).
Conclusions
NGAL positivity adds prognostic information regardless of RIFLE or KDIGO classification or cutoff selection methodology. The risk of adverse events depends on the methodology of cutoff selection and AKI classification system.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
New Issues With Neutrophil Gelatinase-associated Lipocalin in Acute Kidney Injury
Sun Young Cho, Mina Hur
Ann Lab Med. 2023;43(6):529-530. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.6.529.
Reference
-
1. Hoste EAJ, Bagshaw SM, Bellomo R, Cely CM, Colman R, Cruz DN, et al. 2015; Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: the multinational AKI-EPI study. Intensive Care Med. 41:1411–23. DOI: 10.1007/s00134-015-3934-7. PMID: 26162677.
Article2. Nadim MK, Forni LG, Bihorac A, Hobson C, Koyner JL, Shaw A, et al. 2018; Cardiac and vascular surgery-associated acute kidney injury: the 20th International Consensus Conference of the ADQI (Acute Disease Quality Initiative) Group. J Am Heart Assoc. 7:e008834. DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.118.008834. PMID: 29858368. PMCID: PMC6015369.
Article3. Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, Mehta RL, Palevsky P. Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative Workgroup. 2004; Acute renal failure - definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care. 8:R204–12.4. Kidney Disease Improving Outcome, Acute Kidney Injury Working Group. 2012; KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int Suppl. 2:1–141.5. Albert C, Albert A, Kube J, Bellomo R, Wettersten N, Kuppe H, et al. 2018; Urinary biomarkers may provide prognostic information for subclinical acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 155:2441–52.e13. DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2017.12.056. PMID: 29366580.
Article6. Di Somma S, Magrini L, De Berardinis B, Marino R, Ferri E, Moscatelli P, et al. 2013; Additive value of blood neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin to clinical judgement in acute kidney injury diagnosis and mortality prediction in patients hospitalized from the emergency department. Crit Care. 17:R29. DOI: 10.1186/cc12510. PMID: 23402494. PMCID: PMC4056001.
Article7. Nickolas TL, Schmidt-Ott KM, Canetta P, Forster C, Singer E, Sise M, et al. 2012; Diagnostic and prognostic stratification in the emergency department using urinary biomarkers of nephron damage: a multicenter prospective cohort study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 59:246–55. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.10.854. PMID: 22240130. PMCID: PMC3487165.8. Albert C, Haase M, Albert A, Kropf S, Bellomo R, Westphal S, et al. 2020; Urinary biomarkers may complement the Cleveland Score for prediction of adverse kidney events after cardiac surgery: a pilot study. Ann Lab Med. 40:131–41. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2020.40.2.131. PMID: 31650729. PMCID: PMC6822001.
Article9. Albert C, Zapf A, Haase M, Röver C, Pickering JW, Albert A, et al. 2020; Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin measured on clinical laboratory platforms for the prediction of acute kidney injury and the associated need for dialysis therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 76:826–41.e1. DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.05.015. PMID: 32679151. PMCID: PMC8283708.
Article10. Ostermann M, Zarbock A, Goldstein S, Kashani K, Macedo E, Murugan R, et al. 2020; Recommendations on acute kidney injury biomarkers from the acute disease quality initiative consensus conference: a consensus statement. JAMA Netw Open. 3:e2019209. DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19209. PMID: 33021646.11. Habibzadeh F, Habibzadeh P, Yadollahie M. 2016; On determining the most appropriate test cut-off value: the case of tests with continuous results. Biochem Med. 26:297–307. DOI: 10.11613/BM.2016.034. PMID: 27812299. PMCID: PMC5082211.
Article12. Cho E, Kim SC, Kim MG, Jo SK, Cho WY, Kim HK. 2014; The incidence and risk factors of acute kidney injury after hepatobiliary surgery: a prospective observational study. BMC Nephrol. 15:169. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2369-15-169. PMID: 25342079. PMCID: PMC4221681.
Article13. Yang CH, Chang CH, Chen TH, Fan PC, Chang SW, Chen CC, et al. 2016; Combination of urinary biomarkers improves early detection of acute kidney injury in patients with heart failure. Circ J. 80:1017–23. DOI: 10.1253/circj.CJ-15-0886. PMID: 26888148.
Article14. Rozenfeld KL, Zahler D, Shtark M, Goldiner I, Keren G, Banai S, et al. 2020; Elevated neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for the assessment of structural versus functional renal damage among ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients. Blood Purif. 49:560–6. DOI: 10.1159/000506175. PMID: 32074603.
Article15. Pickering JW, Endre ZH. 2013; Linking injury to outcome in acute kidney injury: a matter of sensitivity. PLoS One. 8:e62691. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062691. PMID: 23626850. PMCID: PMC3633852.
Article16. Albert C, Haase M, Albert A, Zapf A, Braun-Dullaeus RC, Haase-Fielitz A. 2021; Biomarker-guided risk assessment for acute kidney injury: time for clinical implementation? Ann Lab Med. 41:1–15. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2021.41.1.1. PMID: 32829575. PMCID: PMC7443517.
Article17. Haase M, Haase-Fielitz A, Plass M, Kuppe H, Hetzer R, Hannon C, et al. 2013; Prophylactic perioperative sodium bicarbonate to prevent acute kidney injury following open heart surgery: a multicenter double-blinded randomized controlled trial. PLoS Med. 10:e1001426. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001426. PMID: 23610561. PMCID: PMC3627643.
Article18. Albert C, Albert A, Bellomo R, Kropf S, Devarajan P, Westphal S, et al. 2018; Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin-guided risk assessment for major adverse kidney events after open-heart surgery. Biomark Med. 12:975–85. DOI: 10.2217/bmm-2018-0071. PMID: 30088425. PMCID: PMC6219442.
Article19. Grenier FC, Ali S, Syed H, Workman R, Martens F, Liao M, et al. 2010; Evaluation of the ARCHITECT urine NGAL assay: assay performance, specimen handling requirements and biological variability. Clin Biochem. 43:615–20. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2009.12.008. PMID: 20026020.20. Hanley JA, McNeil BJ. 1982; The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology. 143:29–36. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.143.1.7063747. PMID: 7063747.21. Waikar SS, Betensky RA, Emerson SC, Bonventre JV. 2012; Imperfect gold standards for kidney injury biomarker evaluation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 23:13–21. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010111124. PMID: 22021710. PMCID: PMC3695762.22. Haase M, Devarajan P, Haase-Fielitz A, Bellomo R, Cruz DN, Wagener G, et al. 2011; The outcome of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin-positive subclinical acute kidney injury: a multicenter pooled analysis of prospective studies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 57:1752–61. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.11.051. PMID: 21511111. PMCID: PMC4866647.23. Youden WJ. 1950; Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer. 3:32–5. DOI: 10.1002/1097-0142(1950)3:1<32::AID-CNCR2820030106>3.0.CO;2-3. PMID: 15405679.24. Perkins NJ, Schisterman EF. 2006; The inconsistency of "optimal" cutpoints obtained using two criteria based on the receiver operating characteristic curve. Am J Epidemiol. 163:670–5. DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwj063. PMID: 16410346. PMCID: PMC1444894.25. Haase M, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, Schlattmann P, Haase-Fielitz A. NGAL Meta-analysis Investigator Group. 2009; Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 54:1012–24. DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.07.020. PMID: 19850388.
Article26. The R Development Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. http://www.R-project.org. R Foundation for Statistical Computing;Updated on Mar 2023.27. Singer E, Elger A, Elitok S, Kettritz R, Nickolas TL, Barasch J, et al. 2011; Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin distinguishes pre-renal from intrinsic renal failure and predicts outcomes. Kidney Int. 80:405–14. DOI: 10.1038/ki.2011.41. PMID: 21412214. PMCID: PMC3870593.
Article28. O'Neal JB, Shaw AD, Billings FT. 2016; Acute kidney injury following cardiac surgery: current understanding and future directions. Crit Care. 20:187. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-016-1352-z. PMID: 27373799. PMCID: PMC4931708.29. Thiele RH, Isbell JM, Rosner MH. 2015; AKI associated with cardiac surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 10:500–14. DOI: 10.2215/CJN.07830814. PMID: 25376763. PMCID: PMC4348689.
Article30. Brenner H, Gefeller O. 1997; Variation of sensitivity, specificity, likelihood ratios and predictive values with disease prevalence. Stat Med. 16:981–91. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0258(19970515)16:9<981::AID-SIM510>3.0.CO;2-N.
Article31. Cook NR. 2007; Use and misuse of the receiver operating characteristic curve in risk prediction. Circulation. 115:928–35. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.672402. PMID: 17309939.
Article32. Rodrigues CE, Endre ZH. 2023; Definitions, phenotypes, and subphenotypes in acute kidney injury-moving towards precision medicine. Nephrology. 28:83–96. DOI: 10.1111/nep.14132. PMID: 36370326. PMCID: PMC10100386.
Article33. Huen SC, Parikh CR. 2015; Molecular phenotyping of clinical AKI with novel urinary biomarkers. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 309:F406–13. DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00682.2014. PMID: 26084933. PMCID: PMC4556889.
Article34. Kellum JA, Devarajan P. 2014; What can we expect from biomarkers for acute kidney injury? Biomark Med. 8:1239–45. DOI: 10.2217/bmm.14.82. PMID: 25525984. PMCID: PMC5672550.
Article35. Zapf A, Albert C, Frömke C, Haase M, Hoyer A, Jones HE, et al. 2021; Meta‐analysis of diagnostic accuracy studies with multiple thresholds: comparison of different approaches. Biom J. 63:699–711. DOI: 10.1002/bimj.202000091. PMID: 33475187.
Article36. Jäntti T, Tarvasmäki T, Harjola VP, Pulkki K, Turkia H, Sabell T, et al. 2021; Predictive value of plasma proenkephalin and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in acute kidney injury and mortality in cardiogenic shock. Ann Intensive Care. 11:25. DOI: 10.1186/s13613-021-00814-8. PMID: 33547528. PMCID: PMC7865050.
Article37. Kim H, Hur M, Cruz DN, Moon HW, Yun YM. 2013; Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker for acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with suspected sepsis. Clin Biochem. 46:1414–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2013.05.069. PMID: 23747960.
Article38. L'Acqua C, Sisillo E, Salvi L, Introcaso G, Biondi ML. Nephrocheck after cardiac surgery: does it play a role in daily practice? A sequel of "Nephrocheck results should be corrected for dilution.". Int J Artif Organs. 2019; 42:665–7. DOI: 10.1177/0391398819852958. PMID: 31151359.39. Albert C, Haase M, Albert A, Ernst M, Kropf S, Bellomo R, et al. 2021; Predictive value of plasma NGAL:Hepcidin-25 for major adverse kidney events after cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a pilot study. Ann Lab Med. 41:357–65. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2021.41.4.357. PMID: 33536353. PMCID: PMC7884201.
Article40. Greenland S. 1995; Avoiding power loss associated with categorization and ordinal scores in dose-response and trend analysis. Epidemiology. 6:450–4. DOI: 10.1097/00001648-199507000-00025. PMID: 7548361.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Hepcidin and Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as a Biomarker for Acute Kidney Injury Linked Iron Metabolism
- Current knowledge about biomarkers of acute kidney injury in liver cirrhosis
- Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Kidney Diseases
- New Biomarkers of Acute Kidney Injury and the Cardio-renal Syndrome
- Clinical Significance of the Interval Change of Plasma Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Acute Kidney Injury and Acute Kidney Injury Superimposed on Chronic Kidney Disease