Implications of the 5th Edition of the World Health Organization Classification and International Consensus Classification of Myeloid Neoplasm in Myelodysplastic Syndrome With Excess Blasts and Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Korea University Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2551999
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.5.503
Abstract
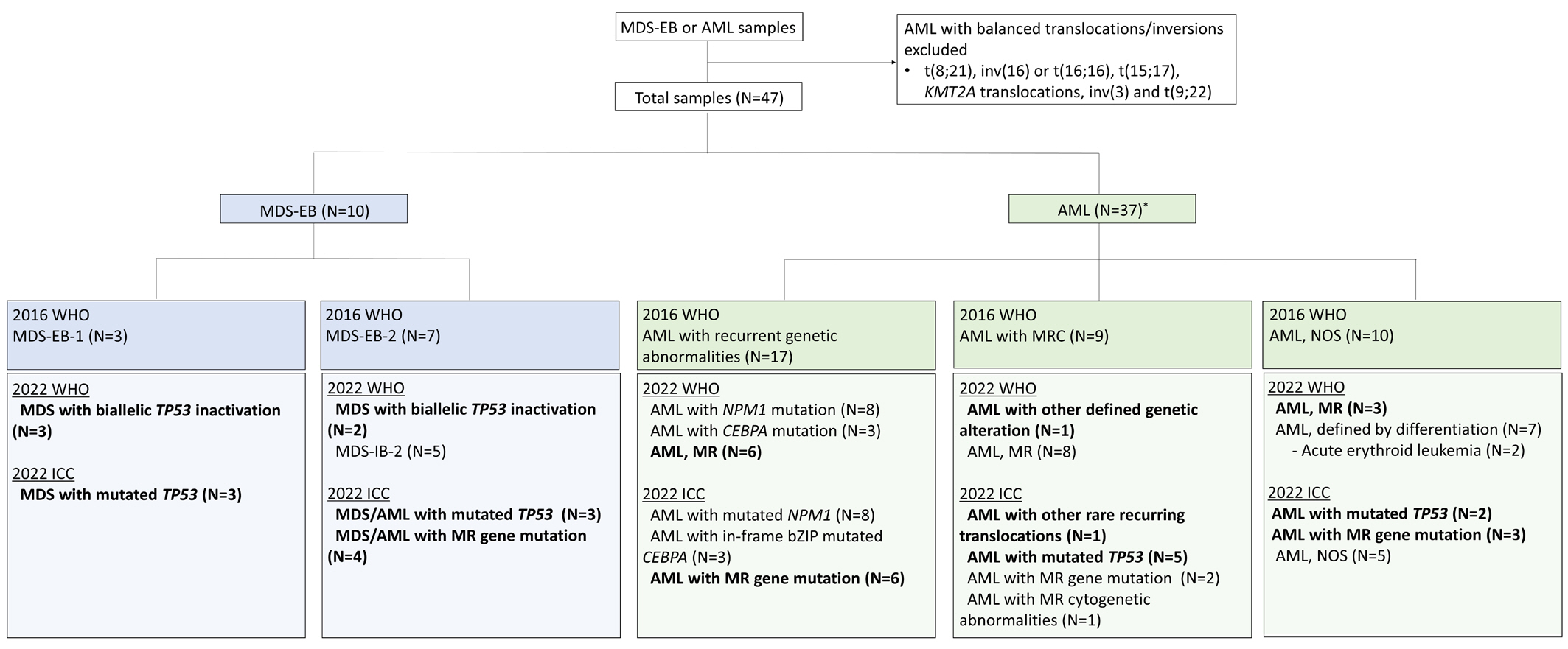
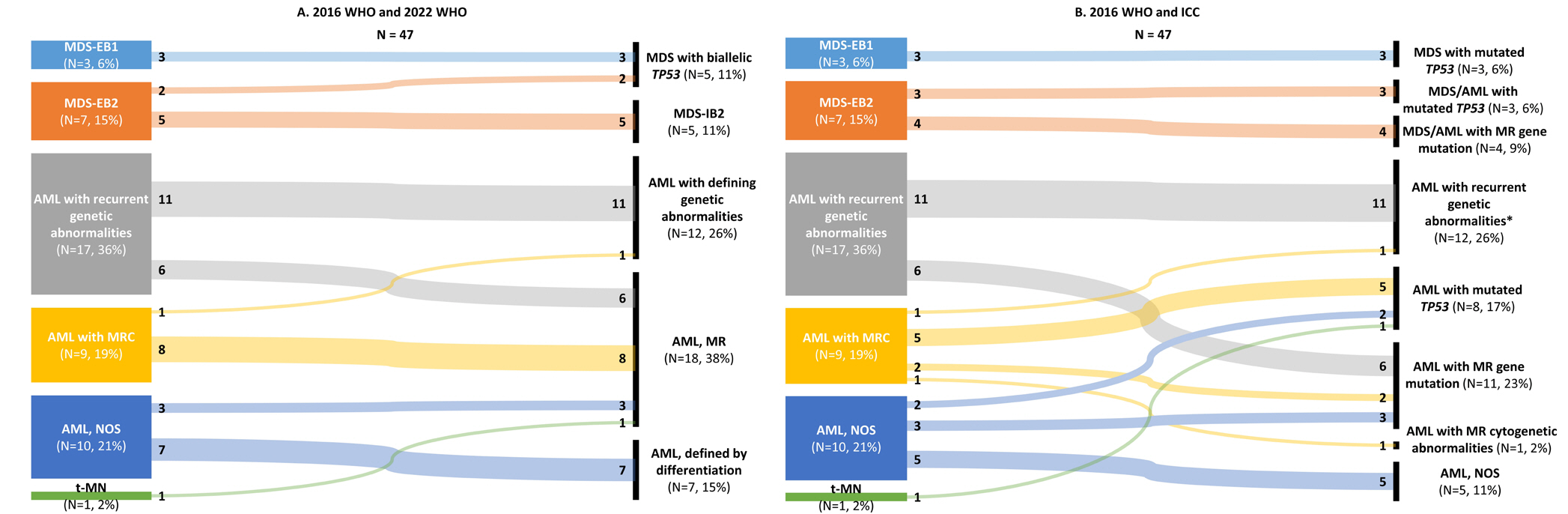
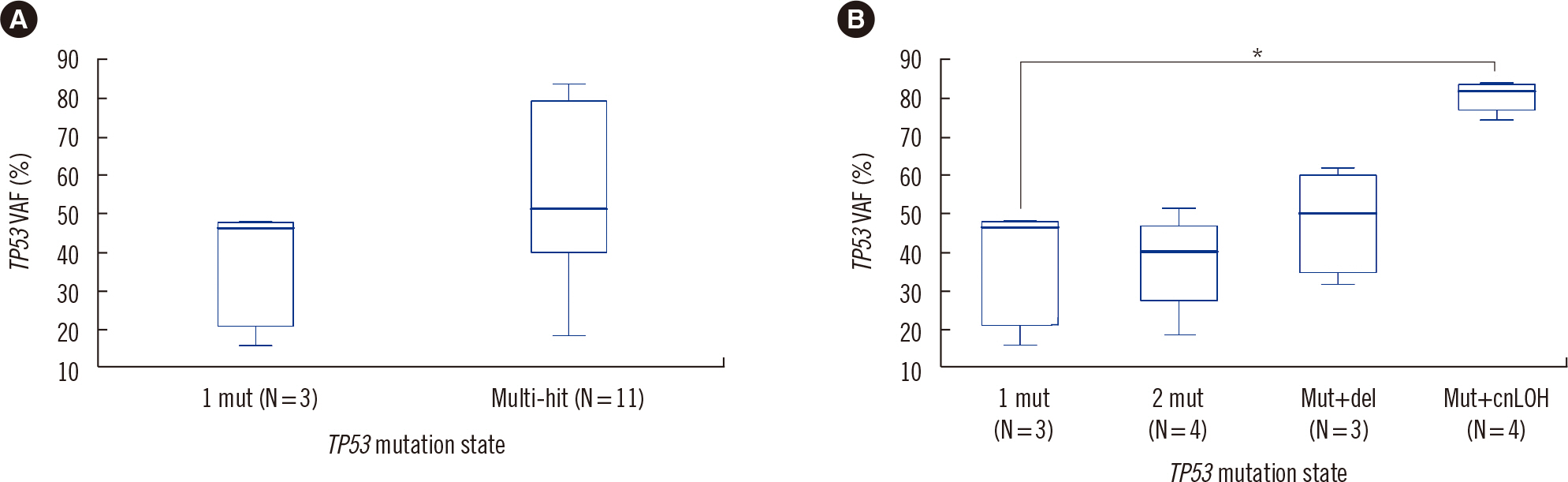
- The fifth edition of the WHO classification (2022 WHO) and the International Consensus Classification (2022 ICC) of myeloid neoplasms have been recently published. We reviewed the changes in the diagnosis distribution in patients with MDS with excess blasts (MDS-EB) or AML using both classifications. Forty-seven patients previously diagnosed as having AML or MDS-EB with available mutation analysis data, including targeted next-generation and RNA-sequencing data, were included. We reclassified 15 (31.9%) and 27 (57.4%) patients based on the 2022 WHO and 2022 ICC, respectively. One patient was reclassified as having a translocation categorized as a rare recurring translocation in both classifications. Reclassification was mostly due to the addition of mutation-based diagnostic criteria (i.e., AML, myelodysplasia-related) or a new entity associated with TP53 mutation. In both classifications, MDS diagnosis required the confirmation of multi-hit TP53 alterations. Among 14 patients with TP53 mutations, 11 harbored multi-hit TP53 alterations, including four with TP53 mutations and loss of heterozygosity. Adverse prognosis was associated with multi-hit TP53 alterations (P=0.009) in patients with MDS-EB, emphasizing the importance of detecting the mutations at diagnosis. The implementation of these classifications may lead to the identification of different subtypes from previously heterogeneous diagnostic categories based on genetic characteristics.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic neoplasms: clinical implications of myelodysplasia‑related genes mutations and
TP53 aberrations
Hyunwoo Kim, Ja Young Lee, Sinae Yu, Eunkyoung Yoo, Hye Ran Kim, Sang Min Lee, Won Sik Lee
Blood Res. 2024;59:41. doi: 10.1007/s44313-024-00044-4.TP53 Mutation Status in Myelodysplastic Neoplasm and Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Impact of Reclassification Based on the 5th WHO and International Consensus Classification Criteria: A Korean Multicenter Study
Hyun-Young Kim, Saeam Shin, Jong-Mi Lee, In-Suk Kim, Boram Kim, Hee-Jin Kim, Yu Jeong Choi, Byunggyu Bae, Yonggoo Kim, Eunhui Ji, Hyerin Kim, Hyerim Kim, Jee-Soo Lee, Yoon Hwan Chang, Hyun Kyung Kim, Ja Young Lee, Shinae Yu, Miyoung Kim, Young-Uk Cho, Seongsoo Jang, Myungshin Kim
Ann Lab Med. 2025;45(2):160-169. doi: 10.3343/alm.2024.0351.Reclassification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia According to the 2022 World Health Organization Classification and the International Consensus Classification Using Open-Source Data
Jiwon Yun
Ann Lab Med. 2025;45(2):170-177. doi: 10.3343/alm.2024.0194.
Reference
-
1. Bernard E, Tuechler H, Greenberg PL, Hasserjian RP, Arango Ossa JE, Nannya Y, et al. 2022; Molecular international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. NEJM Evid. 1:EVIDoa2200008. DOI: 10.1056/EVIDoa2200008.
Article2. Döhner H, Wei AH, Appelbaum FR, Craddock C, DiNardo CD, Dombret H, et al. 2022; Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood. 140:1345–77. DOI: 10.1182/blood.2022016867. PMID: 35797463.
Article3. Ley TJ, Miller C, Ding L, Raphael BJ, Mungall AJ, et al. Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. 2013; Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 368:2059–74. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1301689. PMID: 23634996. PMCID: PMC3767041.
Article4. Park HS, Son SM, Kwon J. Serial analysis and comparison of mutation profiles in decitabine-treated myeloid sarcoma and subsequent acute myeloid leukemia using next-generation sequencing. Ann Lab Med. 2022; 42:602–5. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.5.602. PMID: 35470279. PMCID: PMC9057818.
Article5. Khoury JD, Solary E, Abla O, Akkari Y, Alaggio R, Apperley JF, et al. 2022; The 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification of haematolymphoid tumours: myeloid and histiocytic/dendritic neoplasms. Leukemia. 36:1703–19. DOI: 10.1038/s41375-022-01613-1. PMID: 35732831. PMCID: PMC9252913.
Article6. Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian RP, Borowitz MJ, Calvo KR, Kvasnicka HM, et al. 2022; International Consensus Classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemias: integrating morphologic, clinical, and genomic data. Blood. 140:1200–28. DOI: 10.1182/blood.2022015850. PMID: 35767897.7. Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, et al. 2016; The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 127:2391–405. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-03-643544. PMID: 27069254.
Article8. McGowan-Jordan J, Hastings RJ, editors. 2020. ISCN 2020: An International System for Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature. Karger;Basel:9. Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Jha S, et al. 2013; STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 29:15–21. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts635. PMID: 23104886. PMCID: PMC3530905.
Article10. Arriba [Computer software]. (2018). ESMO Open, 3(Suppl 2), A179. https://github.com/suhrig/arriba. Updated on January 2022.11. R [Computer software]. (2021). https://www.R-project.org/. Updated on November 2017.12. Bolouri H, Farrar JE, Triche T Jr, Ries RE, Lim EL, Alonzo TA, et al. 2018; The molecular landscape of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia reveals recurrent structural alterations and age-specific mutational interactions. Nat Med. 24:103–12. DOI: 10.1038/nm.4439. PMID: 29227476. PMCID: PMC5907936.
Article13. Bernard E, Nannya Y, Hasserjian RP, Devlin SM, Tuechler H, Medina-Martinez JS, et al. 2020; Implications of TP53 allelic state for genome stability, clinical presentation and outcomes in myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat Med. 26:1549–56. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-020-1008-z. PMID: 32747829. PMCID: PMC8381722.
Article14. Grob T, Al Hinai ASA, Sanders MA, Kavelaars FG, Rijken M, Gradowska PL, et al. 2022; Molecular characterization of mutant TP53 acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood. 139:2347–54. DOI: 10.1182/blood.2021014472. PMID: 35108372.15. Haase D, Stevenson KE, Neuberg D, Maciejewski JP, Nazha A, Sekeres MA, et al. 2019; TP53 mutation status divides myelodysplastic syndromes with complex karyotypes into distinct prognostic subgroups. Leukemia. 33:1747–58. DOI: 10.1038/s41375-018-0351-2. PMID: 30635634. PMCID: PMC6609480.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Classification of acute myeloid leukemia
- What is new in acute myeloid leukemia classification?
- Comparison of FAB and WHO Classifications and Validation of WHO Classifications in 218 Korean Patients with Myelodysplastic Syndrome
- Acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic neoplasms: clinical implications of myelodysplasia‑related genes mutations and TP53 aberrations
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia with t(8;21)(q22;q22) (AML1/ETO) in a Patient with Marked Hypocellularity and Low Blasts Count