Ann Lab Med.
2023 Sep;43(5):477-484. 10.3343/alm.2023.43.5.477.
Reducing Microbial Contamination in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Products and Quality Improvement Strategy: Retrospective Analysis of 1996-2021 Data
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, School of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Korea
- 3Cell and Gene Therapy Institute, Research Institute for Future Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2551996
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.5.477
Abstract
- Background
Sterility and safety assurance of hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) products is critical in transplantation. Microbial contamination can lead to product disposal and increases the risk of unsuccessful clinical outcomes. Therefore, it is important to implement and maintain good practice guidelines and regulations for the HSC collection and processing unit in each hospital. We aimed to share our experiences and suggest strategies to improve the quality assurance of HSC processing.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed microbial culture results of 11,743 HSC products processed over a 25-year period (January 1996 to May 2021). Because of reorganization of the HSC management system in 2008, the 25-year period was divided into periods 1 (January 1996 to December 2007) and 2 (January 2008 to May 2021). We reviewed all culture results of the HSC products and stored aliquot samples and collected culture results for peripheral blood and catheter samples.
Results
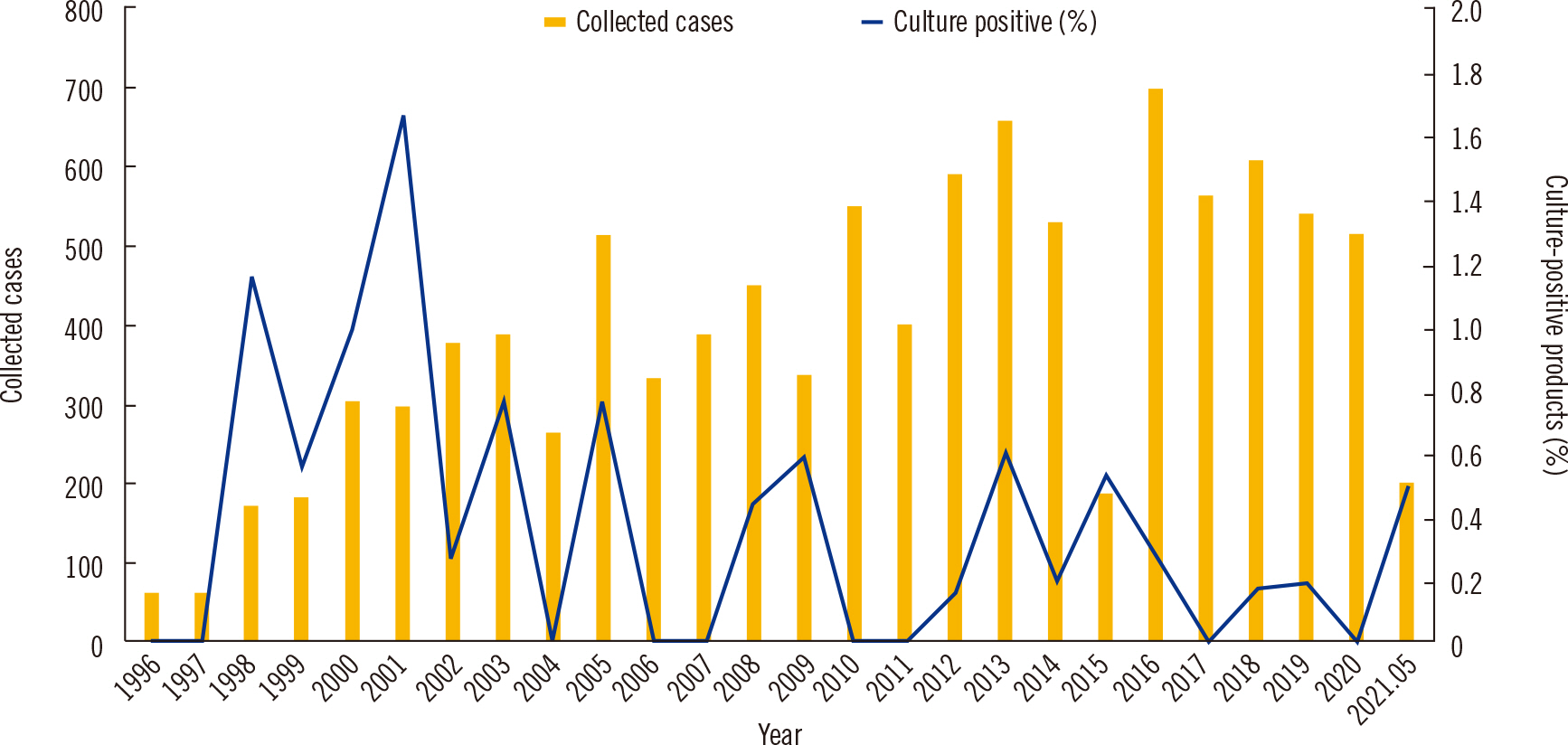
Of the 11,743 products in total, 35 (0.3%) were contaminated by microorganisms, including 19 (0.5%) of 3,861 products during period 1 and 16 (0.2%) of 7,882 products during period 2. Penicillium was the most commonly identified microorganism (15.8%) during period 1 and coagulase-negative Staphylococcus was the most commonly identified (31.3%) during period 2. HSC product contamination occurred most often during HSC collection and processing.
Conclusions
The contamination rate decreased significantly during period 2, when the HSC management system was reorganized. Our results imply that handling HSC products by trained personnel and adopting established protocols, including quality assurance programs, aid in decreasing the contamination risk.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gratwohl A. 2002; The role of the EBMT activity survey in the management of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. European Group for Blood Marrow Transplantation. Int J Hematol. 76(S1):386–92. DOI: 10.1007/BF03165290. PMID: 12430888.
Article2. Gratwohl A, Pasquini MC, Aljurf M, Atsuta Y, Baldomero H, Foeken L, et al. 2015; One million haemopoietic stem-cell transplants: a retrospective observational study. Lancet Haematol. 2:e91–100. DOI: 10.1016/S2352-3026(15)00028-9. PMID: 26687803.
Article3. Cobo F, Stacey GN, Hunt C, Cabrera C, Nieto A, Montes R, et al. 2005; Microbiological control in stem cell banks: approaches to standardisation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 68:456–66. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-005-0062-2. PMID: 16012832. PMCID: PMC7080164.
Article4. Matuszak P, Bembnista E, Kubiak A, Kozlowska-Skrzypczak M. 2016; Liquid storage of hematopoietic stem cells versus proliferative potential colony-forming unit granulocyte-monocytes: validation of cell processing. Transplant Proc. 48:1810–3. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2016.03.010. PMID: 27496497.
Article5. Gianassi S, Bisin S, Bindi B, Spitaleri I, Bambi F. 2010; Risk analysis of hematopoietic stem cell transplant process: failure mode, effect, and criticality analysis and hazard analysis critical control point methods integration based on guidelines to good manufacturing practice for medicinal product ANNEX 20 (February 2008). Transplant Proc. 42:2252–3. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2010.05.041. PMID: 20692457.
Article6. Arlt N, Rothe R, Sielaff S, Juretzek T, Peltroche H, Moog R. 2018; Sterility release testing of peripheral blood stem cells for transplantation: impact of culture bottles and incubation temperature. Transfusion. 58:2918–23. DOI: 10.1111/trf.14910. PMID: 30260478.
Article7. Majado MJ, García-Hernández A, Morales A, González C, Martínez-Sánchez V, Menasalvas A, et al. 2007; Influence of harvest bacterial contamination on autologous peripheral blood progenitor cells post-transplant. Bone Marrow Transplant. 39:121–5. DOI: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1705549. PMID: 17173054.
Article8. Gratwohl A, Brand R, McGrath E, van Biezen A, Sureda A, Ljungman P, et al. 2014; Use of the quality management system "JACIE" and outcome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica. 99:908–15. DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2013.096461. PMID: 24488562. PMCID: PMC4008105.
Article9. Kamble R, Pant S, Selby GB, Kharfan-Dabaja MA, Sethi S, Kratochvil K, et al. 2005; Microbial contamination of hematopoietic progenitor cell grafts-incidence, clinical outcome, and cost-effectiveness: an analysis of 735 grafts. Transfusion. 45:874–8. DOI: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2005.04178.x. PMID: 15934984.
Article10. Lazarus HM, Magalhaes-Silverman M, Fox RM, Creger RJ, Jacobs M. 1991; Contamination during in vitro processing of bone marrow for transplantation: clinical significance. Bone Marrow Transplant. 7:241–6.11. Watz E, Remberger M, Ringden O, Ljungman P, Sundin M, Mattsson J, et al. 2015; Quality of the hematopoietic stem cell graft affects the clinical outcome of allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Transfusion. 55:2339–50. DOI: 10.1111/trf.13143. PMID: 25968813.
Article12. Cobo F, Cortés JL, Cabrera C, Nieto A, Concha A. 2007; Microbiological contamination in stem cell cultures. Cell Biol Int. 31:991–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.cellbi.2007.03.010. PMID: 17452110.
Article13. Wuchter P. Carreras E, Dufour C, editors. 2019. Processing, cryopreserving and controlling the quality of HSCs. The EBMT handbook: hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and cellular therapies. 7th ed. Springer;Cham: p. 127–30.
Article14. Donmez A, Aydemir S, Arik B, Tunger A, Cilli F, Orman M, et al. 2012; Risk factors for microbial contamination of peripheral blood stem cell products. Transfusion. 52:777–81. DOI: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2011.03359.x. PMID: 21981571.
Article15. Clark P, Trickett A, Saffo S, Stark D. 2014; Effects of cryopreservation on microbial-contaminated cord blood. Transfusion. 54:532–40. DOI: 10.1111/trf.12323. PMID: 23808601.
Article16. Klein MA, Kadidlo D, McCullough J, McKenna DH, Burns LJ. 2006; Microbial contamination of hematopoietic stem cell products: incidence and clinical sequelae. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 12:1142–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2006.06.011. PMID: 17085307.
Article17. Snowden JA, Saccardi R, Orchard K, Ljungman P, Duarte RF, Labopin M, et al. 2020; Benchmarking of survival outcomes following haematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a review of existing processes and the introduction of an international system from the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) and the Joint Accreditation Committee of ISCT and EBMT (JACIE). Bone Marrow Transplant. 55:681–94. DOI: 10.1038/s41409-019-0718-7. PMID: 31636397. PMCID: PMC7113189.18. Kang ES, Lim CS, Han KS, Kim DW. 2020; Hematopoietic stem cell registry report: 2018. Korean J Blood Transfus. 31:109–18. DOI: 10.17945/kjbt.2020.31.2.109.
Article19. Almeida ID, Schmalfuss T, Röhsig LM, Goldani LZ. 2012; Autologous transplant: microbial contamination of hematopoietic stem cell products. Braz J Infect Dis. 16:345–50. DOI: 10.1016/j.bjid.2012.06.012. PMID: 22846122.
Article20. Jacobs MR, Good CE, Fox RM, Roman KP, Lazarus HM. 2013; Microbial contamination of hematopoietic progenitor and other regenerative cells used in transplantation and regenerative medicine. Transfusion. 53:2690–6. DOI: 10.1111/trf.12150. PMID: 23461309.
Article21. Owers KL, James E, Bannister GC. 2004; Source of bacterial shedding in laminar flow theatres. J Hosp Infect. 58:230–2. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhin.2004.06.028. PMID: 15501339.
Article22. Anatoliotaki M, Mantadakis E, Galanakis E, Samonis G. 2003; Rhodotorula species fungemia: a threat to the immunocompromised host. Clin Lab. 49:49–55.23. Goenaga Sánchez MA, Alberdi F, Carrera JA, Millet Sampedro M, Garde Orbaiz C. 2003; [Leuconostoc spp bacteremia in a patient with intestinal pseudoobstruction]. An Med Interna. 20:53–4. DOI: 10.4321/S0212-71992003000100020. PMID: 12666318.24. Prince HM, Page SR, Keating A, Saragosa RF, Vukovic NM, Imrie KR, et al. 1995; Microbial contamination of harvested bone marrow and peripheral blood. Bone Marrow Transplant. 15:87–91.25. Parienti JJ, Mongardon N, Mégarbane B, Mira JP, Kalfon P, Gros A, et al. 2015; Intravascular complications of central venous catheterization by insertion site. N Engl J Med. 373:1220–9. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1500964. PMID: 26398070.
Article26. O'Grady NP, Alexander M, Dellinger EP, Gerberding JL, Heard SO, Maki DG, et al. 2002; Guidelines for the prevention of intravascular catheter-related infections. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. MMWR Recomm Rep. 51:1–29.27. Shi Y, Yang N, Zhang L, Zhang M, Pei HH, Wang H. 2019; Chlorhexidine disinfectant can reduce the risk of central venous catheter infection compared with povidone: a meta-analysis. Am J Infect Control. 47:1255–62. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajic.2019.02.024. PMID: 30948152.
Article28. Namdaroğlu S, Tekgündüz E, Bozdağ SC, Durgun G, Sarıca A, Demiriz IŞ, et al. 2013; Microbial contamination of hematopoietic progenitor cell products. Transfus Apher Sci. 48:403–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.transci.2013.04.026. PMID: 23664302.
Article29. Patah PA, Parmar S, McMannis J, Sadeghi T, Karandish S, Rondon G, et al. 2007; Microbial contamination of hematopoietic progenitor cell products: clinical outcome. Bone Marrow Transplant. 40:365–8. DOI: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1705731. PMID: 17572714.
Article30. Damonti L, Buetti N, Droz S, Bacher U, Pabst T, Taleghani BM, et al. 2021; Prevalence and significance of bacterial contamination of autologous stem cell products. J Hosp Infect. 114:175–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhin.2021.04.006. PMID: 33864895.
Article31. Dal MS, Tekgündüz E, Çakar MK, Kaya AH, Namdaroğu S, Batgi H, et al. 2016; Does microbial contamination influence the success of the hematopoietic cell transplantation outcomes? Transfus Apher Sci. 55:125–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.transci.2016.05.001. PMID: 27184293.
Article32. Kozlowska-Skrzypczak M, Bembnista E, Kubiak A, Matuszak P, Schneider A, Komarnicki M. 2014; Microbial contamination of peripheral blood and bone marrow hematopoietic cell products and environmental contamination in a stem cell bank: a single-center report. Transplant Proc. 46:2873–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2014.09.002. PMID: 25380939.
Article33. Corrias MV, Haupt R, Carlini B, Parodi S, Rivabella L, Garaventa A, et al. 2006; Peripheral blood stem cell tumor cell contamination and survival of neuroblastoma patients. Clin Cancer Res. 12:5680–5. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0740. PMID: 17020970.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Microbial Contamination of Autologous Peripheral Blood Stem Cell
- Factors Affecting Fear of Cancer Recurrence in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Patients
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- Current Trends and Prospect of Cell Therapy using Hematopoietic Stem Cells
- Opening the era of in vivo xenotransplantation model for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation