Ann Lab Med.
2023 Jul;43(4):386-388. 10.3343/alm.2023.43.4.386.
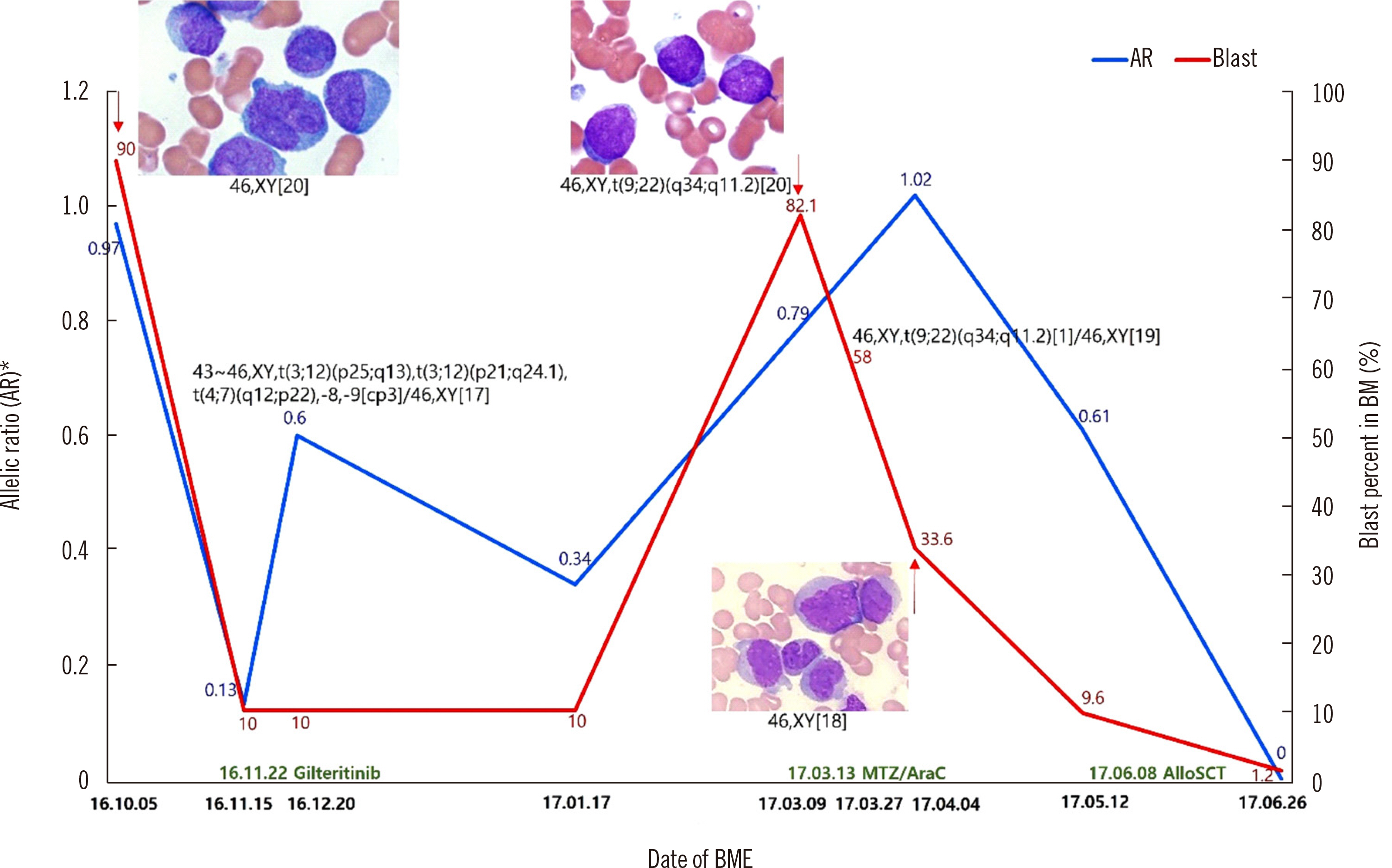
Emergence of BCR-ABL1 (p190) in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Post-Gilteritinib Therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
- KMID: 2551957
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.4.386
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
NUP214 Rearrangements in Leukemia Patients: A Case Series From a Single Institution
Yu Jeong Choi, Young Kyu Min, Seung-Tae Lee, Jong Rak Choi, Saeam Shin
Ann Lab Med. 2024;44(4):335-342. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.0301.
Reference
-
1. Papaemmanuil E, Gerstung M, Bullinger L, Gaidzik VI, Paschka P, Roberts ND, et al. 2016; Genomic classification and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 374:2209–21. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1516192. PMID: 27276561. PMCID: PMC4979995.
Article2. Daver N, Schlenk RF, Russell NH, Levis MJ. 2019; Targeting FLT3 mutations in AML: review of current knowledge and evidence. Leukemia. 33:299–312. DOI: 10.1038/s41375-018-0357-9. PMID: 30651634. PMCID: PMC6365380.
Article3. Pulte ED, Norsworthy KJ, Wang Y, Xu Q, Qosa H, Gudi R, et al. 2021; FDA approval summary: gilteritinib for relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia with a FLT3 mutation. Clin Cancer Res. 27:3515–21. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-4271. PMID: 33632926. PMCID: PMC8506653.4. McMahon CM, Ferng T, Canaani J, Wang ES, Morrissette JJD, Eastburn DJ, et al. 2019; Clonal selection with RAS pathway activation mediates secondary clinical resistance to selective FLT3 inhibition in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Discov. 9:1050–63. DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1453. PMID: 31088841.
Article5. Piloto O, Wright M, Brown P, Kim KT, Levis M, Small D. 2007; Prolonged exposure to FLT3 inhibitors leads to resistance via activation of parallel signaling pathways. Blood. 109:1643–52. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-05-023804. PMID: 17047150. PMCID: PMC1794049.
Article6. Kropp EM, Li Q. 2022; Mechanisms of resistance to targeted therapies for relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Exp Hematol. 111:13–24. DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2022.04.001. PMID: 35417742.
Article7. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, editors. 2017. World Health Organization classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Revised 4th ed. IARC;Lyon:8. Alotaibi AS, Yilmaz M, Loghavi S, DiNardo C, Borthakur G, Kadia TM, et al. 2020; Emergence of BCR-ABL1 fusion in AML post-FLT3 inhibitor-based therapy: a potentially targetable mechanism of resistance - a case series. Front Oncol. 10:588876. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.588876. PMID: 33194747. PMCID: PMC7606916.9. Staudt D, Murray HC, McLachlan T, Alvaro F, Enjeti AK, Verrills NM, et al. 2018; Targeting oncogenic signaling in mutant FLT3 acute myeloid leukemia: the path to least resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 19:3198. DOI: 10.3390/ijms19103198. PMID: 30332834. PMCID: PMC6214138.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia with Co-existence of BCR-ABL1 and PML-RARA Rearrangements Detected by PCR
- Isolated monocytosis was the flag preceding abnormalities in other parameters of complete blood counts in chronic myeloid leukemia with e1a2 (minor, P190) BCR-ABL1 chimeric transcripts
- A case of e1a2 (minor, P190) BCR-ABL1-positive chronic myeloid leukemia in Korea
- A Case of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia with Micro BCR::ABL1 Rearrangement: Precaution in Reverse Transcription PCR to Prevent False Negativity
- Genomic Profiling of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: Basic and Clinical Approach