Ann Lab Med.
2023 Jul;43(4):337-344. 10.3343/alm.2023.43.4.337.
Comparison of the International Normalized Ratio Between a Point-of-Care Test and a Conventional Laboratory Test: the Latter Performs Better in Assessing Warfarin-induced Changes in Coagulation Factors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 3Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2551951
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.4.337
Abstract
- Background
Point-of-care testing (POCT) coagulometers are increasingly used for monitoring warfarin therapy. However, in high international normalized ratio (INR) ranges, significant discrepancy in the INR between POCT and conventional laboratory tests occurs. We compared the INR of POCT (CoaguChek XS Plus; Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) with that of a conventional laboratory test (ACL TOP 750; Instrumentation Laboratory SpA, Milan, Italy) and explored possible reasons for discrepancy.
Methods
Paired POCT and conventional laboratory test INRs were analyzed in 400 samples from 126 patients undergoing warfarin therapy after cardiac surgery. Coagulation factor and thrombin generation tests were compared using the Mann–Whitney U test. Correlations between coagulation factors and INRs were determined using Pearson correlation coefficients.
Results
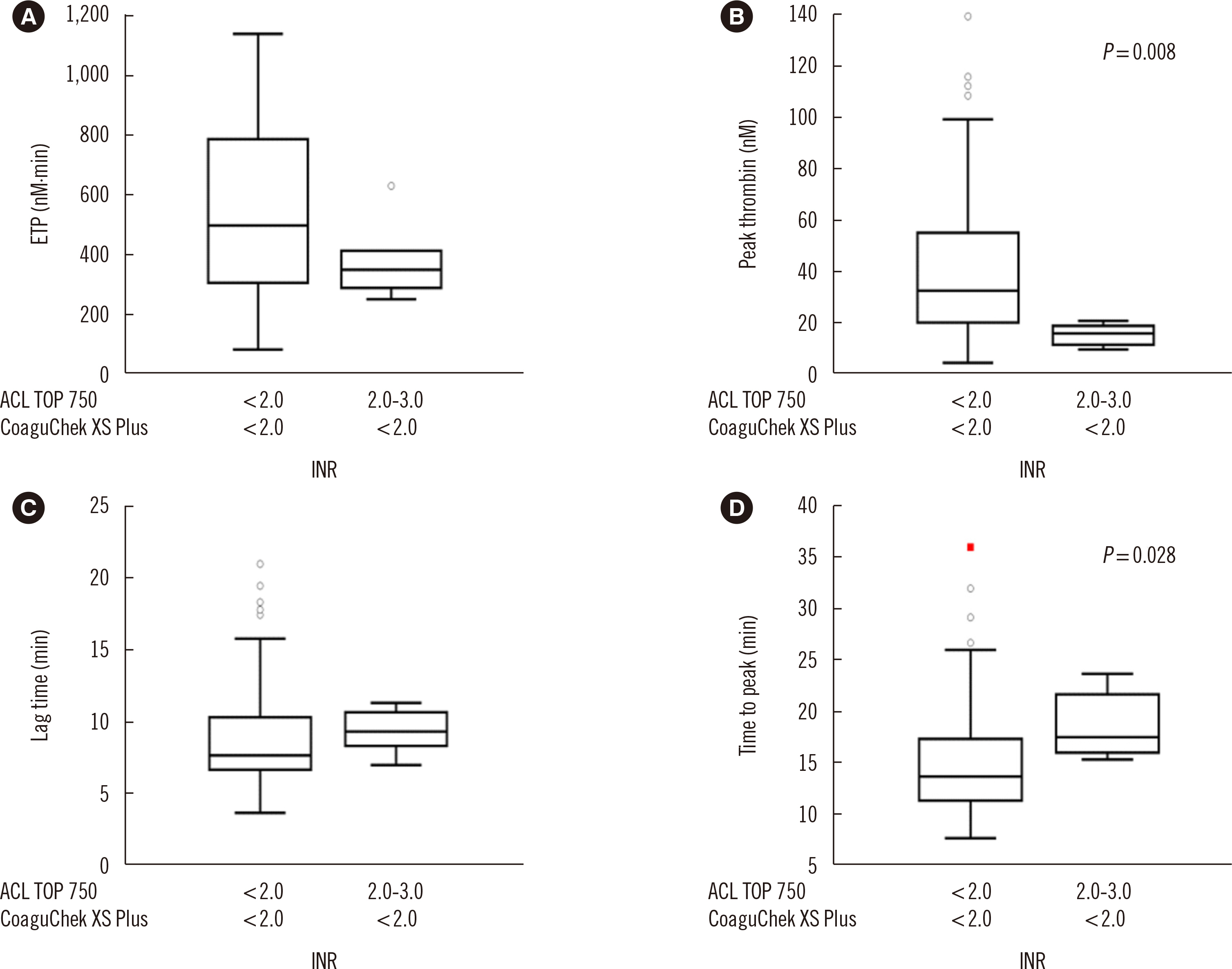
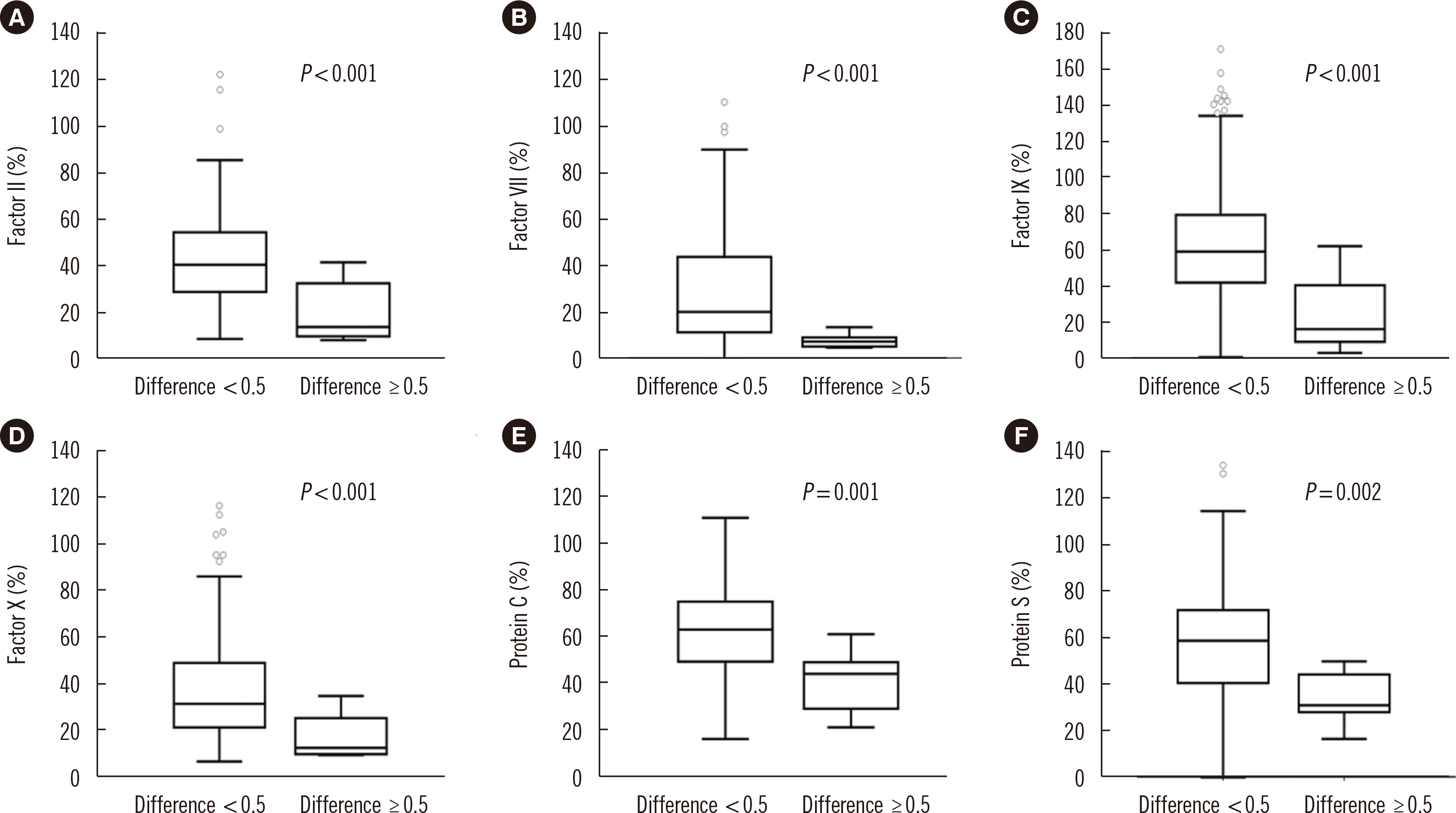
The mean difference in the INR between the tests increased at high INR ranges. Endogenous thrombin potential levels were decreased at INR <2.0 for CoaguChek XS Plus and 2.0< INR <3.0 for ACL TOP 750 compared with those at INR <2.0 for both tests, indicating a better performance of ACL TOP 750 in assessing thrombin changes. The correlation coefficients of coagulation factors were stronger for ACL TOP 750 INR than for CoaguChek XS Plus INR. Vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors were found to contribute to the INR discrepancy.
Conclusions
Decreases in vitamin K-dependent coagulation and anticoagulation factors can explain the significant discrepancy between the two tests in high INR ranges. Since conventional laboratory test INR values are more reliable than POCT INR values, a confirmatory conventional laboratory test is required for high INR ranges.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ansell J, Hirsh J, Hylek E, Jacobson A, Crowther M, Palareti G. 2008; Pharmacology and management of the vitamin K antagonists: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th edition). Chest. 133(6S):160S–98S. DOI: 10.1378/chest.08-0670. PMID: 18574265.2. Choi Q, Kim JE, Hyun J, Han KS, Kim HK. 2013; Contributions of procoagulants and anticoagulants to the international normalized ratio and thrombin generation assay in patients treated with warfarin: potential role of protein Z as a powerful determinant of coagulation assays. Thromb Res. 132:e70–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.thromres.2013.05.015. PMID: 23769659.
Article3. Ageno W, Gallus AS, Wittkowsky A, Crowther M, Hylek EM, Palareti G. 2012; Oral anticoagulant therapy: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 141(2S):e44S–e88S. DOI: 10.1378/chest.11-2292. PMID: 22315269. PMCID: PMC3278051.4. Hur M, Kim H, Park CM, La Gioia A, Choi SG, Choi JH, et al. 2013; Comparison of international normalized ratio measurement between CoaguChek XS Plus and STA-R coagulation analyzers. Biomed Res Int. 2013:213109. DOI: 10.1155/2013/213109. PMID: 23509691. PMCID: PMC3591144.
Article5. Biedermann JS, Leebeek FW, Buhre PN, de Lathouder S, Barends JP, de Maat MP, et al. 2015; Agreement between Coaguchek XS and STA-R Evolution (Hepato Quick) INR results depends on the level of INR. Thromb Res. 136:652–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.thromres.2015.06.037. PMID: 26164396.
Article6. Kako H, Raman VT, Tumin D, Rice J, Tobias JD. 2017; Point-of-care testing for coagulation function: CoaguChek® XS System versus standard laboratory testing in pediatric patients with normal and abnormal coagulation function. J Anesth. 31:345–50. DOI: 10.1007/s00540-017-2317-3. PMID: 28213667.
Article7. Kim JA, Kim JE, Song SH, Kim HK. 2015; Influence of blood lipids on global coagulation test results. Ann Lab Med. 35:15–21. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2015.35.1.15. PMID: 25553275. PMCID: PMC4272949.
Article8. Hemker HC, Giesen P, Al Dieri R, Regnault V, de Smedt E, Wagenvoord R, et al. 2003; Calibrated automated thrombin generation measurement in clotting plasma. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb. 33:4–15. DOI: 10.1159/000071636. PMID: 12853707.
Article9. Kim SY, Kim JE, Kim HK, Kim I, Yoon SS, Park S. 2013; Influence of coagulation and anticoagulant factors on global coagulation assays in healthy adults. Am J Clin Pathol. 139:370–9. DOI: 10.1309/AJCPC5C4AGFRDKMX. PMID: 23429374.
Article10. Kim SJ, Lee EY, Park R, Kim J, Song J. 2015; Comparison of prothrombin time derived from CoaguChek XS and laboratory test according to fibrinogen level. J Clin Lab Anal. 29:28–31. DOI: 10.1002/jcla.21722. PMID: 24687901. PMCID: PMC6807023.
Article11. Wool GD. 2019; Benefits and pitfalls of point-of-care coagulation testing for anticoagulation management: an ACLPS critical review. Am J Clin Pathol. 151:1–17. DOI: 10.1093/ajcp/aqy087. PMID: 30215666.
Article12. Murray ET, Fitzmaurice DA, McCahon D. 2004; Point of care testing for INR monitoring: where are we now? Br J Haematol. 127:373–8. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2004.05154.x. PMID: 15521913.
Article13. Fitzmaurice DA, Gardiner C, Kitchen S, Mackie I, Murray ET, Machin SJ, et al. 2005; An evidence-based review and guidelines for patient self-testing and management of oral anticoagulation. Br J Haematol. 131:156–65. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05739.x. PMID: 16197444.
Article14. Baker WS, Albright KJ, Berman M, Spratt H, Mann PA, Unabia J, et al. 2017; POCT PT INR - is it adequate for patient care? A comparison of the Roche Coaguchek XS vs. Stago Star vs. Siemens BCS in patients routinely seen in an anticoagulation clinic. Clin Chim Acta. 472:139–45. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2017.07.027. PMID: 28774502.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Severe Airway Obstruction due to Massive Retropharyngeal Hematoma in a Warfarin-Taking Patient with a Normal International Normalized Ratio
- Clinical Utility and Accuracy of Coaguchek(R) XS, a Reliable Alternative to Laboratory International Normalized Ratio Monitoring in Korean Patients With Atrial Fibrillation
- Coagulopathy Caused by Concurrent Ciprofloxacin and Warfarin Use: What Other Factors Induce Coagulopathy?
- Extremely Elevated International Normalized Ratio of Warfarin in a Patient with CYP2C9*1/*3 and Thyrotoxicosis
- Warfarin-induced Primary Dissection of Lower Peripheral Arteries: A Case Report