Ann Lab Med.
2023 Mar;43(2):174-179. 10.3343/alm.2023.43.2.174.
Performance Comparison Between Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy–based IR Biotyper and Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry for Strain Diversity
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, National Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 2Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Cheongju University, Cheongju, Korea
- 3Department of Health Administration & Healthcare, Cheongju University, Cheongju, Korea
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, National Police Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 5Research Institute of Bacterial Resistance and Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 6Seoul Clinical Laboratories, Yongin, Korea
- KMID: 2551694
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.2.174
Abstract
- Background
Development of an accessible method to routinely evaluate the clonality of strains is needed in microbiology laboratories. We compared the discriminatory power of the Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy–based IR Biotyper (Bruker Daltonics GmbH, Bremen, Germany) to matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS), using whole-genome sequencing (WGS) as the reference method.
Methods
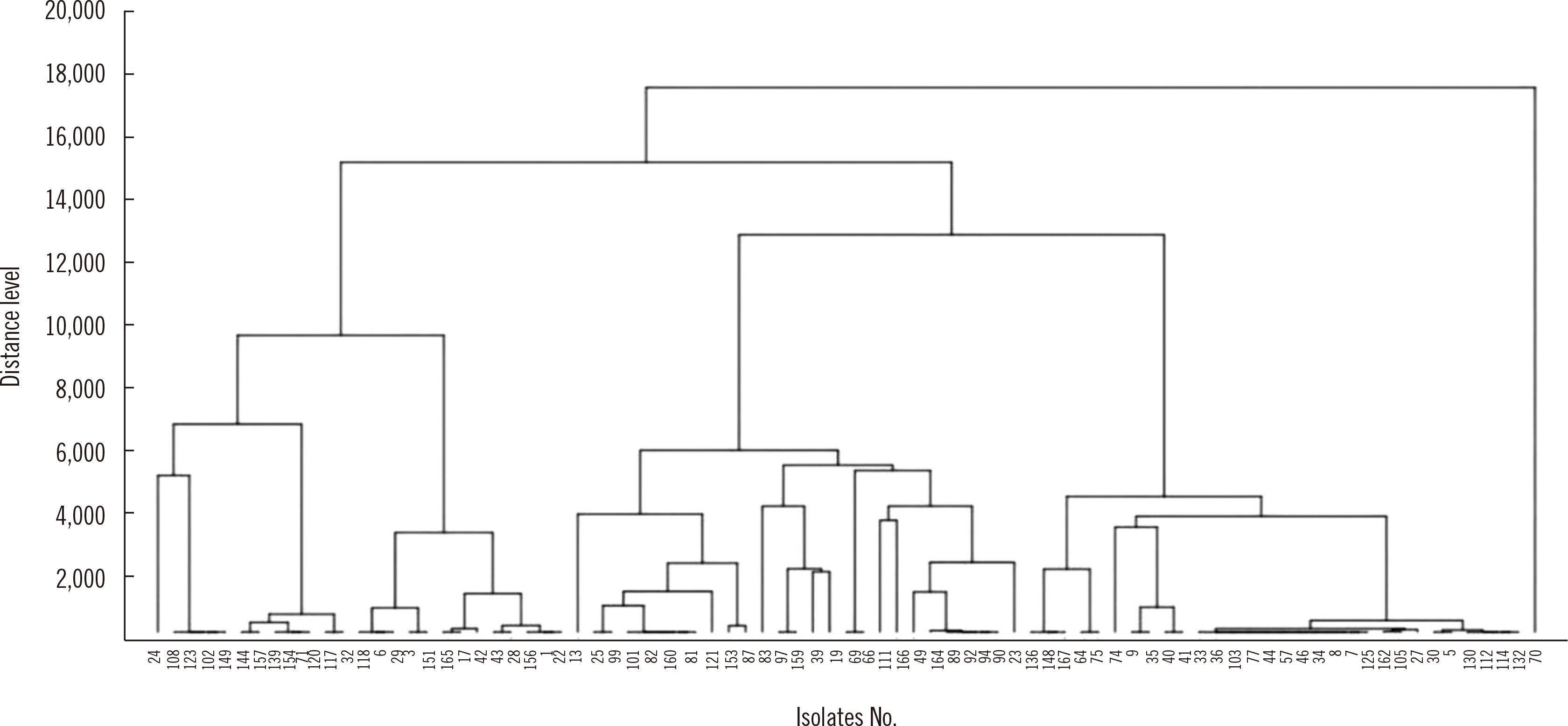
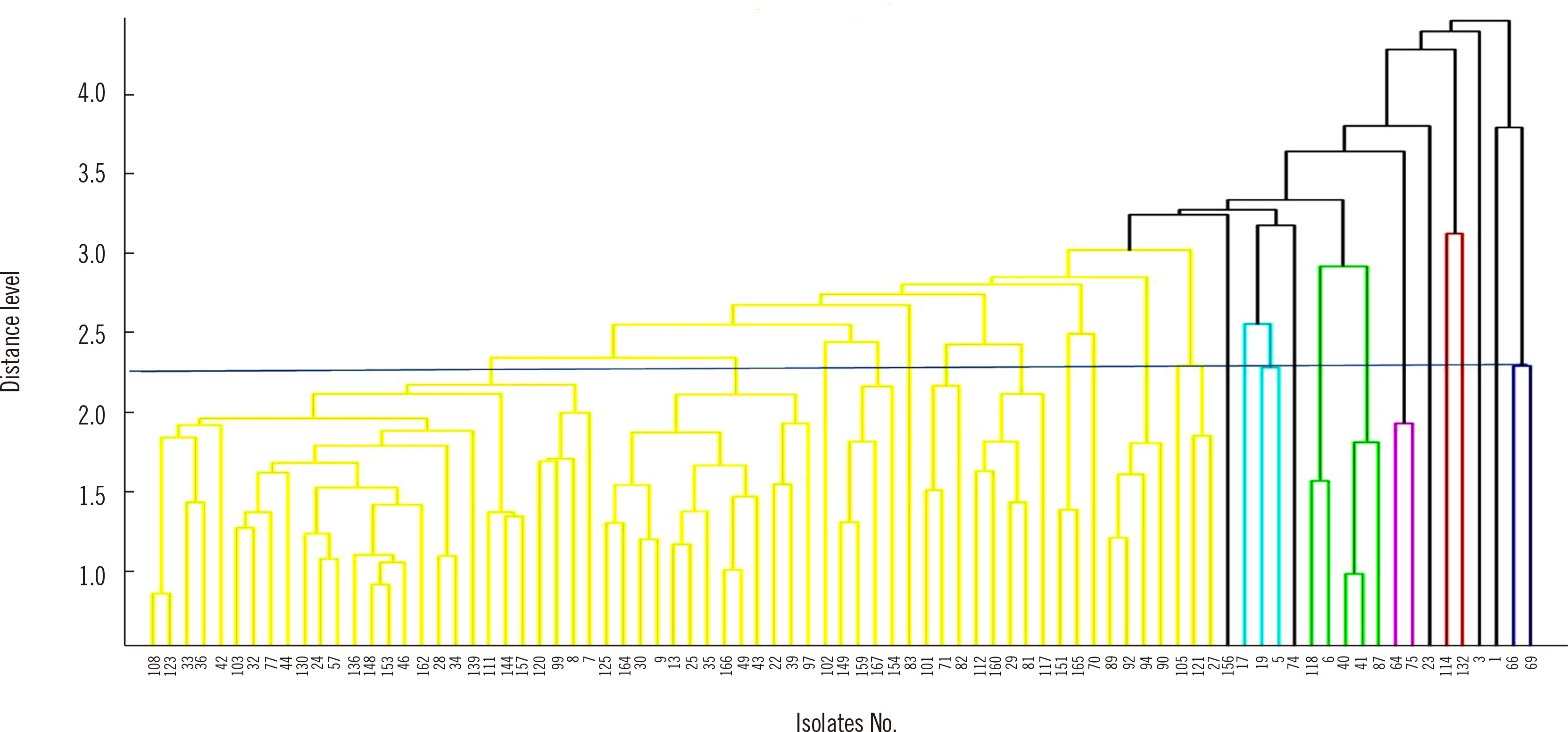
Eighty-three extended-spectrum β-lactamase–producing Escherichia coli isolates were tested using WGS, MALDI-TOF MS, and IR Biotyper. Simpson’s diversity index (SDI), a statistical analysis for testing the homogeneity of a dendrogram, and the adjusted Rand index (aRI) were used to compare the discriminatory ability between typing tests.
Results
The SDI (95% confidence interval) was 0.969 (0.952–0.985) for WGS, 0.865 (0.807–0.924) for MALDI-TOF MS, and 0.974 (0.965–0.983) for IR Biotyper. Compared with WGS, IR Biotyper showed compatible diversity, whereas MALDI-TOF MS did not. The concordance and aRI improved from 66.3% to 84.3% and from 0.173 to 0.538, respectively, for IR Biotyper versus MALDI-TOF MS with WGS as the reference method. IR Biotyper showed substantially improved performance in strain typing compared with MALDI-TOF MS.
Conclusions
IR Biotyper is useful for diversity analysis with improved discriminatory power over MALDI-TOF MS in comparison with WGS as a reference method. IR Biotyper is an accessible method to evaluate the clonality of strains and could be applied in epidemiological analysis during an outbreak of a health care facility, as well as for research on the transmission of resistant bacteria in community settings.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Melles DC, van Leeuwen WB, Snijders SV, Horst-Kreft D, Peeters JK, Verbrugh HA, et al. 2007; Comparison of multilocus sequence typing (MLST), pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE), and amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) for genetic typing of Staphylococcus aureus. J Microbiol Methods. 69:371–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.mimet.2007.01.013. PMID: 17346834.2. Quainoo S, Coolen JPM, van Hijum SAFT, Huynen MA, Melchers WJG, van Schaik W, et al. 2017; Whole-genome sequencing of bacterial pathogens: the future of nosocomial outbreak analysis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 30:1015–63. DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00016-17. PMID: 28855266. PMCID: PMC5608882.
Article3. Sauget M, Valot B, Bertrand X, Hocquet D. 2017; Can MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry reasonably type bacteria? Trends Microbiol. 25:447–55. DOI: 10.1016/j.tim.2016.12.006. PMID: 28094091.
Article4. Veenemans J, Welker M, van Belkum A, Saccomani MC, Girard V, Pettersson A, et al. 2016; Comparison of MALDI-TOF MS and AFLP for strain typing of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 35:829–38. DOI: 10.1007/s10096-016-2604-1. PMID: 26922068.
Article5. Kim YA, Yong D, In YH, Park HS, Lee K. 2016; Application of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry to screen the extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing ST131 Escherichia coli strains. Ann Clin Microbiol. 19:65–9. DOI: 10.5145/ACM.2016.19.3.65.
Article6. Rakovitsky N, Frenk S, Kon H, Schwartz D, Temkin E, Solter E, et al. 2020; Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy is a new option for outbreak investigation: a retrospective analysis of an extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae outbreak in a neonatal intensive care unit. J Clin Microbiol. 58:e00098–20. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00098-20. PMID: 32161093. PMCID: PMC7180251.7. Hu Y, Zhou H, Lu J, Sun Q, Liu C, Zeng Y, et al. 2021; Evaluation of the IR Biotyper for Klebsiella pneumoniae typing and its potentials in hospital hygiene management. Microb Biotechnol. 14:1343–52. DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.13709. PMID: 33205912. PMCID: PMC8313285.8. Kim H, Kim YA, Seo YH, Lee H, Lee K. 2021; Prevalence and molecular epidemiology of extended-spectrum-β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli from multiple sectors of poultry industry in Korea. Antibiotics. 10:1050. DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10091050. PMID: 34572632. PMCID: PMC8466054.
Article9. Prjibelski A, Antipov D, Meleshko D, Lapidus A, Korobeynikov A. 2020; Using SPAdes de novo assembler. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 70:e102. DOI: 10.1002/cpbi.102. PMID: 32559359.
Article10. Seemann T. 2014; Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics. 30:2068–9. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153. PMID: 24642063.
Article11. Center for Genomic Epidemiology. http://www.genomicepidemiology.org/. Updated on Aug 2022.12. Hammer Ø, Harper DA, Ryan PD. 2001; PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontologia Electronica. 4:9.13. FlexControl 3.4 User Manual. https://researchservices.pitt.edu/sites/default/files/flexControl%20User%20Manual.pdf. Updated on Aug 2022.14. Bruker. OPUS: Vibrational spectroscopy software. https://www.bruker.com/en/products-and-solutions/infrared-and-raman/opus-spectroscopy-software.html. Updated on Aug 2022.15. Comparing partitions. Online tool for quantitative assessment of classification agreement. http://www.comparingpartitions.info. Updated on Mar 2022.16. Grundmann H, Hori S, Tanner G. 2001; Determining confidence intervals when measuring genetic diversity and the discriminatory abilities of typing methods for microorganisms. J Clin Microbiol. 39:4190–2. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.11.4190-4192.2001. PMID: 11682558. PMCID: PMC88515.
Article17. Pinto FR, Carriço JA, Ramirez M, Almeida JS. 2007; Ranked adjusted Rand: integrating distance and partition information in a measure of clustering agreement. BMC Bioinformatics. 8:44. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-44. PMID: 17286861. PMCID: PMC1802093.
Article18. Rim JH, Lee Y, Hong SK, Park Y, Kim M, D'Souza R, et al. 2015; Insufficient discriminatory power of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry dendrograms to determine the clonality of multi-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from an intensive care unit. BioMed Res Int. 2015:535027. DOI: 10.1155/2015/535027. PMID: 26101775. PMCID: PMC4458526.19. Wenning M, Scherer S. 2013; Identification of microorganisms by FTIR spectroscopy: perspectives and limitations of the method. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 97:7111–20. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-013-5087-3. PMID: 23860713.
Article20. Hernando-Amado S, Coque TM, Baquero F, Martínez JL. 2019; Defining and combating antibiotic resistance from one health and global health perspectives. Nat Microbiol. 4:1432–42. DOI: 10.1038/s41564-019-0503-9. PMID: 31439928.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of the Bruker Biotyper and VITEK MS Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Systems Using a Formic Acid Extraction Method to Identify Common and Uncommon Yeast Isolates
- Comparison of a New Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Platform, ASTA MicroIDSys, With Bruker Biotyper for Species Identification
- Evaluation of two commercial kits for rapid pathogen identification directly from positive blood cultures by matrix-associated laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry
- MALDI-TOF-MS Fingerprinting Provides Evidence of Urosepsis caused by Aerococcus urinae
- Application of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Imaging Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF IMS) for Premalignant Gastrointestinal Lesions