Ann Lab Med.
2023 Jan;43(1):104-107. 10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.104.
Proposed Model for Evaluating Real-world Laboratory Results for Big Data Research
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hwaseong, Korea
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, School of Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital and College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- 7Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea
- KMID: 2551611
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.104
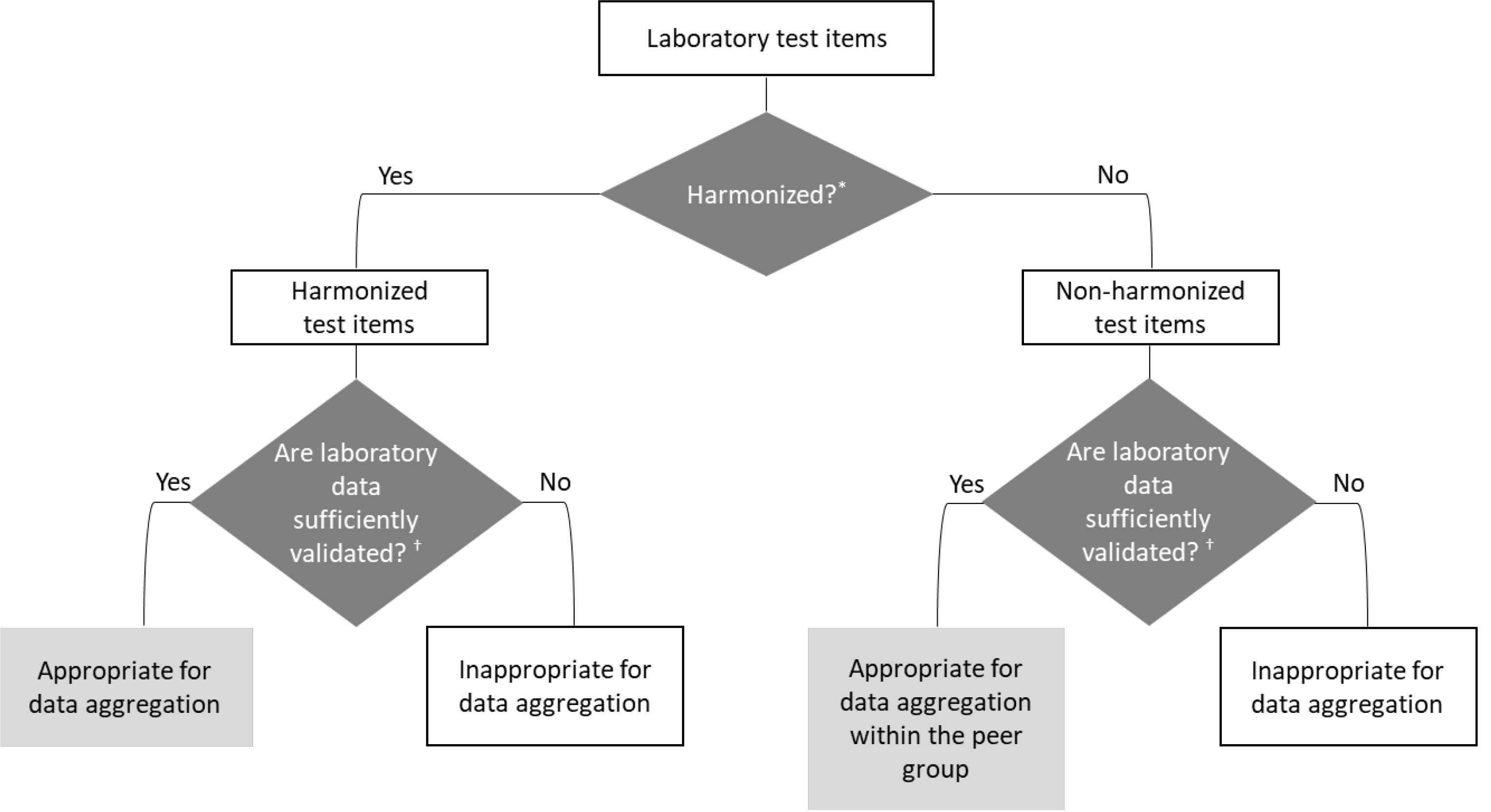
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Laboratory Data Quality Evaluation in the Big Data Era
Sollip Kim
Ann Lab Med. 2023;43(5):399-400. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.5.399.A New Strategy for Evaluating the Quality of Laboratory Results for Big Data Research: Using External Quality Assessment Survey Data (2010–2020)
Eun-Jung Cho, Tae-Dong Jeong, Sollip Kim, Hyung-Doo Park, Yeo-Min Yun, Sail Chun, Won-Ki Min
Ann Lab Med. 2023;43(5):425-433. doi: 10.3343/alm.2023.43.5.425.Effectiveness of Unified Computerized Reporting of Point-of-Care Glucose Meter Test
Sooin Choi, Dughyun Choi, Soo Jeong Choi, Jin Kuk Kim, You Kyoung Lee, Yong-Wha Lee
Ann Lab Med. 2024;44(1):103-106. doi: 10.3343/alm.2024.44.1.103.
Reference
-
1. EurA1c Trial Group. 2018; EurA1c: the European HbA1c trial to investigate the performance of HbA1c assays in 2166 laboratories across 17 countries and 24 manufacturers by use of the IFCC model for quality targets. Clin Chem. 64:1183–92. DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2018.288795. PMID: 29921723.2. Thompson S, Chesher D. 2018; Lot-to-lot variation. Clin Biochem Rev. 39:51–60.3. Thaler MA, Iakoubov R, Bietenbeck A, Luppa PB. 2015; Clinically relevant lot-to-lot reagent difference in a commercial immunoturbidimetric assay for glycated hemoglobin A1c. Clin Biochem. 48:1167–70. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2015.07.018. PMID: 26187005.
Article4. ICHCLR. The International Consortium for Harmonization of Clinical Laboratory Results. https://www.harmonization.net. Updated on Apr 2022.5. Jeong TD, Cho EJ, Lee K, Lee W, Yun YM, Chun S, et al. 2021; Recent trends in creatinine assays in Korea: long-term accuracy-based proficiency testing survey data by the Korean Association of External quality assessment service (2011-2019). Ann Lab Med. 41:372–9. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2021.41.4.372. PMID: 33536355. PMCID: PMC7884186.
Article6. Kim S, Lee K, Park HD, Lee YW, Chun S, Min WK. 2021; Schemes and performance evaluation criteria of Korean Association of External Quality Assessment (KEQAS) for improving laboratory testing. Ann Lab Med. 41:230–9. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2021.41.2.230. PMID: 33063686. PMCID: PMC7591290.
Article7. Weykamp C, John G, Gillery P, English E, Ji L, Lenters-Westra E, et al. 2015; Investigation of 2 models to set and evaluate quality targets for hb a1c: biological variation and sigma-metrics. Clin Chem. 61:752–9. DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2014.235333. PMID: 25737535. PMCID: PMC4946649.
Article8. IFCC (International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine). IFCC network for standardization of HbA1c. Updated on May 2022. https://ifcchba1c.org/.