Cancer Res Treat.
2024 Jan;56(1):115-124. 10.4143/crt.2023.600.
Aggressive Local Ablative Radiotherapy Mitigates Progression Risk in Oligometastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei Cancer Center, Heavy Ion Therapy Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Division of Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei Cancer Center, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Radiation Oncology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2550328
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2023.600
Abstract
- Purpose
This study aimed to determine the role of local ablative radiotherapy (LART) in oligometastatic/oligoprogressive lung adenocarcinoma.
Materials and Methods
Patients (n=176) with oligometastatic lung adenocarcinoma treated with LART were identified, and those treated with LART at the initial diagnosis of synchronous oligometastatic disease (OMD group) or treated with LART when they presented with repeat oligoprogression (OPD group) were included.
Results
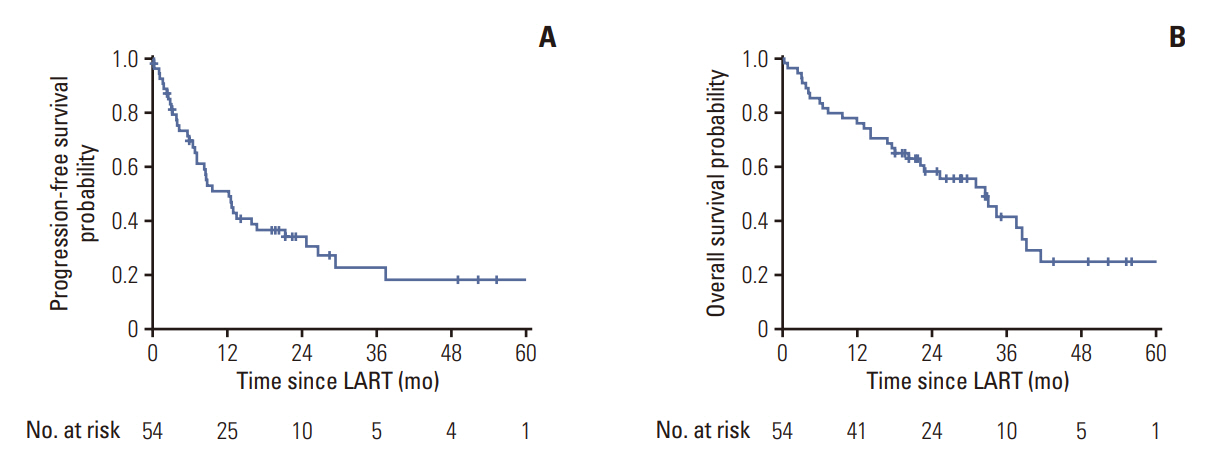
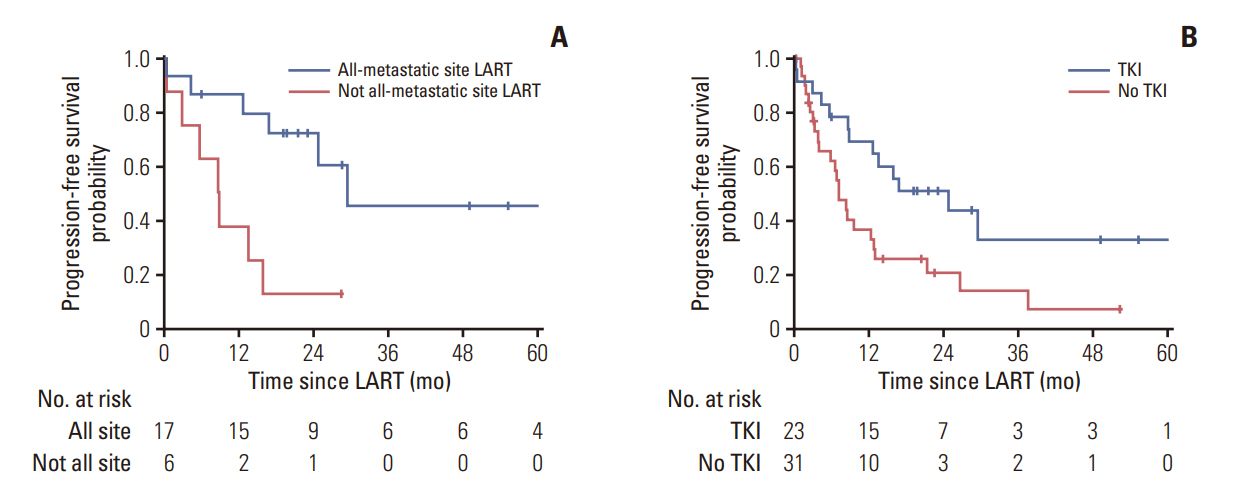
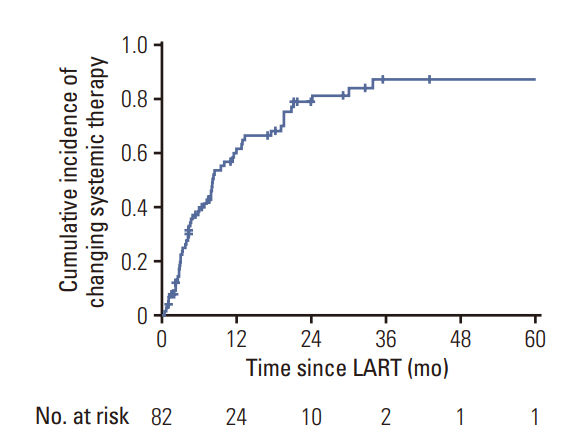
In the OMD group (n=54), the 1- and 3-year progression-free survival (PFS) were 50.9% and 22.5%, respectively, whereas the 1- and 3-year overall survival in the OPD group were 75.9% and 58.1%, respectively. Forty-one patients (75.9%) received LART at all gross disease sites. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) use and all-metastatic site LART were significant predictors of higher PFS (p=0.018 and p=0.046, respectively). In patients treated with TKIs at the time of LART (n=23) and those treated with all-metastatic site LART, the 1-year PFS was 86.7%, while that of patients not treated with all-metastatic site LART was 37.5% (p=0.006). In the OPD group (n=122), 67.2% of the patients (n=82) maintained a systemic therapy regimen after LART. The cumulative incidence of changing systemic therapy was 39.6%, 62.9%, and 78.5% at 6 months, 1 year, and 2 years after LART, respectively.
Conclusion
Aggressive LART can be an option to improve survival in patients with oligometastatic disease. Patients with synchronous oligometastatic disease receiving TKI and all-metastatic site LART may have improved PFS. In patients with repeat oligoprogression, LART might potentially extend survival by delaying the need to change the systemic treatment regimen.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Hellman S, Weichselbaum RR. Oligometastases. J Clin Oncol. 1995; 13:8–10.2. Casiraghi M, De Pas T, Maisonneuve P, Brambilla D, Ciprandi B, Galetta D, et al. A 10-year single-center experience on 708 lung metastasectomies: the evidence of the “international registry of lung metastases”. J Thorac Oncol. 2011; 6:1373–8.3. Aitken K, Tree A, Thomas K, Nutting C, Hawkins M, Tait D, et al. Initial UK experience of stereotactic body radiotherapy for extracranial oligometastases: can we change the therapeutic paradigm? Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2015; 27:411–9.4. Milano MT, Katz AW, Zhang H, Okunieff P. Oligometastases treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy: long-term follow-up of prospective study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012; 83:878–86.5. Rim CH, Cho WK, Lee JH, Kim YS, Suh YG, Kim KH, et al. Role of Local treatment for oligometastasis: a comparability-based meta-analysis. Cancer Res Treat. 2022; 54:953–69.6. Kroese TE, van Laarhoven HW, Nilsson M, Lordick F, Guckenberger M, Ruurda JP, et al. Definition of oligometastatic esophagogastric cancer and impact of local oligometastasis-directed treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. 2022; 166:254–69.7. Gutiontov SI, Pitroda SP, Tran PT, Weichselbaum RR. (Oligo) metastasis as a spectrum of disease. Cancer Res. 2021; 81:2577–83.8. Iyengar P, Wardak Z, Gerber DE, Tumati V, Ahn C, Hughes RS, et al. Consolidative radiotherapy for limited metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018; 4:e173501.9. Gomez DR, Tang C, Zhang J, Blumenschein GR Jr, Hernandez M, Lee JJ, et al. Local consolidative therapy vs. maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: long-term results of a multi-institutional, phase II, randomized study. J Clin Oncol. 2019; 37:1558–65.10. Palma DA, Olson R, Harrow S, Gaede S, Louie AV, Haasbeek C, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for the comprehensive treatment of oligometastatic cancers: long-term results of the SABR-COMET phase II randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 2020; 38:2830–8.11. Cheung P. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligoprogressive cancer. Br J Radiol. 2016; 89:20160251.12. Guckenberger M, Lievens Y, Bouma AB, Collette L, Dekker A, deSouza NM, et al. Characterisation and classification of oligometastatic disease: a European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology and European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer consensus recommendation. Lancet Oncol. 2020; 21:e18–28.13. Patel PH, Palma D, McDonald F, Tree AC. The Dandelion dilemma revisited for oligoprogression: treat the whole lawn or weed selectively? Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2019; 31:824–33.14. Tree AC, Khoo VS, Eeles RA, Ahmed M, Dearnaley DP, Hawkins MA, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastases. Lancet Oncol. 2013; 14:e28–37.15. Lievens Y, Guckenberger M, Gomez D, Hoyer M, Iyengar P, Kindts I, et al. Defining oligometastatic disease from a radiation oncology perspective: an ESTRO-ASTRO consensus document. Radiother Oncol. 2020; 148:157–66.16. Lazzari R, Ronchi S, Gandini S, Surgo A, Volpe S, Piperno G, et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for oligometastatic ovarian cancer: a step toward a drug holiday. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018; 101:650–60.17. Merino Lara T, Helou J, Poon I, Sahgal A, Chung HT, Chu W, et al. Multisite stereotactic body radiotherapy for metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: delaying the need to start or change systemic therapy? Lung Cancer. 2018; 124:219–26.18. Santini D, Ratta R, Pantano F, De Lisi D, Maruzzo M, Galli L, et al. Outcome of oligoprogressing metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with locoregional therapy: a multicenter retrospective analysis. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:100708–16.19. Pembroke CA, Fortin B, Kopek N. Comparison of survival and prognostic factors in patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastases or oligoprogression. Radiother Oncol. 2018; 127:493–500.20. Triggiani L, Alongi F, Buglione M, Detti B, Santoni R, Bruni A, et al. Efficacy of stereotactic body radiotherapy in oligorecurrent and in oligoprogressive prostate cancer: new evidence from a multicentric study. Br J Cancer. 2017; 116:1520–5.21. Sutera P, Clump DA, Kalash R, D’Ambrosio D, Mihai A, Wang H, et al. Initial results of a multicenter phase 2 trial of stereotactic ablative radiation therapy for oligometastatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019; 103:116–22.22. Lin JJ, Cardarella S, Lydon CA, Dahlberg SE, Jackman DM, Janne PA, et al. Five-year survival in EGFR-mutant metastatic lung adenocarcinoma treated with EGFR-TKIs. J Thorac Oncol. 2016; 11:556–65.23. Charloux A, Quoix E, Wolkove N, Small D, Pauli G, Kreisman H. The increasing incidence of lung adenocarcinoma: reality or artefact?: a review of the epidemiology of lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Epidemiol. 1997; 26:14–23.24. Mitchell KG, Farooqi A, Ludmir EB, Corsini EM, Zhang J, Sepesi B, et al. Improved overall survival with comprehensive local consolidative therapy in synchronous oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2020; 21:37–46.25. Gomez DR, Blumenschein GR Jr, Lee JJ, Hernandez M, Ye R, Camidge DR, et al. Local consolidative therapy versus maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer without progression after first-line systemic therapy: a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016; 17:1672–82.26. Ruers T, Van Coevorden F, Punt CJ, Pierie JE, Borel-Rinkes I, Ledermann JA, et al. Local treatment of unresectable colorectal liver metastases: results of a randomized phase II trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017; 109:djx015.27. Shirvani SM, Huntzinger CJ, Melcher T, Olcott PD, Voronenko Y, Bartlett-Roberto J, et al. Biology-guided radiotherapy: redefining the role of radiotherapy in metastatic cancer. Br J Radiol. 2021; 94:20200873.28. Bauml JM, Mick R, Ciunci C, Aggarwal C, Davis C, Evans T, et al. Pembrolizumab after completion of locally ablative therapy for oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a phase 2 trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019; 5:1283–90.29. Gan GN, Weickhardt AJ, Scheier B, Doebele RC, Gaspar LE, Kavanagh BD, et al. Stereotactic radiation therapy can safely and durably control sites of extra-central nervous system oligoprogressive disease in anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive lung cancer patients receiving crizotinib. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014; 88:892–8.30. Thompson R, Cheung P, Chu W, Myrehaug S, Poon I, Sahgal A, et al. Outcomes of extra-cranial stereotactic body radiotherapy for metastatic colorectal cancer: dose and site of metastases matter. Radiother Oncol. 2020; 142:236–45.31. Farooqi A, Ludmir EB, Mitchell KG, Antonoff MB, Tang C, Lee P, et al. Increased biologically effective dose (BED) to the primary tumor is associated with improved survival in patients with oligometastatic NSCLC. Radiother Oncol. 2021; 163:114–8.32. Onishi H, Araki T, Shirato H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Gomi K, et al. Stereotactic hypofractionated high-dose irradiation for stage I nonsmall cell lung carcinoma: clinical outcomes in 245 subjects in a Japanese multiinstitutional study. Cancer. 2004; 101:1623–31.33. Moreno AC, Fellman B, Hobbs BP, Liao Z, Gomez DR, Chen A, et al. Biologically effective dose in stereotactic body radiotherapy and survival for patients with early-stage NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol. 2020; 15:101–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Top Ten Lessons Learned from Trials in Oligometastatic Cancers
- Local ablative radiotherapy for oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer
- Long-term survival after multimodal treatment involving radiotherapy for huge hepatocellular carcinoma with oligometastasis: a case report
- Bone-only oligometastatic prostate cancer: can SABR improve outcomes? A single-center experience
- The Role of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Early-Stage and Oligometastatic Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Evidence for Changing Paradigms